It has been virtually a 12 months because the most formidable — and dear — space telescope ever constructed was launched towards the L2 Lagrange level on the far facet of the Earth from the sun.
Following a nerve-shredding deployment that noticed its mirrors and sunshield efficiently unfold whereas navigating 344 potential points of failure, the $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope (Webb or JWST) has been churning out improbable astronomical information because the summer time.
Even lower than six months into observations, this information is transformative, and scientists have already used it to make a number of necessary and record-breaking discoveries. JWST was heralded as a revolutionary telescope earlier than it launched; now that it’s in enterprise, we take a look at a few of the many ways in which it’s already succeeding in remodeling astronomy.
Seeing farther into the previous than ever earlier than
To see the valuable uncommon photons from essentially the most distant galaxies within the universe, the larger the telescope, the higher — and space telescopes do not come greater than JWST, with its 21-foot (6.5 meters) major mirror.
However that is solely half the job finished, as a result of the extra distant an object is, the extra its gentle is redshifted. The farther a galaxy is from us, the sooner it’s receding from us due to the growth of the universe, so the extra its gentle turns into stretched, shifting the sunshine towards redder wavelengths.
Essentially the most distant galaxies, that are additionally the earliest galaxies we will see, emit gentle that’s shifted all the best way into near-infrared wavelengths by the point it reaches Earth. It is this redshift that prompted scientists to design JWST to specialise in near- and mid-infrared gentle.
The mix of the massive mirror and infrared imaginative and prescient has enabled JWST to see extra distant, earlier galaxies than astronomers ever have earlier than, promising to remodel our understanding how these galaxies form.
Previous to JWST’s launch, essentially the most distant identified galaxy was one known as GN-z11. It has a redshift of 11.1, which corresponds to seeing the galaxy because it was 13.4 billion years in the past, simply 400 million years after the Big Bang. That was absolutely the restrict of what telescopes earlier than JWST might detect.
However very quickly after the primary information from JWST was launched, that file was smashed. Astronomers took benefit of foreground galaxy clusters like Abell 2744 that act as gravitational lenses: Objects of nice mass, comparable to galaxy clusters, warp space with their gravity, making a magnifying lens-like impact that amplifies gentle from extra distant objects. Astronomers started discovering faint, purple smudges within the background of those lenses — and these smudges have turned out to be essentially the most distant galaxies ever seen.
First was a galaxy at a redshift of 12.5, known as GLASS-z12 (GLASS is the identify of a particular survey program, the “Grism Lens-Amplified Survey from House”). We see this galaxy because it existed 13.45 billion years in the past, or 350 million years after the Large Bang, astronomers calculated.
Galaxies with even greater redshifts quickly adopted. One, nicknamed Maisie’s Galaxy, is seen because it existed simply 280 million years after the Large Bang, at a redshift of 14.3, whereas one other, at redshift 16.7, is seen simply 250 million years after the Large Bang. There have even been claims for a galaxy at an astounding redshift of 20, which if confirmed would have existed simply 200 million years after the Large Bang.
JWST can also be working to verify these finds as properly, utilizing a second instrument to separate gentle by wavelength. Astronomers have already confirmed a galaxy with a redshift of 13.2, which we see because it was when the universe was simply 325 million years outdated.
Discovering what lit up the universe
Following the Large Bang, however earlier than stars and galaxies had shaped, the universe was darkish and shrouded in a fog of impartial hydrogen fuel. In the end gentle, significantly ultraviolet radiation, ionized that fog. However the place did that gentle initially come from to finish the cosmic darkish ages?
Astronomers consider that gentle got here both from younger galaxies full of stars, or from energetic supermassive black holes, that are surrounded by accretion disks of brilliantly scorching fuel and shoot highly effective jets into space. The query of which got here first — galaxies or their black holes — is without doubt one of the largest conundrums in cosmology, a sort of rooster or egg query.
Already, JWST has discovered that the early galaxies it’s detecting are brighter and extra structured than anticipated, with distinct disks round bulbous cores already full of stars. This attribute means that fully-formed galaxies had been on the scene rapidly — however whether or not they already contained supermassive black holes stays to be seen. Happily, JWST is designed to reply this query, and when it does it can present an enormous piece of the jigsaw that’s the puzzle of the early universe.
