When an enormous star explodes as a supernova on the finish of its life, its core can collapse right into a tiny and superdense object with not rather more than our sun’s mass. These small, extremely dense cores of exploded stars are neutron stars. They’re among the many most weird objects within the universe.
A typical neutron star has about 1.4 occasions our sun’s mass. They usually can vary as much as about two solar masses. Now take into account that our sun has over 100 occasions Earth’s diameter. In a neutron star, all that mass is squeezed right into a sphere that’s solely about 12-25 miles (20-40 km) throughout, or in regards to the dimension of an earthly metropolis.
So maybe you’ll be able to see that neutron stars are very, very dense! A tablespoon of a neutron star materials would weigh greater than 1 billion U.S. tons (900 billion kg). That’s greater than the burden of Mount Everest, Earth’s highest mountain.

Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
Right here’s how a neutron star types.
All through a lot of their lives, stars keep a fragile balancing act. Gravity tries to compress the star whereas the star’s inner stress exerts an outward push. And nuclear fusion on the star’s core causes the outer stress. Actually, this fusion burning is the method by which stars shine.
In a supernova explosion, gravity all of a sudden and catastrophically will get the higher hand within the battle it has been waging with the star’s inner stress for thousands and thousands or billions of years. With its nuclear gasoline exhausted and the outward stress eliminated, gravity all of a sudden compresses the star inward. A shock wave travels to the core and rebounds, blowing the star aside. This complete course of takes maybe a few seconds.
However gravity’s victory is just not but full. With a lot of the star blown into space, the core stays, which can solely be twice our sun’s mass. Gravity continues to compress it, to some extent the place the atoms develop into so compacted and so shut collectively that electrons are violently thrust into their dad or mum nuclei, combining with the protons to type neutrons.
Thus the neutron star will get its title from its composition. What gravity has created is a superdense, neutron-rich materials – referred to as neutronium – in a city-sized sphere. The precise inner construction of this sphere is the topic of a lot debate. Present pondering is that the star possesses a skinny crust of iron, maybe a mile or so thick. Beneath that, the composition is basically neutrons, taking numerous types the additional down within the neutron star they’re positioned.
It’s all about mass.
If, after the supernova, the core of the star has sufficient mass, scientists consider that the gravitational collapse will proceed, and a black hole will type as a substitute of a neutron star. By way of mass, the dividing line between neutron stars and black holes varies by sources. Sometimes, astronomers take into account the mass of a neutron star to vary from 1.4 to 2.9 solar plenty. Then, if the collapsed core has greater than three solar plenty it turns into a black hole.
What are the properties of a neutron star?
As a result of neutron stars are so dense, they’ve intense gravitational and magnetic fields. The gravity of a neutron star is a few thousand billion occasions stronger than that of the Earth. Thus the floor of a neutron star is exceedingly easy; gravity doesn’t allow something tall to exist. Neutron stars could have “mountains”, however they’re solely inches tall.
Neutron stars with abnormally sturdy magnetic fields are often called magnetars. The origin of those irregular stars with ultra-powerful magnetic fields is unknown.
Unimaginably violent neutron star collisions, one of which was detected in 2017 by the LIGO gravitational wave observatories, are considered the place heavy components like gold and platinum are created. And that’s as a result of regular supernovae will not be thought to generate the requisite pressures and temperatures.
Neutron stars are additionally considered chargeable for a number of little-understood phenomena, together with the mysterious Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) and the so-called Soft Gamma Repeaters (SGRs).
A neutron star doesn’t generate any mild or warmth of its personal after its formation. Over thousands and thousands of years its latent warmth will step by step cool from an preliminary 600,000 levels Kelvin (1 million levels Fahrenheit), finally ending its life because the chilly, useless remnant of a once-glorious star. It’s estimated there are greater than 100 million neutron stars in our Milky Way galaxy, however many can be too outdated and chilly to be simply detected.
Pulsars: How we learn about neutron stars.
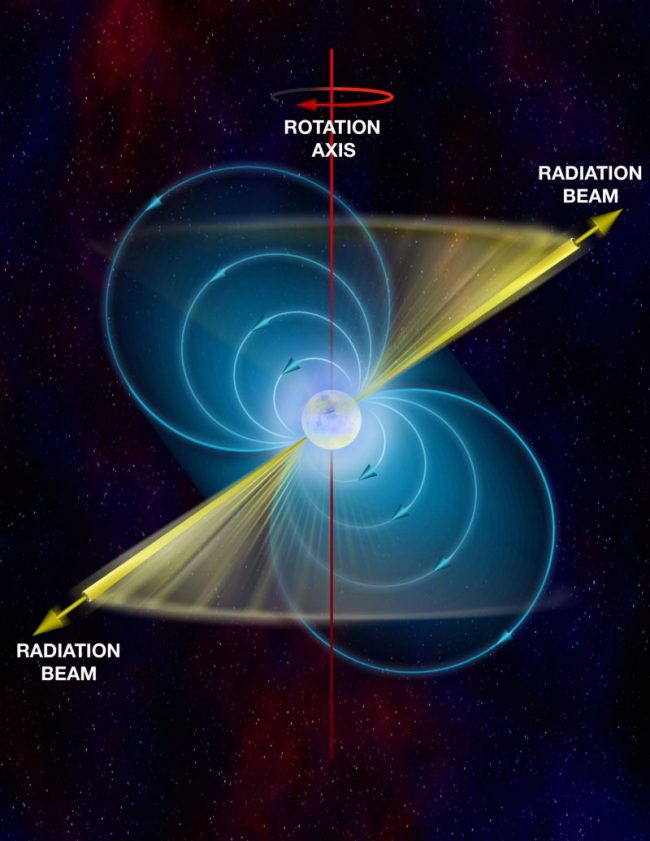
Though neutron stars had been lengthy predicted in astrophysical concept, it wasn’t till 1967 that the primary was found, as a pulsar, by Dame Jocelyn Bell Burnell. Since then, we all know of lots of extra, together with the well-known pulsar on the coronary heart of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant noticed by the Chinese language in 1054.
On a neutron star, intense magnetic fields focus radio waves into two beams firing into space from its magnetic poles, very similar to the beam of a lighthouse. If the neutron star is oriented exactly in order that these beams develop into seen from our earthly viewpoint, we see flashes of radio mild at common and very actual intervals. Neutron stars are, actually, the celestial timekeepers of the cosmos, their accuracy rivaling that of atomic clocks.
Neutron stars rotate extraordinarily quickly, and we are able to use the radio beams of a pulsar to measure simply how briskly. The fastest-rotating neutron star yet discovered rotates an unbelievable 716 occasions per second, which is a few quarter of the velocity of sunshine.
Read more about Jocelyn Bell Burnell, who discovered pulsars

Sci fi alert!
“Dragon’s Egg” by Robert L. Forward (out of print) depicts the imaginary inhabitants residing on the floor of a neutron star. Claudia commented: “They had been tiny and dense (after all) and lived at an incredible velocity. It’s been some time, however I keep in mind it as a great learn.” Andy added: “Sure, I do not forget that ebook! Very entertaining. It’s unbelievable to assume that if the floor of a neutron star slips by as little as a millimeter, it causes a starquake.”
Extra assets on neutron stars:
Read more: Introduction to neutron stars
Five extreme facts about neutron stars
Read more: How high are pulsar mountains?
Backside line: Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of previously huge stars which have been crushed to an excessive density by supernova explosions. A neutron star isn’t as dense as a black hole, however it’s denser than another recognized sort of star.




