Found! Long-sought gravitational wave background
Gravitational waves are ripples within the construction of spacetime. A lot as a ship touring throughout the floor of a peaceful sea leaves a wake behind it, so shifting objects within the universe create gravitational waves. The “ships” within the case of gravitational waves are extraordinarily violent and cataclysmic occasions far off within the cosmos: black hole mergers, neutron star collisions, supernovae. All of those generate waves within the construction of spacetime, stretching and squeezing it because the ripples journey throughout the universe.
As a result of gravitational waves are extraordinarily weak as noticed from our earthly vantage level, the expertise to detect them has grow to be obtainable solely in recent times. Like all waves, gravitational waves diminish in dimension with distance, shrinking to faint echoes of these distant “shipwrecks” – these distant violent occasions within the cosmos – by the point they attain us. From our location, many light-years from a black hole merger or a neutron star collision, the waves compress and stretch space, and the whole lot in it, by a thousandth of the diameter of a proton as they cross by way of the Earth. That’s a billionth of a billionth of a meter. We require very superior expertise certainly to see that change. It’s like seeing the space between the sun and its closest neighbor among the many stars – Alpha Centauri, 4.3 mild years distant – change by the thickness of a human hair.
It was Albert Einstein who, in his General Theory of Relativity of 1915, first postulated the existence of gravitational waves. His suggestion that gravity travels in waves appeared logical: each sort of sunshine on the electromagnetic spectrum, from ultraviolet to seen to radio, travels in waves. Sound travels in waves. Why ought to gravity not be propagated in the identical approach? Einstein calculated that extraordinarily violent occasions within the cosmos would trigger space to ring like a bell. This was distinct from the thought of the static, unchanging gravitational fields which can be generated by any object that has mass, like a star or a planet.
Nevertheless, for many years after 1915, Einstein himself was unconvinced of the existence of gravitational waves. In 1936, he and colleague Nathan Rosen printed a paper entitled Do Gravitational Waves Exist? which, initially, was rejected by one journal due to a mathematical error.
It was the error that had prompted the authors to conclude that gravitational waves don’t exist. When Einstein had corrected the error, the paper’s conclusion grew to become precisely the alternative! Though the proof now pointed to their existence, Einstein remained unconvinced, and believed that even when gravitational waves did exist, they might be so very weak that people might by no means develop the expertise to detect them.

It needs to be famous that Einstein was not the one theorist who labored on gravitational waves. Necessary contributions have been made by different well-known scientists, amongst them Robert Oppenheimer, Roger Penrose, Karl Schwarzschild, Arthur Eddington, Kip Thorne and Richard Feynman. However it was Feynman who, in January 1957, lastly satisfied the doubters that not solely do gravitational waves do exist, however they will carry power as properly, explaining this through the use of one thing he known as his Sticky Bead argument.
Feynman’s work straight paved the best way for right this moment’s gravitational wave detectors.
But it will be one other 50 years earlier than the primary gravitational waves have been detected. Growing the ideas and the expertise to take action took a long time of laborious work by many scientists. Lastly, LIGO, the Laser Interferometry Gravitational-wave Observatory located at two sites in america, began observing in 2002. It took a number of upgrades to LIGO, between 2002 and 2015, to offer it the sensitivity to make its historic first detection.
The primary detection, of two black holes merging some 1.3 billion mild years distant, got here in September 2015 and was announced to the world in February 2016 after months of labor verifying that the sign, which had lasted a mere tenth of a second in good settlement with Einstein’s predictions, was actual. Extremely, LIGO had not but begun its official observing run when the detection got here: after its newest in a sequence of upgrades to enhance its vary and sensitivity, LIGO had been turned on for engineering assessments. The black hole merger was detected virtually instantly the detector was operational.
One other key prediction of Einstein was that gravitational waves would journey on the velocity of sunshine. By measuring the distinction in time between when the gravitational wave sign arrived on the two LIGO observatories – in Hanford, Washington, and Livingston, Louisiana, separated by practically 2,000 miles (3,000 km) – scientists have been in a position to decide that Einstein’s prediction was utterly right. Gravitational waves do certainly propagate on the velocity of sunshine.
LIGO was joined in 2018 by the European Virgo detector in Italy, which has tremendously improved the flexibility of scientists to pinpoint the placement on the sky the place the gravitational waves originated. Since then, LIGO/Virgo have detected some 50 black hole mergers, but in addition eight neutron star collisions and 6 neutron star-black hole collisions. A few of these might find yourself being to as a consequence of so-called “terrestrial interference”: vibrations from passing visitors and even distant ocean waves could cause false positives.
On January 14, 2020, LIGO additionally detected an event of completely unknown origin, which doesn’t match any fashions or predictions, maybe, excitingly, pointing to the existence of a hitherto-unknown cosmic phenomenon.
Very quickly the Japanese KAGRA observatory will be a part of Virgo and LIGO within the detection of gravitational waves. Within the 2030s, the European Area Company will launch LISA, a space-based gravitational wave detector, which ought to allow the detection of low-frequency gravitational waves emanating from supermassive black holes and from supernova explosions. China has started work on constructing three gravitational wave observatories, its avowed intent to grow to be the world chief in Earth- and space-based gravitational wave detection.
All the gravitational wave occasions detected up to now agree perfectly with Einstein’s predictions and with laptop simulations derived from his calculations. Einstein would certainly have been amazed that he was flawed, that human mind and ingenuity has certainly triumphed and created the expertise he thought inconceivable. He would additionally most likely have regretted doubting his personal work in predicting the existence of gravitational waves. However he would additionally, certainly, have been joyful that the detection of gravitational waves can be a affirmation of his concept of Relativity. There are actually few locations left to run for many who doubt Einstein’s best triumph.
Gravitational-wave astronomy is a completely new science and one which guarantees to unlock most of the universe’s mysteries. It’s no exaggeration to say {that a} revolution in our view of the universe is underway. Sooner or later, it’d even be doable to detect gravitational waves from the Big Bang itself, to listen to the sound of Creation ringing out throughout billions of years.
If you want to maintain updated with the most recent gravitational wave occasions, the College of Birmingham within the U.Okay. has created this page, which is a database of LIGO and Virgo detections throughout their present observing run. The database can be obtainable as a free app for Android/Apple telephones, downloadable from their respective shops.
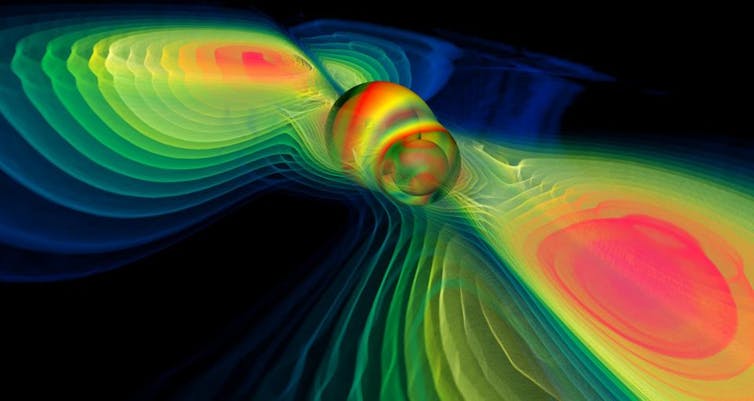
Backside line: First postulated by Albert Einstein in 1916 however not noticed straight till September 2015, gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime.
Read more and watch a video explainer: What are gravitational waves?