Measuring exoplanet atmospheres
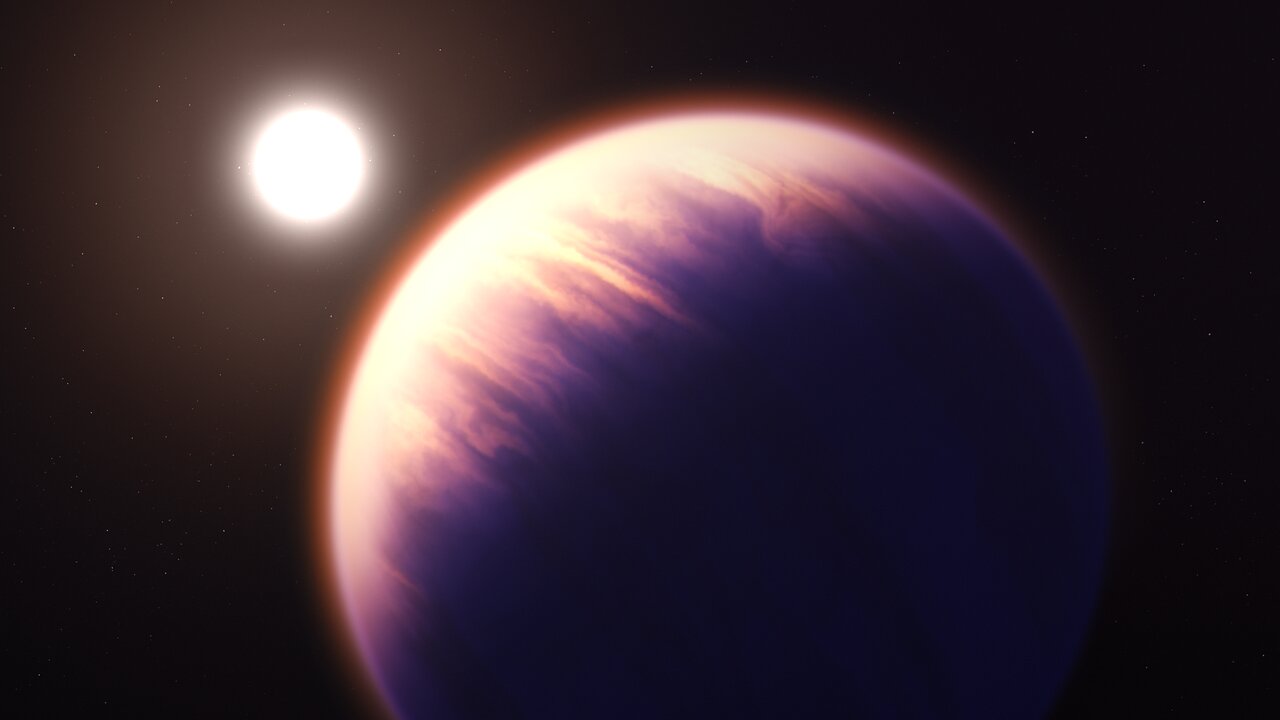

Astronomers have now discovered greater than 5,000 exoplanets and counting, however regardless of this outstanding haul, we nonetheless know subsequent to nothing about lots of them. JWST is not designed to find new exoplanets, nevertheless it does intention to color rather more detailed footage of identified worlds by conducting one thing known as transit spectroscopy.
When a planet passes in entrance of its star, a few of the star’s gentle filters by way of the planet’s ambiance, and molecules within the ambiance can take up a few of that starlight, creating darkish strains within the star’s spectrum, a barcode-like breakdown of sunshine by wavelength. Realizing what’s in a planet’s ambiance, and even whether or not it has an environment in any respect, can educate astronomers about how a planet might need shaped and advanced, what its circumstances are like and what chemical processes are happening in that ambiance.
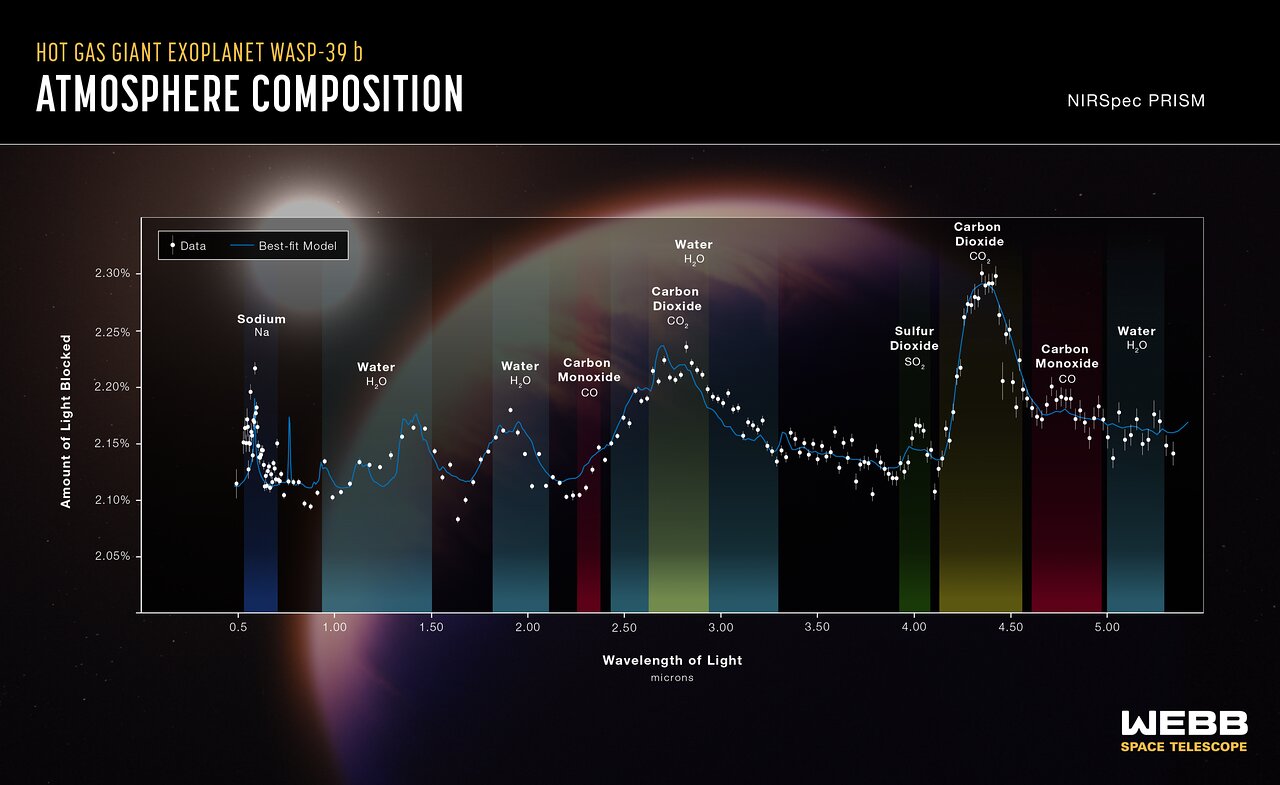
Early outcomes have been massively encouraging. In August, astronomers introduced that JWST had made the first confirmed detection of carbon dioxide fuel within the ambiance of an exoplanet, on this case WASP-39b, which is 700 gentle years-away. Later, in November, astronomers launched a extra complete spectrum exhibiting the absorption strains of components and molecules in WASP-39b’s ambiance, together with not solely carbon dioxide but in addition carbon monoxide, potassium, sodium, sulfur dioxide and water vapor.
