Future historians would possibly look again on this time and name it the “exoplanet age.” We have discovered over 5,000 exoplanets, and we’ll preserve discovering extra. Subsequent, we’ll transfer past simply discovering them, and we’ll flip our efforts to discovering biosignatures, the particular chemical fingerprints that residing processes imprint on exoplanet atmospheres.
However there’s extra to biosignatures than atmospheric chemistry. On a planet with numerous flowers, gentle generally is a biosignature, too.
The seek for biosignatures on exoplanets acquired a lift of vitality when the James Webb Area Telescope started observations. One of many telescope’s science targets is to characterize exoplanet atmospheres with its highly effective infrared spectrometry. If Webb finds giant quantities of oxygen, for instance, it is a sign that organic processes may be at work and are altering a planet’s environment. However the JWST and different telescopes may detect one other sort of biosignature.
Earth’s ample flowers modifications our planet’s “gentle signature.” The change relies on photosynthesis and the way flowers absorbs some gentle frequencies whereas reflecting others. The ensuing phenomenon is named the vegetation purple edge (VRE.)
Exoplanet scientists have labored on the thought of the VRE as a biosignature for a couple of years. It is primarily based on the truth that chlorophyll absorbs gentle within the seen a part of the spectrum and is nearly clear within the infrared. Different mobile constructions within the vegetation replicate the infrared. This helps vegetation keep away from overheating throughout photosynthesis. This absorption and reflection make it doable for remote sensing to gauge plant well being, protection, and exercise, and agricultural scientists use it to watch crops.
In a brand new paper, a group of researchers checked out chlorophyll and its solar-induced fluorescence (SIF.) SIF is the identify of the electromagnetic sign emitted by chlorophyll a, probably the most widely-distributed chlorophyll molecule. A part of the vitality absorbed by chlorophyll a isn’t used for photosynthesis however is emitted at longer wavelengths as a two-peak spectrum. It covers roughly the 650–850 nm spectral vary.
The paper is “Photosynthetic Fluorescence from Earth-Like Planets round sun-Like and Cool Stars,” and is revealed in The Astrophysical Journal. The lead writer is Yu Komatsu, a researcher on the Nationwide Institutes of Pure Sciences Astrobiology Heart, Nationwide Astronomical Observatory of Japan.
The paper focuses on how the fluorescence from chlorophyll could possibly be detected on planets just like Earth. “This examine examined the detectability of organic fluorescence from two forms of photosynthetic pigments, chlorophylls (Chls) and bacteriochlorophylls (BChls), on Earth-like planets with oxygen-rich/poor and anoxic atmospheres across the sun and M dwarfs,” the authors clarify.
Detecting the presence of chlorophyll on one other world is difficult. There is a advanced interaction between flowers, starlight, land/ocean protection, and atmospheric composition. This examine is a part of an ongoing effort to know among the limitations to detection and what spectroscopic knowledge can inform scientists about exoplanets. Over time, exoplanet scientists need to decide which detections will be biosignatures in several circumstances.
The VRE is a pointy drop in noticed gentle between infrared and visual gentle. Mild within the near-infrared (beginning at about 800 nm) is far brighter than the sunshine within the optical (between about 350 to 750 nm.) On Earth, that is the sunshine signature of flowers and its chlorophyll. The chlorophyll absorbs the sunshine as much as 750 nm, and different plant tissues replicate gentle above 750 nm.
Satellites like NASA’s Terra can observe completely different areas on Earth’s floor over time and watch how the sunshine reflectance modifications. Scientists measure what’s referred to as the Normalized Distinction Vegetation Index (NVDI.) A dense forest location throughout peak rising season provides peak values for the NDVI, whereas vegetation-poor areas give low values.
Scientists may also observe Earthshine, the sunshine mirrored from Earth onto the moon. That gentle is the whole thing of the sunshine mirrored by Earth, what scientists name a disk-averaged spectrum. “Whereas distant sensing observes native areas on Earth, Earthshine observations present disk-averaged spectra of the Earth, resulting in fruitful insights into exoplanet functions,” the authors write. “The obvious reflectance change within the Earth’s disk-averaged spectrum on account of floor vegetation is lower than 2%.”
