Astronomers from the Cosmic Daybreak Middle have unveiled the character of the densest area of galaxies seen with the James Webb House telescope within the early universe. They discover it to be doubtless the progenitor of an enormous, Milky Way-like galaxy, seen at a time the place it’s nonetheless assembling from smaller galaxies. The invention corroborates our understanding of how galaxies type.
In response to our present understanding of construction formation within the universe, galaxies type in a hierarchical method, with small buildings forming first within the very early universe, later merging to construct up bigger buildings. That is the prediction of theories and computer simulations, and is verified by observations of galaxies at numerous epochs within the historical past of the universe.
To watch the very first buildings assembling, we’ve got to look as far again in time, and therefore as distant, as attainable. However these sources are each very small and really faint, and their detection requires superior applied sciences.
In a brand new research, the early progenitor of what right now will doubtless have developed to an enormous, Milky Way-sized galaxy, has been detected. This group of smaller galaxies, dubbed CGG-z5, was discovered by the observational program referred to as “CEERS” with the James Webb House Telescope, and is seen when the universe was only one.1 billion years outdated, 8% of its present age.
CGG-z5 was found utilizing the code GalCluster, which was created by Nikolaj Sillassen, MSc scholar on the Cosmic Daybreak Middle (DAWN).
“I developed the software program throughout my research to detect this sort of buildings, and now we utilized it to information from the CEERS program,” says Nikolaj Sillassen, who already discovered an analogous however extra close by group whereas testing the software program.
“It is nice to see how helpful my code is changing into.”
Unattainable with out James Webb
The brightest members of the galaxy group was found beforehand with the Hubble House Telescope. However the CEERS program revealed new and smaller members.
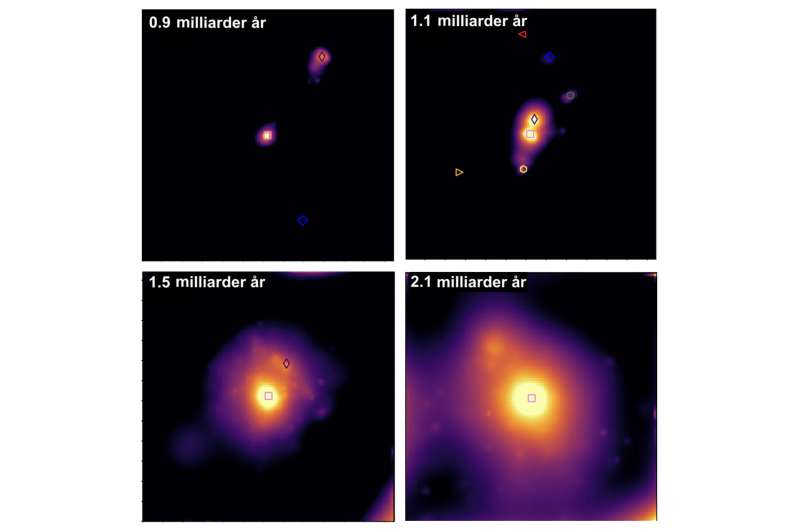
“The opposite members of the group are each small and faint. With out the sensitivity and the spatial decision of James Webb, we merely would not have the ability to detect them,” explains Shuowen Jin, Marie Curie Fellow on the Cosmic Daybreak Middle (DAWN) and lead creator of the present research.
Precisely what’s the “future” of the galaxy group CGG-z5 will probably be, is in fact unknown. Relatively than forming a single galaxy, it might be that the group evolves into a big cluster of galaxies at later occasions. Yet one more risk is that the members are in actuality not so intently packed because it appears, however as an alternative is part of a filamentary construction that we simply occur to view from one finish to the opposite.
Assist from laptop simulations
To differentiate between these situations, extra exact observations involving the extra time-consuming spectroscopy is required. However within the meantime, assist is accessible from laptop simulations:
“With a purpose to higher perceive the character and evolution of CGG-z5, we looked for comparable buildings in large-scale, hydrodynamical simulations,” says Aswin Vijiayan, Postdoctoral Fellow on the Cosmic Daybreak Middle who carried out the simulation evaluation within the research. “We discovered 14 buildings that match intently the physical properties of our noticed group CGG-z5, after which traced the evolution of those buildings by time within the simulations, from the early universe to the current epoch.
Though the precise unfolding of the evolution of those 14 buildings are completely different, all of them shared the identical destiny: Roughly 0.5 to 1 billion years later, they merge to type a single galaxy which, by the point the universe is half its present age, have plenty corresponding to our personal Milky Way.
“Given the predictions of the simulations, it’s subsequently tempting to invest that the CGG-z5 system can even comply with an analogous evolutionary path, and that we captured the method of small galaxies assembling right into a single huge galaxy,” Shuowen Jin says.
“Curiously, the variety of these early teams like CGG-z5 in a given quantity of space is just like the variety of huge galaxies at later cosmic occasions,” says Georgios Magdis, affiliate professor at DAWN and partaker within the research. “This makes merging teams interesting as the primary progenitors of huge galaxies at later epochs.”
The research is printed within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Extra info:
S. Jin et al, Huge galaxy formation caught in motion at z~5 with JWST, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2023). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202245724
Supplied by
Niels Bohr Institute
Quotation:
Webb telescope catches early galaxy formation in motion (2023, January 31)
retrieved 1 February 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-01-webb-telescope-early-galaxy-formation.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