The findings had been described as essentially the most detailed evaluation of an exoplanet’s ambiance but.
The spectrum confirmed that there was much more oxygen within the planet’s ambiance than carbon, in addition to an abundance of sulfur. Scientists assume that sulfur will need to have come from quite a few collisions that WASP-39b skilled with smaller planetesimals when it was forming, giving us clues to the planet’s evolution that might additionally trace at how the fuel giants in our personal solar system, Jupiter and Saturn, shaped. As well as, the existence of sulfur dioxide is the primary instance of a product of photochemistry on a planet past the solar system, because the compound types when a star’s ultraviolet gentle reacts with molecules in a planetary ambiance.
Looking for hints of life and habitability

Research of planets comparable to WASP-39b are one factor, however one of many holy grails of exoplanet science is to search out one other planet that’s liveable, like Earth, and JWST is properly positioned to characterize alien worlds.
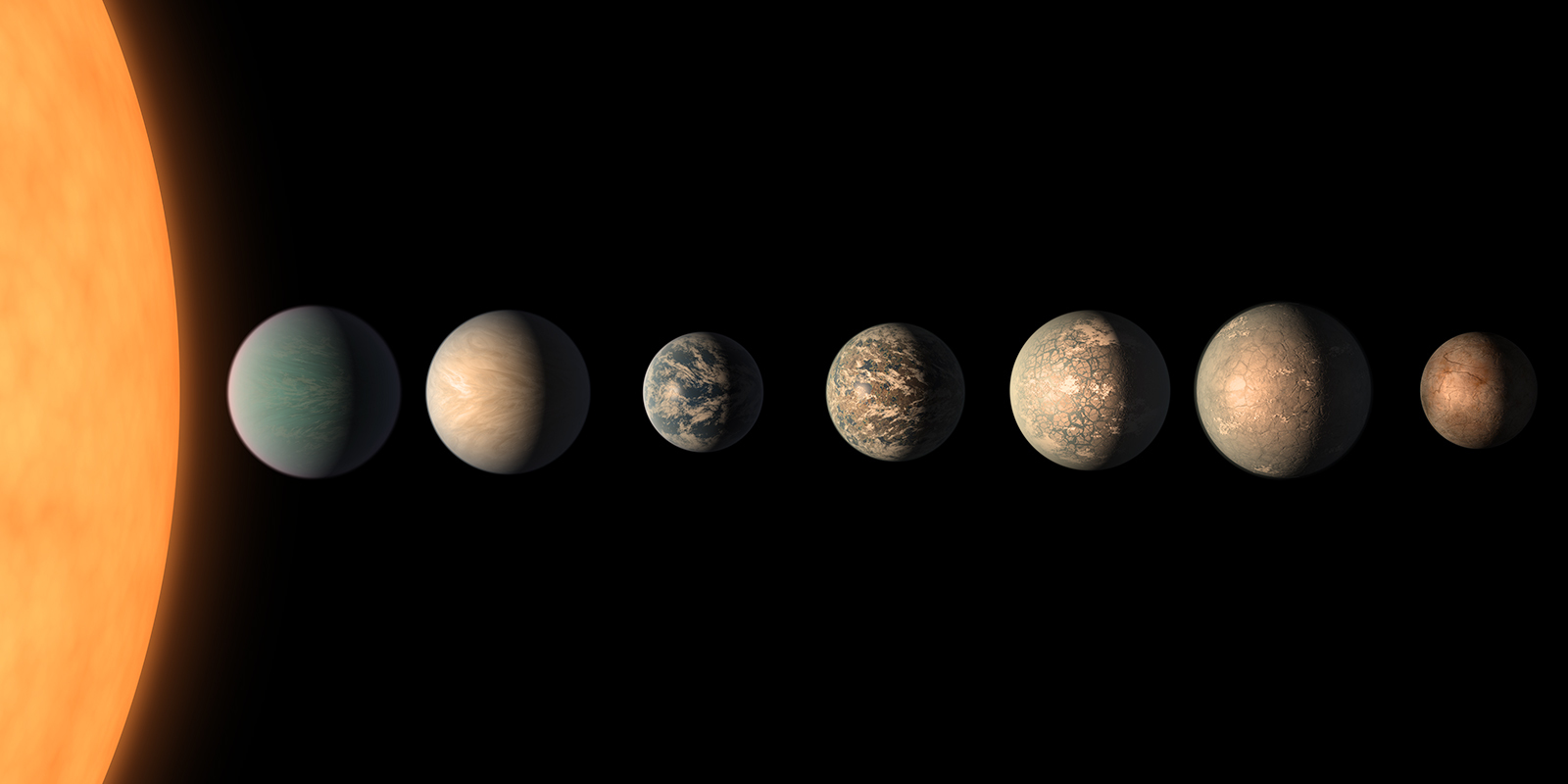
The aforementioned observations of WASP-39b bode properly for forthcoming research of the planets of the TRAPPIST-1 system of seven rocky planets orbiting a red dwarf star positioned 40.7 light-years away from Earth. 4 of those worlds lie within the star’s putative liveable zone, the place temperatures would allow liquid water to persist on the floor; given the appropriate circumstances they might doubtlessly be liveable to various levels.
