A fragile tracery of dust and vivid star clusters threads throughout this picture from the James Webb Area Telescope. The intense tendrils of fuel and stars belong to the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068, whose vivid central bar is seen within the higher left of this picture—a composite from two of Webb’s devices. NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson revealed the picture Friday throughout an occasion with college students on the Copernicus Science Heart in Warsaw, Poland.
NGC 5068 lies round 20 million light-years from Earth within the constellation Virgo. This picture of the central, vivid star-forming areas of the galaxy is a part of a marketing campaign to create an astronomical treasure trove, a repository of observations of star formation in close by galaxies. Earlier gems from this assortment will be seen here (IC 5332) and here (M74). These observations are notably priceless to astronomers for 2 causes. The primary is as a result of star formation underpins so many fields in astronomy, from the physics of the tenuous plasma that lies between stars to the evolution of total galaxies. By observing the formation of stars in close by galaxies, astronomers hope to kick-start main scientific advances with a number of the first accessible information from Webb.
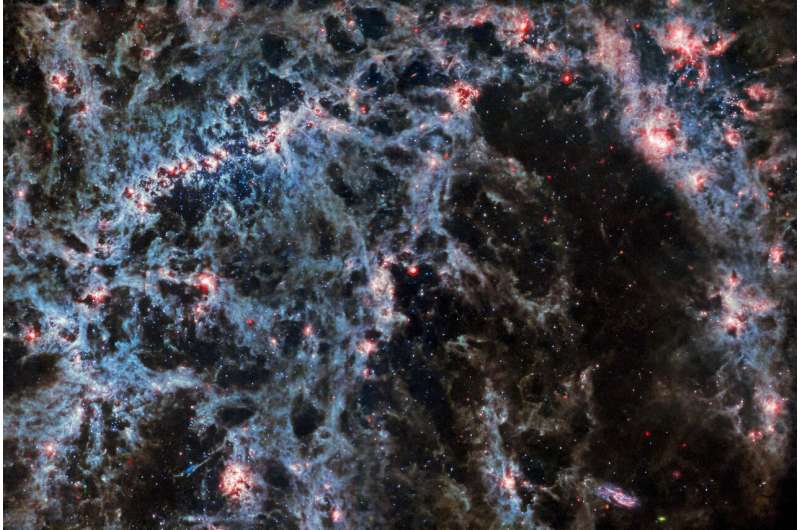
The second purpose is that Webb’s observations construct on different research utilizing telescopes together with the Hubble Area Telescope and ground-based observatories. Webb collected photos of 19 close by star-forming galaxies which astronomers may then mix with Hubble photos of 10,000 star clusters, spectroscopic mapping of 20,000 star-forming emission nebulae from the Very Giant Telescope (VLT), and observations of 12,000 darkish, dense molecular clouds recognized by the Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). These observations span the electromagnetic spectrum and provides astronomers an unprecedented alternative to piece collectively the trivia of star formation.
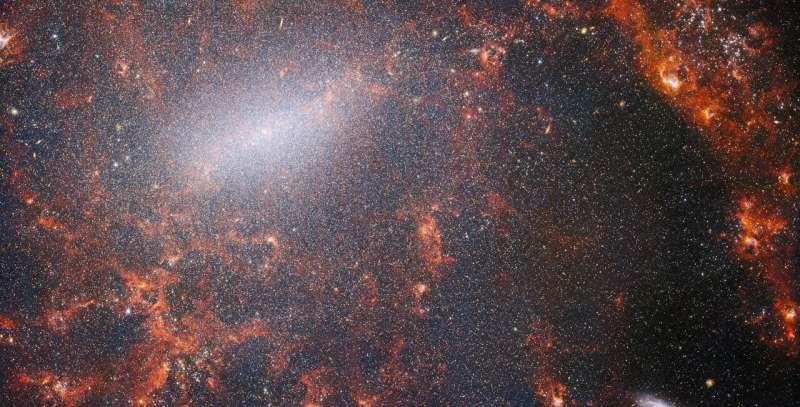

With its capability to look by the fuel and dust enshrouding new child stars, Webb is especially well-suited to discover the processes governing star formation. Stars and planetary systems are born amongst swirling clouds of fuel and dust which can be opaque to visible-light observatories like Hubble or the VLT. The eager imaginative and prescient at infrared wavelengths of two of Webb’s devices—MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) and NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera)—allowed astronomers to see proper by the gargantuan clouds of dust in NGC 5068 and seize the processes of star formation as they occurred. This picture combines the capabilities of those two devices, offering a very distinctive take a look at the composition of NGC 5068.
Quotation:
Webb Area Telescope friends behind barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068 (2023, June 5)
retrieved 5 June 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-webb-space-telescope-peers-barred.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