The Earthshine we see on the moon is just like the sunshine we detect from distant exoplanets. It is the totality of the sunshine vs. regional floor gentle. However there’s an infinite quantity of complexity concerned in finding out that gentle, and there are not any simple comparisons between Earth and exoplanets. “The VRE alerts from exoplanets round stars aside from a sun-like star are difficult to foretell as a result of complexity of photosynthetic mechanisms in several gentle environments,” the authors clarify. However there’s nonetheless worth in searching for a VRE on exoplanets. If scientists observe an exoplanet ceaselessly, they can acknowledge how the VRE modifications seasonally, they usually could acknowledge an analogous VRE-like step within the planet’s spectroscopy, although it could possibly be at completely different wavelengths than on Earth.
Of their paper, the researchers thought-about an Earth-like planet in several phases of atmospheric evolution. In every case, the planets orbited the sun, a well-studied red dwarf named Gliese 667 C, or the much more well-known red dwarf TRAPPIST-1. (Each purple dwarfs have planets of their liveable zones, and each signify frequent forms of purple dwarfs.) They modeled the reflectance from every case for vegetation chlorophyll, bacterial chlorophyll-based vegetation, and organic fluorescence with none floor vegetation.
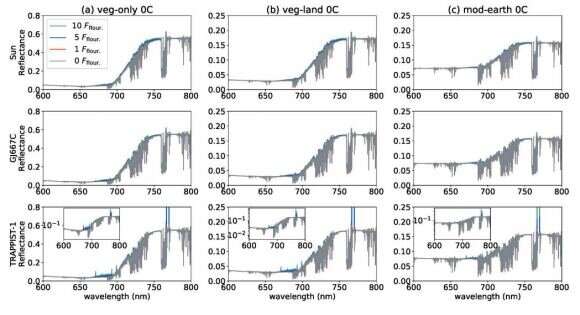
What they got here up with is a group of sunshine curves that exhibits what completely different VREs would possibly seem like on Earth-like exoplanets in several phases of atmospheric evolution round completely different stars. It is necessary to have a look at completely different phases of atmospheric evolution as a result of Earth’s environment modified from oxygen-poor to oxygen-rich whereas life was current.
“We thought-about fluorescence emissions from Chl- and BChl-based vegetation in a clear-sky situation on an Earth-like planet across the sun and two M dwarfs,” the authors write.
The examine produced a variety of reflectance knowledge for Earth-like planets round completely different stars. The planets had been modeled with completely different atmospheres that correspond to Earth’s completely different atmospheres over its 4 billion-year historical past. The researchers additionally different the quantity of land cowl vs. ocean cowl, the quantity of shoreline, and whether or not the floor was coated in vegetation or in photosynthetic micro organism.
Sooner or later, we’ll be wielding ever extra highly effective space telescopes like LUVOIR (Massive UV/Optical/IR Surveyor) and HabEx (Liveable Exoplanet Observatory.) Floor-based telescopes just like the Thirty Meter Telescope, the Large Magellan Telescope, and the European Extraordinarily Massive Telescope can even be coming on-line within the close to future. These telescopes are going to generate an unprecedented quantity of information on exoplanets, and this examine is a part of making ready for that.
We’re detecting increasingly exoplanets and are constructing a statistical understanding of different solar programs and the distributions, plenty, and orbits of exoplanets. The following is to realize a deeper understanding of the traits of exoplanets. Telescopes just like the E-ELT will do this with its 39.3-meter mirror. It will be capable of separate an exoplanet’s gentle from the star’s gentle and instantly picture some exoplanets. It will unleash a flood of information on exoplanet reflectance and potential biosignatures, and all of that knowledge should be evaluated.
If we ever find an Earth-like planet, one which’s liveable and at the moment supporting life, it will not simply seem in certainly one of our telescopes and announce its presence. As a substitute, there will be tantalizing hints, there will be indications and contra-indications. Scientists will slowly and thoroughly work their means ahead, and one day we’d be capable of say we have discovered a planet with life. This analysis has a task to play within the endeavor.
“You will need to quantitatively consider the detectability of any potential floor biosignature utilizing anticipated specs of particular future missions,” the authors clarify. “This examine made the primary try to analyze the detectability of photosynthetic fluorescence on Earth-like exoplanets.”
Extra data:
Yu Komatsu et al, Photosynthetic Fluorescence from Earthlike Planets round Sunlike and Cool Stars, The Astrophysical Journal (2023). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/aca3a5
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Worlds bustling with flowers ought to shine in a detectable wavelength of infrared, say exoplanet scientists (2023, January 18)
retrieved 18 January 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-01-worlds-bustling-life-wavelength-infrared.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