Preliminary observations with JWST are specializing in TRAPPIST-1c, which is the best to look at. Fashions predict that it’ll have an environment just like Venus, with a lot of carbon dioxide. Whereas TRAPPIST-1c is probably going too scorching to be liveable, figuring out whether or not it has an environment and, in that case, whether or not that ambiance possesses carbon dioxide will probably be an enormous step towards characterizing Earth-size worlds. It’ll even be an enormous activity, requiring 100 hours of observing time with JWST, which is tackling about 10,000 hours of observations throughout its first 12 months of science.
From TRAPPIST-1c, issues might turn out to be extra formidable, with JWST concentrating on the opposite worlds within the TRAPPIST-1 system which might be extra more likely to be liveable, in addition to comparable worlds round different close by stars. Astronomers will probably be looking out for biosignatures, such because the presence of each methane and oxygen in an environment. The invention of photochemical reactions in WASP-39b’s ambiance can also be an necessary step, since photochemical reactions drive the formation of the carbon-based molecular constructing blocks of life.
Cosmic chemistry and the evolution of galaxies
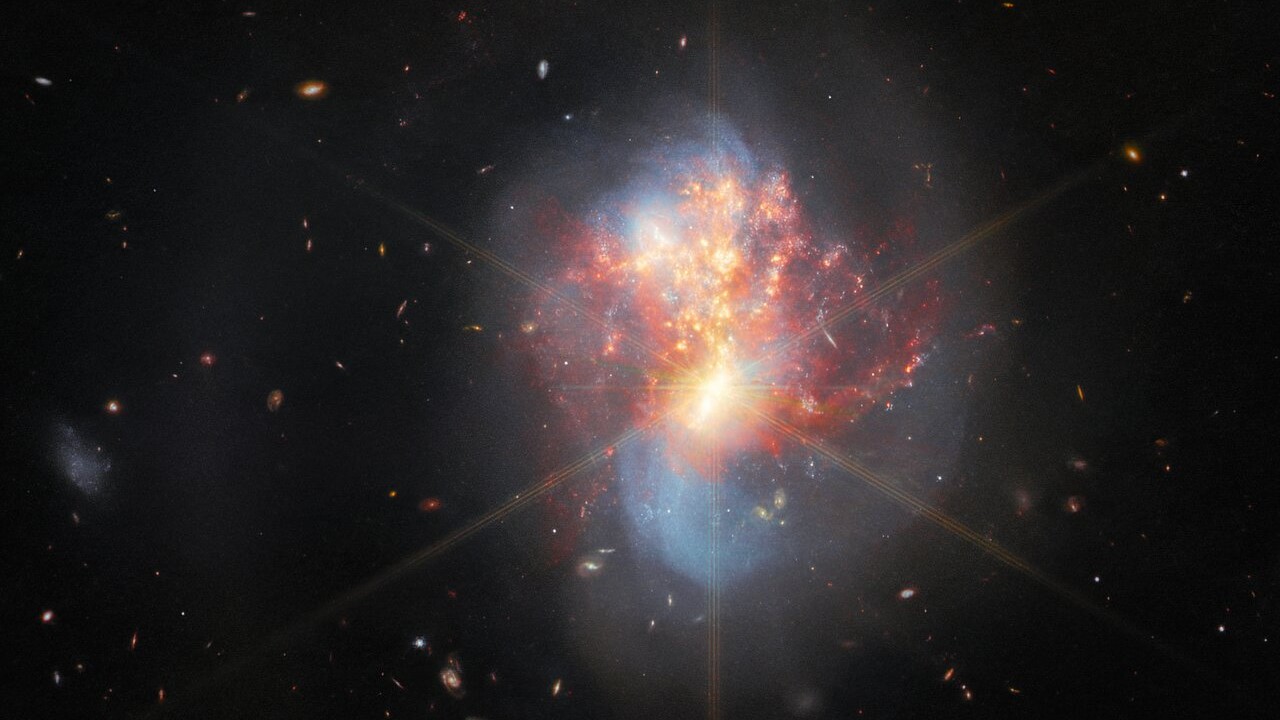

Some stars stay for billions upon billions of years, however others exist for simply a short while earlier than both exploding in a supernova or increasing to turn out to be a red giant that then puffs off its outer layers into deep space. In each conditions, the celebs disperse massive quantities of cosmic dust shaped from components heavier than hydrogen and helium throughout space.
