NASA printed this original post on the Webb House Telescope website on October 19, 2023. Edits by EarthSky.
Webb finds new function in Jupiter’s environment
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has found a brand new, never-before-seen function in Jupiter’s environment. The high-speed jet stream is greater than 3,000 miles (4,800 km) vast, in distinction to only a few tons of of miles vast, at most, for Earth’s jet streams. It sits over Jupiter’s equator, above the principle cloud decks.
Ricardo Hueso of the College of the Basque Nation in Bilbao, Spain, is the lead creator on a brand new paper describing the findings. Hueso said:
That is one thing that absolutely stunned us. What we now have at all times seen as blurred hazes in Jupiter’s environment now seem as crisp options that we are able to observe together with the planet’s quick rotation.
The scientists stated this discovery of the jet offers them insights into how the layers of Jupiter’s famously turbulent environment work together. The peer-reviewed journal Nature printed their findings on October 19, 2023.
New information from Webb
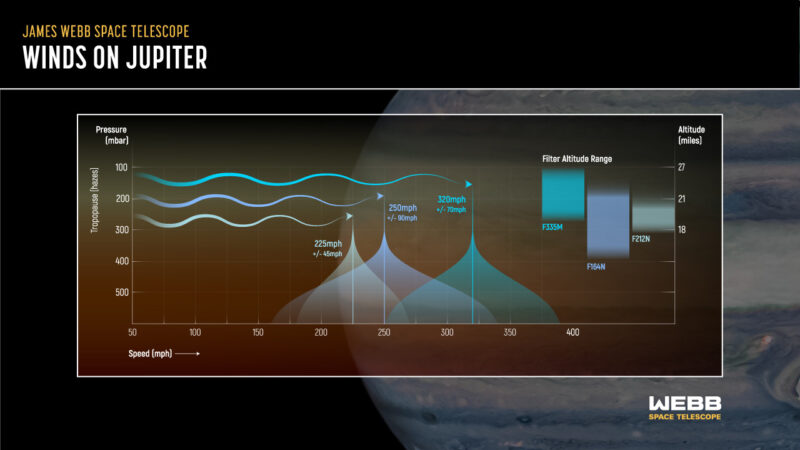
The analysis staff analyzed information that Webb’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) captured in 2022. The info got here from the Early Release Science program, which Imke de Pater from the College of California, Berkeley, and Thierry Fouchet from the Observatory of Paris, collectively lead. This system takes pictures of Jupiter 10 hours aside. That’s the identical as one Jupiter day. It makes use of 4 totally different filters, every uniquely in a position to detect small modifications at totally different altitudes of Jupiter’s environment.
De Pater said:
Although varied ground-based telescopes, spacecraft like NASA’s Juno and Cassini, and NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have noticed the Jovian system’s altering climate patterns, Webb has already supplied new findings on Jupiter’s rings, satellites and its environment.
A view of a better layer in Jupiter’s environment
Jupiter is totally different from Earth in some ways. Jupiter is a gas giant; Earth is a rocky, temperate world. However each planets have layered atmospheres. These different missions have noticed in infrared, seen, radio and ultraviolet-light wavelengths. They might detect the decrease, deeper layers of the planet’s environment, the place gigantic storms and ammonia ice clouds reside.
Alternatively, Webb’s farther-than-before look into the near-infrared is delicate to higher-altitude layers of the environment. These layers are round 15-30 miles (25-50 km) above Jupiter’s cloud tops. In near-infrared imaging, high-altitude hazes usually seem blurry, with enhanced brightness over the equatorial area. With Webb, finer particulars resolve inside the shiny, hazy band.
The newly found jet stream
The newly found jet stream travels at about 320 miles per hour (515 kph), twice the sustained winds of a Category 5 hurricane right here on Earth. Its location is round 25 miles (40 km) above the clouds, in Jupiter’s lower stratosphere.
By evaluating the winds Webb noticed at excessive altitudes to the winds Hubble noticed in deeper layers, the staff may measure how briskly the winds change with altitude and generate wind shears.
Webb and Hubble staff up
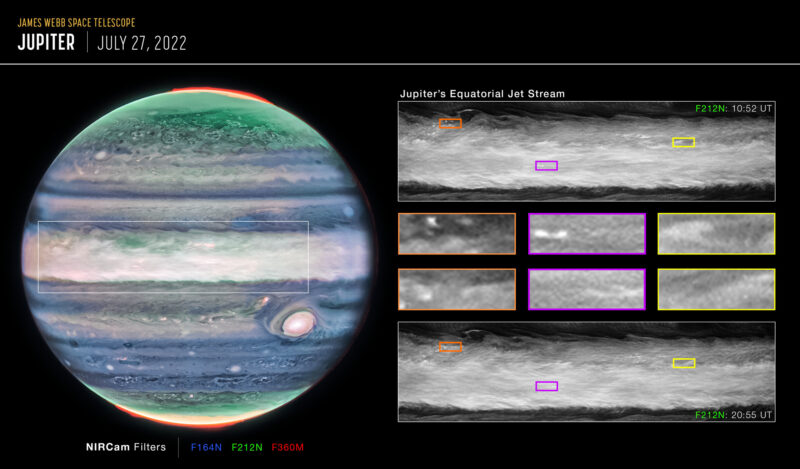
Webb’s beautiful decision and wavelength protection allowed the detection of small cloud features used to trace the jet. In the meantime, complementary observations that Hubble took one day after had been additionally essential to find out the bottom state of Jupiter’s equatorial environment and observe the event of convective storms (or thunderstorms) in Jupiter’s equator not linked to the jet.
Michael Wong of the College of California, Berkeley, who led the related Hubble observations, said:
We knew the totally different wavelengths of Webb and Hubble would reveal the three-dimensional construction of storm clouds. However we had been additionally in a position to make use of the timing of the information to see how quickly storms develop.
What’s subsequent?
The researchers are trying ahead to further observations of Jupiter with Webb to find out if the jet’s pace and altitude change over time. Crew member Leigh Fletcher of the College of Leicester in the UK said:
Jupiter has a sophisticated however repeatable sample of winds and temperatures in its equatorial stratosphere, excessive above the winds within the clouds and hazes measured at these wavelengths. If the energy of this new jet is linked to this oscillating stratospheric sample, we would count on the jet to differ significantly over the following 2 to 4 years. It’ll be actually thrilling to check this idea within the years to return.
It’s wonderful to me that, after years of monitoring Jupiter’s clouds and winds from quite a few observatories, we nonetheless have extra to study Jupiter. And options like this jet can stay hidden from view till these new NIRCam pictures had been taken in 2022.
Backside line: The Webb space telescope revealed a jet stream in Jupiter’s environment above its equatorial area.
Source: An intense narrow equatorial jet in Jupiter’s lower stratosphere observed by JWST
Read more: Jupiter racing toward opposition on November 2-3, 2023




