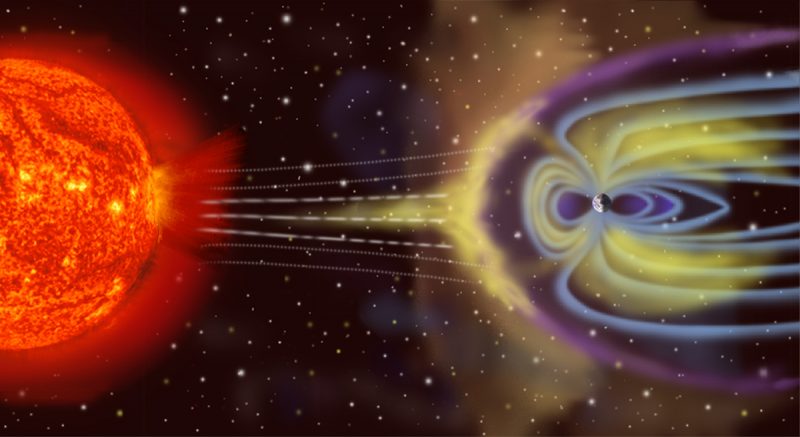
What occurs throughout a geomagnetic storm?
A geomagnetic storm is a brief disturbance within the magnetic area surrounding Earth. Flares on the sun and/or coronal mass ejections (aka CMEs) trigger these storms. When a flare erupts on the sun’s floor – and a CME, or cloud of charged particles, goes hurtling outward from the sun – a geomagnetic storm would possibly observe just a few days later. Earth would should be within the path of the CME to ensure that the geomagnetic storm to happen.
The frequency of geomagnetic storms will increase and reduces with the 11-year cycle of exercise on the sun. So throughout solar maximum, geomagnetic storms happen extra typically.
Throughout geomagnetic storms, folks at far northern and southern latitudes on Earth see elevated shows of the gorgeous aurorae, or northern and southern lights.
The final solar cycle – cycle quantity 24 – peaked in April 2014. It was a considerably quieter peak than different current solar cycles, with sunspot numbers and different exercise on the sun right down to a degree that hadn’t been seen since cycles 12 to fifteen (1878-1923).
The present solar cycle
The present solar cycle – cycle quantity 25 – has been fairly lively to this point and can proceed by way of 2030. The truth is, it’s anticipated to peak round 2025.
Lately, on March 23, 2023, EarthSky warned of a geomagnetic storm in our day by day Sun activity submit. And storm it did! Individuals reported seeing the aurora as far south as Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona and Virginia. So keep tuned, we might even see extra geomagnetic storms over the subsequent few years.
For present solar exercise go to EarthSky’s Sun activity post.
By the way in which, auroras are likely to occur extra across the equinoxes.
Backside line: Geomagnetic storms are disturbances in Earth’s magnetic area, brought on by exercise on the sun.
Read more: Aurora photos from the March 24, 2023, geomagnetic storm