It seems that there’s a relationship between a galaxy’s mass, its star-formation fee and its chemical abundances. Deviations from this relationship at excessive redshift would possibly point out that galaxies advanced in another way within the early universe. Previous to JWST, astronomers might solely reliably measure the abundances of varied components in galaxies as much as a redshift of three.3; in different phrases, galaxies that existed about 11.5 billion years in the past. However how plentiful these heavy components had been in galaxies sooner than this can be a little bit of a thriller, and fertile floor for JWST to actually revolutionize our understanding.
Early results from JWST have proven that the connection between star formation and mass does maintain for galaxies at redshifts as high as 8, however that their abundance of heavier components is thrice decrease than anticipated. This discrepancy means that stars and galaxies shaped extra rapidly than we realized, earlier than sufficient generations of stars had the prospect to die out and disperse their components into the cosmos.
JWST units its sights on the solar system
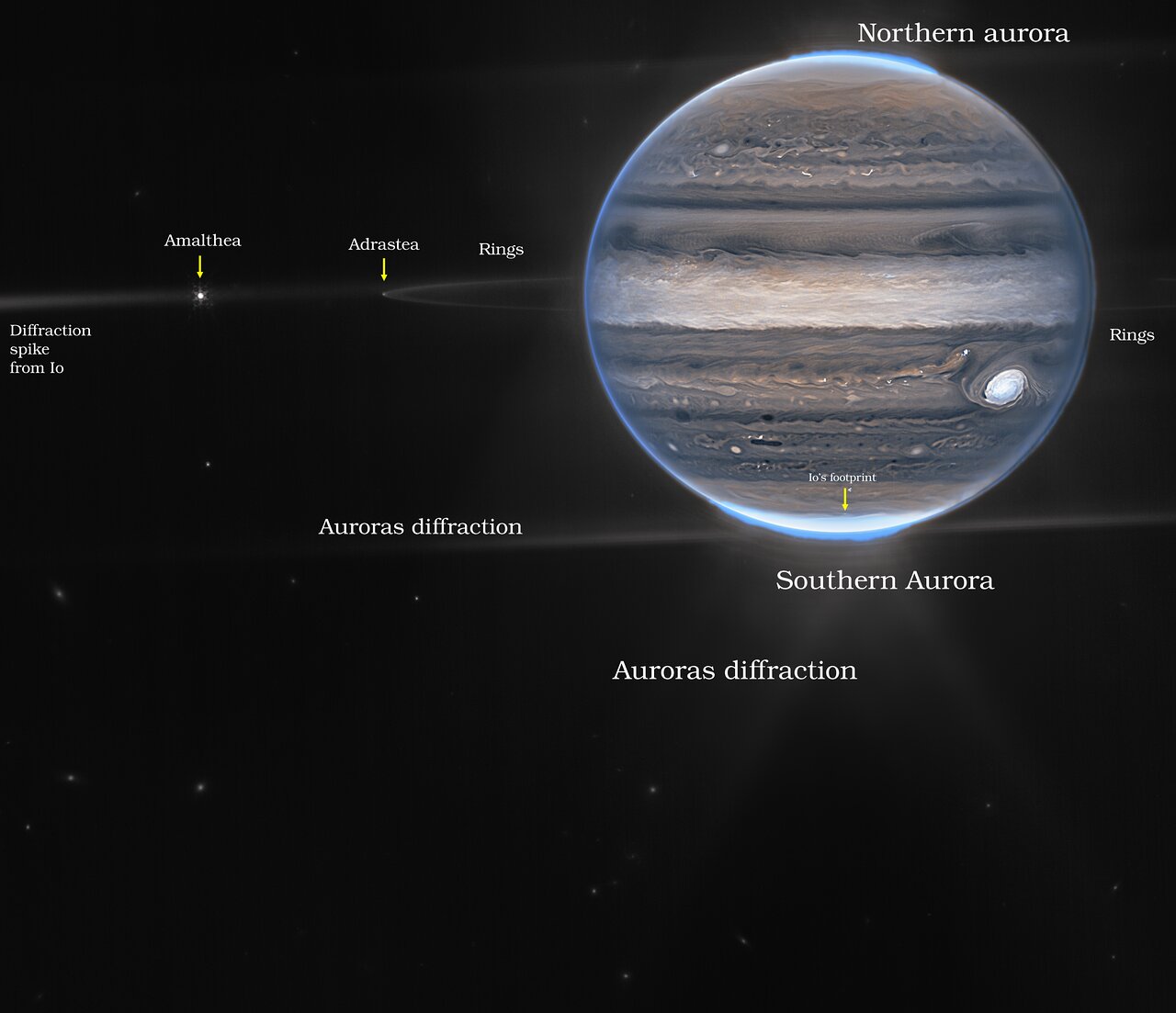

Though JWST was designed to probe deep space, it will also be used to look at our nearest neighbors, and the outcomes have been pleasantly stunning.
