A brown dwarf isn’t a planet or a star. Brown dwarfs are extra large than Jupiter, the largest gas giant planet in our solar system. However brown dwarfs are much less large than the smallest stars. They’re not large sufficient to spark thermonuclear reactions of their cores, that are what allow stars to shine. So brown dwarfs are generally known as failed stars. And so they’re sometimes cool in distinction to stars, cooler than our sun. However this month (August 2023), astronomers reported a brand new hot Jupiter-like brown dwarf, the most well liked discovered thus far. Weirdly, this failed star is hotter than our sun.
Scientists on the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel reported the invention on August 14, 2023.
However why is it so sizzling? The scientists explored the rationale in a brand new paper, published within the peer-reviewed journal Nature Astronomy on August 14, 2023. A free preprint is also available on arXiv.
Why is the brown dwarf sizzling?
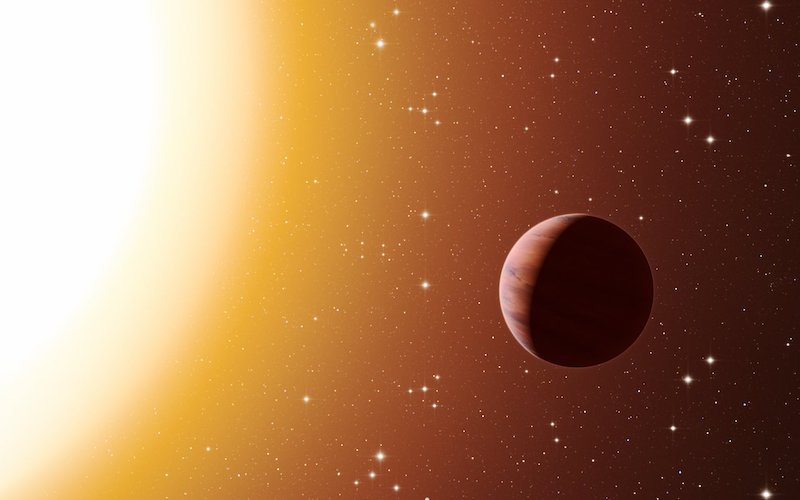
The brown dwarf orbits a white dwarf star. The white dwarf known as WD 0032–317. This odd double system – solely the thirteenth brown dwarf/white dwarf binary found thus far – is positioned some 1,400 light-years from Earth.
The key to the brown dwarf being so sizzling is that it orbits intently with the white dwarf.
It orbits intently sufficient to be tidally locked with the white dwarf, a lot as our moon is tidally locked to Earth. In different phrases, one facet of the brown dwarf all the time faces the white dwarf star.
So the brown dwarf has a everlasting day facet and night time facet. And that truth is the important thing to its excessive floor temperatures. The day facet of the brown dwarf has an estimated temperature starting from 7,250 to 9,800 Kelvin (6,900 to 9,500 Celsius). That makes it as sizzling as an A-type star. It’s additionally about 2,000 levels hotter than the floor of our sun.
Against this, the temperature of the night time facet is considerably decrease, from 1,300 to three,000 Okay (1,000 to 2,700 C).
An ideal laboratory
Na’ama Hallakoun on the Weizmann Institute of Science is the lead creator of the brand new paper. She said:
We’ve recognized a star-orbiting sizzling Jupiter-like object that’s the hottest ever discovered, about 2,000 levels hotter than the floor of the sun.
Most sizzling Jupiters are troublesome to review as a result of they’re obscured by the glare of their stars. However this one is simpler as a result of it’s fairly giant in comparison with its host star, and the star itself is 10,000 occasions fainter than ordinary. Hallakoun mentioned:
This makes it an ideal laboratory for future research of sizzling Jupiters’ excessive circumstances.
An uncommon binary system
Apparently, each objects on this binary system are known as dwarfs. However they’re very several types of objects.
A white dwarf is technically a star. It’s an developed star, what stays of a former sunlike star. A white dwarf star has depleted of its nuclear gas, so it will possibly not shine as our sun and different stars do. It’s basically the new, white core of a star.
If a planet, or brown dwarf, for instance, will get too near its star, the star’s gravity can rip it aside. On this case, nevertheless, the brown dwarf is just too dense to be ripped aside. Hallakoun stated:
Stars’ gravity may cause objects that get too shut to interrupt aside. However this brown dwarf is dense, with 80 occasions the mass of Jupiter squeezed into the scale of Jupiter. This permits it to outlive intact and type a steady, binary system.
Clues about planetary atmospheres
This newly found brown dwarf supplies a novel alternative to be taught extra about planetary atmospheres, researchers say. Particularly, it supplies perception into the results of maximum ultraviolet radiation. On this case, the radiation is coming to the brown dwarf from the white dwarf star. The radiation may cause the fuel that composes the brown dwarf to evaporate. It may break the molecules making up the brown dwarf aside. As Hallakoun explained:
Merely a million years because the formation of the white dwarf on this system – a minuscule quantity of a time on the astronomical scale – we’ve gotten a uncommon glimpse into the early days of this sort of compact binary system.
Scorching Jupiters are the antithesis of liveable planets; they’re dramatically inhospitable locations for all times. Future high-resolution spectroscopic observations of this sizzling Jupiter-like system – ideally made with NASA’s new James Webb Area Telescope – might reveal how sizzling, extremely irradiated circumstances impression atmospheric construction, one thing that might assist us perceive exoplanets elsewhere within the universe.
The outcomes will assist scientists higher perceive the similarities and variations between unique worlds like brown dwarfs and sizzling Jupiters. Each are not like any planets or different our bodies in our personal solar system, making them thrilling objects of examine for astronomers.
Backside line: Astronomers have found a brown dwarf that’s just like a sizzling Jupiter exoplanet. It’s hotter than any sizzling Jupiter seen earlier than, even hotter than our sun.
Source: An irradiated-Jupiter analogue hotter than the sun
Source (preprint): An irradiated-Jupiter analogue hotter than the sun
Via Weizmann Institute of Science
Read more: What are brown dwarfs?
Read more: The unexpected, exotic characteristics of hot Jupiters