Astronomers weren’t certain what to anticipate when JWST pointed at Jupiter due to how briskly it strikes and the way shiny the planet is in comparison with the faint distant galaxies JWST often observes. Scientists anxious that Jupiter would possibly overload JWST’s delicate detectors or wipe out fainter options with its glare, however the results had been higher than might be imagined. JWST’s pictures confirmed Jupiter’s faint rings and a few of its small moons, in addition to the planet’s atmospheric bands and auroras.
By observing in near- and mid-infrared gentle, with the excessive decision that JWST’s large mirror supplies, astronomers are in a position to peer deeper into Jupiter’s ambiance to see what is going on on beneath the cloud tops and find out how deeply the clouds lengthen.
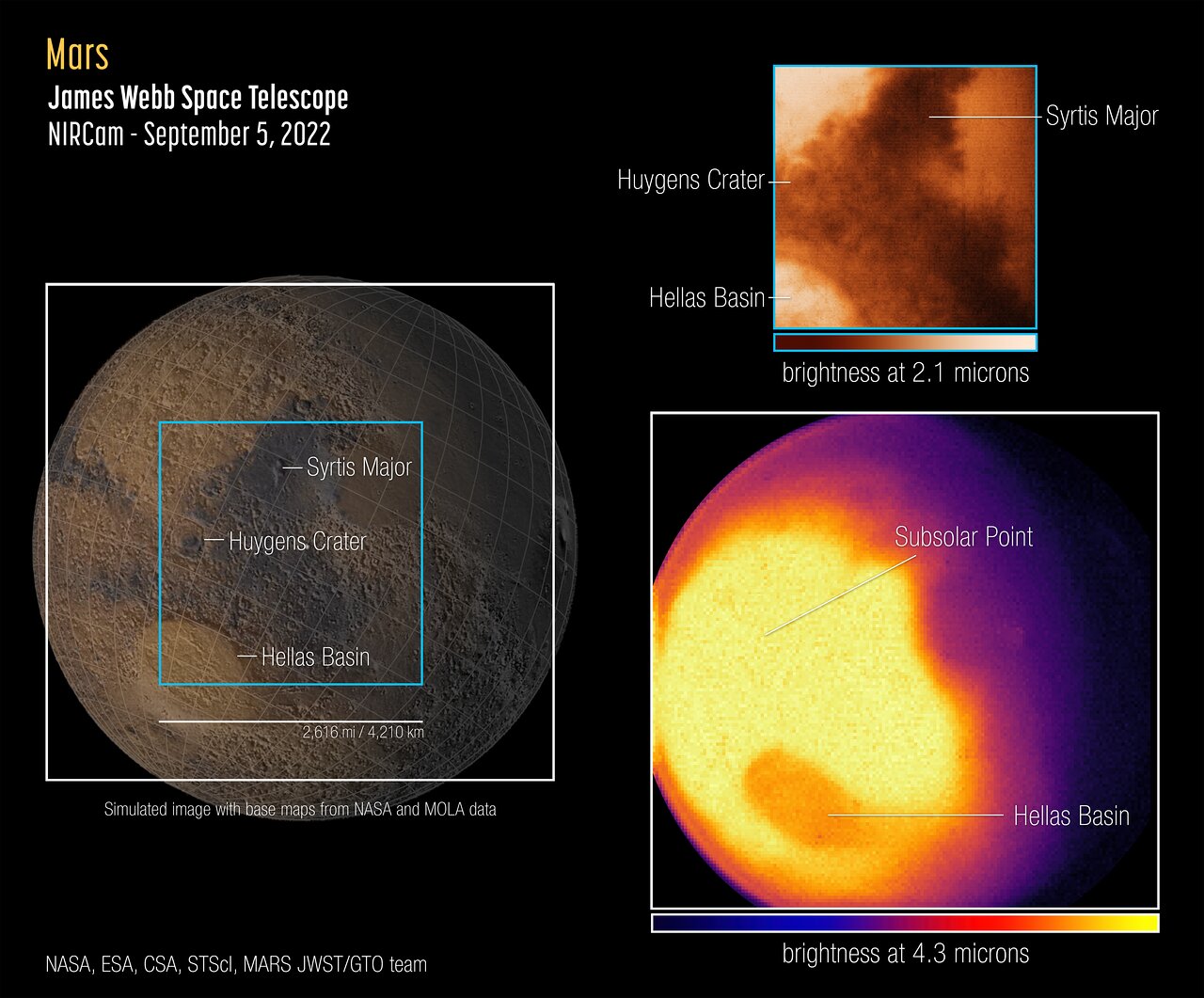
JWST has additionally imaged faraway Neptune, Saturn’s moon Titan and Mars. Whereas JWST’s portrait of the Purple Planet might not be aesthetically pleasing, it reveals temperature variations on Mars‘ floor and absorption by carbon dioxide in its ambiance. Sooner or later, JWST will observe Mars to trace extra tenuous gases, comparable to mysterious seasonal plumes of methane that might originate in both geological or organic exercise.
Star formation
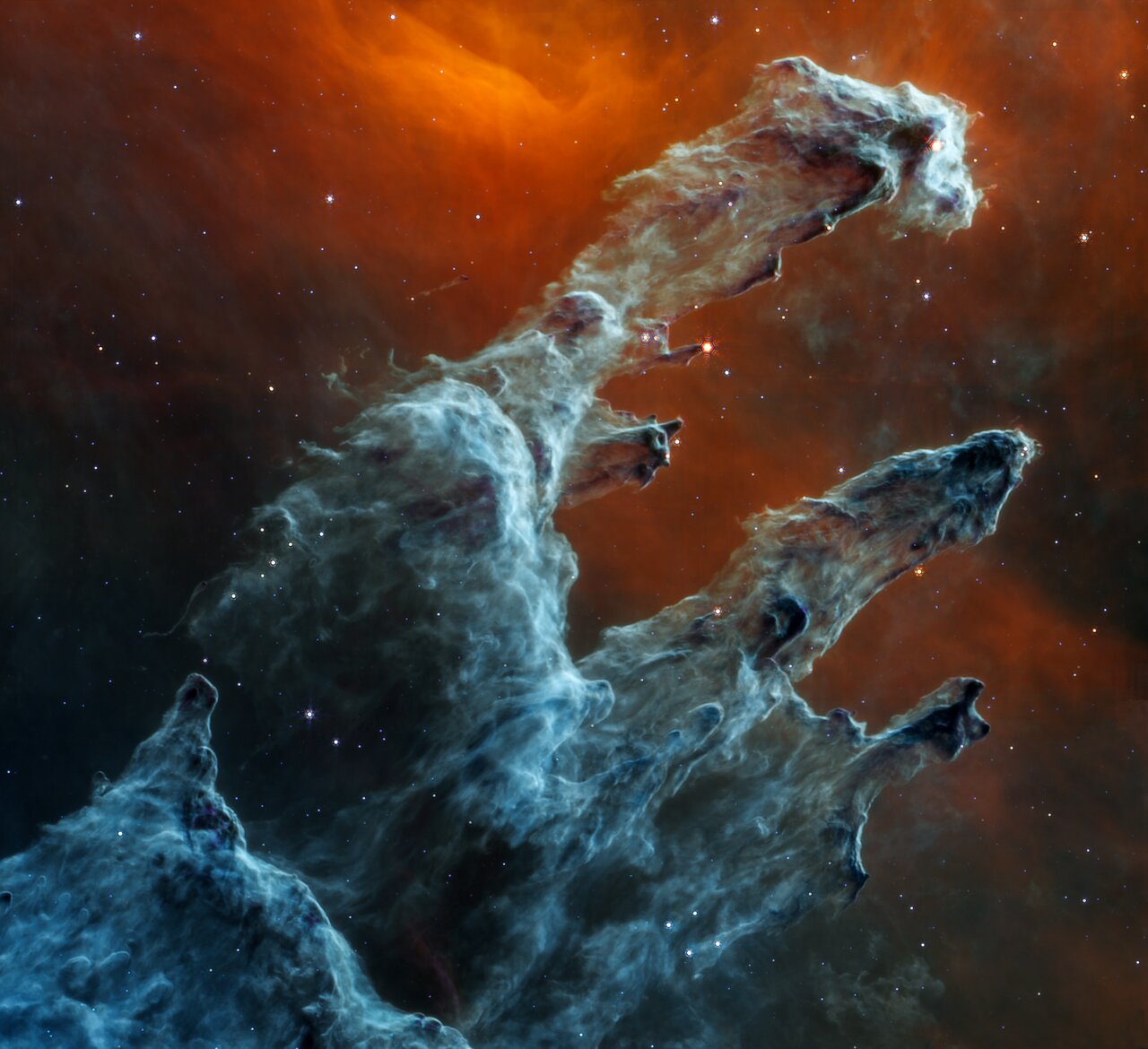

One of many Hubble Space Telescope‘s most iconic images was that of the Pillars of Creation — columns of molecular fuel many light-years lengthy discovered within the Eagle Nebula. These columns are cosmic nurseries the place stars are born. JWST has revisited the Pillars of Creation, and the ensuing pictures in near- and mid-infrared gentle are simply as particular as the unique.
However the brand new views are additionally extra than simply fairly footage. JWST’s infrared imaginative and prescient is ready to penetrate by way of the dust within the Pillars to achieve a greater view of the star formation happening inside, exhibiting knots of molecular fuel on the verge of collapsing into nascent stars. When these stars are only a few hundred thousand years outdated, they start to shoot out jets that erode the sides of the Pillars.
Elsewhere, JWST has offered one of the vital detailed appears to be like at such a protostar, generally known as L1527, and the way it’s interacting with the molecular fuel that’s accreting onto it, prompting outbursts which might be clearing out two cavities within the butterfly-shaped nebula.
Earlier than JWST, optical observations of younger stars had been restricted as a result of dust blocks their gentle. Radio and submillimeter observations can detect a few of what’s going on, and former infrared telescopes might see broad strokes however nothing detailed. JWST now provides the decision essential to reveal the secrets and techniques of star formation in far better element than ever earlier than.
Altering how space telescopes are constructed
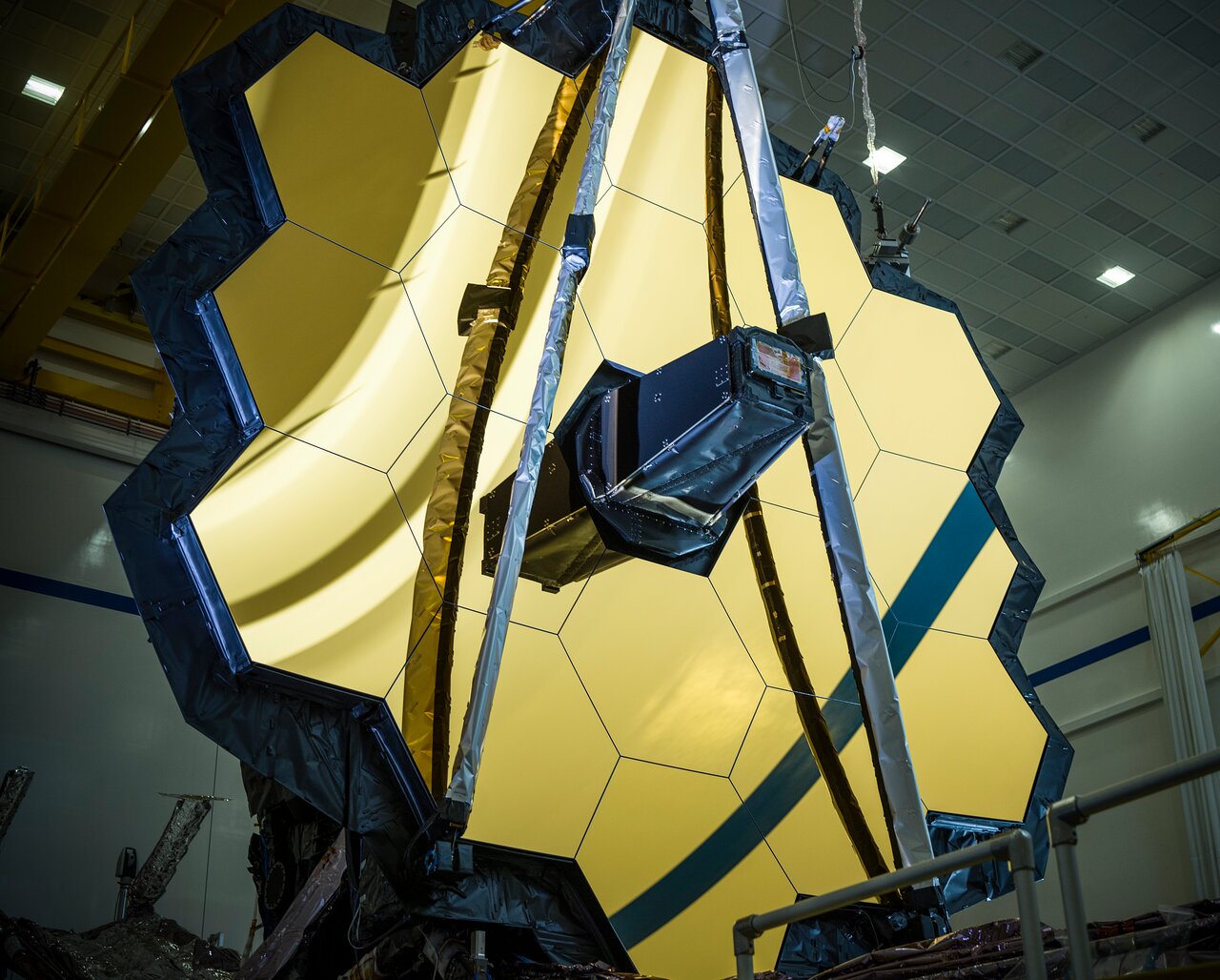

JWST took lots of hassle and cash to ultimately get into orbit. Years overdue and billions of {dollars} over-budget, its revolutionary design has nonetheless blazed a brand new path for space telescopes. Specifically, its huge, golden major mirror, shaped by unfolding 18 hexagonal segments, was brand-new engineering to allow a telescope of such nice measurement to be launched into space.
Sooner or later, the trouble of designing and constructing JWST will repay not solely within the revolutionary scientific discoveries that it’ll make, but in addition in the way it will encourage the design of the subsequent era of huge space telescopes.
The U.S. Nationwide Academies’ decadal report on the astrophysics priorities over the subsequent 10 years recommends because the top-priority undertaking the event of a big optical and ultraviolet telescope to exchange Hubble someday within the 2040s. This telescope would have at minimal a mirror diameter of 26 ft (8 m), a feat that may be achieved solely by the segmented design pioneered by JWST.
The dimensions of a rocket now not constrains the dimensions of your telescope; if it would not match contained in the rocket faring then the telescope may be folded up, identical to JWST was. No matter discoveries these future space telescopes make, we could have JWST to thank.
Comply with Keith Cooper on Twitter @21stCenturySETI. Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.




