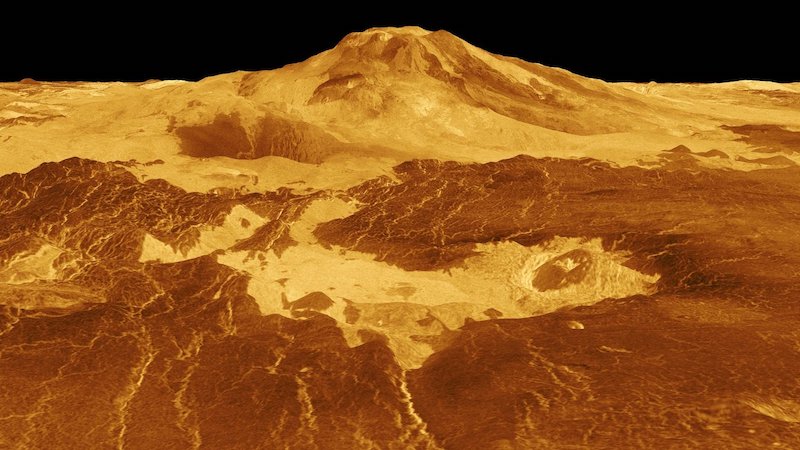
Extra proof for energetic Venus volcanoes
Scientists have discovered 2 extra items of direct geological proof of latest volcanic exercise on the planet next-inward from Earth, Venus. That is the second time such proof has been present in knowledge from the Magellan spacecraft, which mapped 98% of Venus’ floor from 1990 to 1992. The pictures it generated stay our most detailed of Venus up to now. Scientists in Italy analyzed archival knowledge from Magellan. They discovered floor adjustments indicating the formation of latest rock from lava flows linked to volcanoes that have been in eruption whereas the spacecraft orbited the planet. Davide Sulcanese of d’Annunzio College in Pescara, Italy, who led the research, mentioned,
By analyzing the lava flows we noticed in two places on the planet, we have now found that the volcanic exercise on Venus could possibly be corresponding to that on Earth.
This newest discovery builds on the historic 2023 discovery of pictures from Magellan’s artificial aperture radar that exposed adjustments to a vent related to the volcano Maat Mons close to Venus’ equator.
The 2023 radar pictures proved to be the primary direct proof of a latest volcanic eruption on the planet. By evaluating Magellan radar pictures over time, the authors of that earlier research noticed adjustments brought on by the outflow of molten rock from Venus’ subsurface filling the vent’s crater and spilling down the vent’s slopes.
The 2024 research is revealed within the journal Nature Astronomy.
Radar backscatter
For the brand new research, the researchers likewise targeted on archival knowledge from Magellan’s artificial aperture radar. Radio waves despatched by the radar traveled by means of Venus’ thick cloud cowl, then bounced off the planet’s floor and again to the spacecraft. Known as backscatter, these mirrored radar alerts carried details about the rocky surface material they encountered.
The 2 places studied have been the volcano Sif Mons in Eistla Regio and the western a part of Niobe Planitia, which is house to quite a few volcanic options. By analyzing the backscatter knowledge obtained from each places in 1990 and once more in 1992, the researchers discovered that radar sign power elevated alongside sure paths in the course of the later orbits. These adjustments advised the formation of latest rock, probably solidified lava from volcanic exercise that occurred throughout that two-year interval. However additionally they thought-about different prospects, such because the presence of micro-dunes (fashioned from windblown sand) and atmospheric results that might intervene with the radar sign.
To assist verify new rock, the researchers analyzed Magellan’s altimetry (floor peak) knowledge to find out slope of the topography and find obstacles that lava would circulation round. Research co-author Marco Mastrogiuseppe of Sapienza College of Rome mentioned:
We interpret these alerts as flows alongside slopes or volcanic plains that may deviate round obstacles resembling protect volcanoes like a fluid. After ruling out different prospects, we confirmed our greatest interpretation is that these are new lava flows.
Utilizing flows on Earth as a comparability, the researchers estimate new rock that was emplaced in each places to be between 10 and 66 ft (3 and 20 meters) deep, on common. In addition they estimate that the Sif Mons eruption produced about 12 sq. miles (30 sq. kilometers) of rock — sufficient to fill a minimum of 36,000 Olympic-size swimming swimming pools. The Niobe Planitia eruption produced about 17 sq. miles (45 sq. km) of rock, which might fill 54,000 Olympic swimming swimming pools. As a comparability, the 2022 eruption of Mauna Loa in Hawaii, Earth’s largest energetic volcano, produced a lava circulation with sufficient materials to fill 100,000 Olympic swimming pools.
Scott Hensley, senior analysis scientist at JPL and co-author of the 2023 research, mentioned:
This thrilling work gives one other instance of volcanic change on Venus from new lava flows that augments the vent change Dr. Robert Herrick and I reported final 12 months. This consequence, in tandem with the sooner discovery of present-day geologic exercise, will increase the joy within the planetary science neighborhood for future missions to Venus.
Scientists research energetic volcanoes to know how a planet’s inside can form its crust, drive its evolution, and have an effect on its habitability. The invention of latest volcanism on Venus gives a helpful perception to the planet’s historical past and why it took a special evolutionary path than Earth.
Determining volcanoes
Hensley is the undertaking scientist for NASA’s upcoming VERITAS mission, and Mastrogiuseppe is a member of its science group.
Brief for Venus Emissivity, Radio science, InSAR, Topography, And Spectroscopy, VERITAS is slated to launch early subsequent decade, utilizing a state-of-the-art artificial aperture radar to create 3D world maps and a near-infrared spectrometer to determine what Venus’ floor is made from whereas additionally monitoring volcanic exercise. As well as, the spacecraft will measure the planet’s gravitational subject to find out its inner construction. Suzanne Smrekar, a senior scientist at JPL and principal investigator for VERITAS, mentioned:
These new discoveries of latest volcanic exercise on Venus by our worldwide colleagues present compelling proof of the sorts of areas we must always goal with VERITAS when it arrives at Venus. Our spacecraft could have a collection of approaches for figuring out floor adjustments which might be way more complete and better decision than Magellan pictures. Proof for exercise, even within the lower-resolution Magellan knowledge, supercharges the potential to revolutionize our understanding of this enigmatic world.
Backside line: An evaluation of radar knowledge from the Magellan spacecraft has revealed extra proof for energetic Venus volcanoes. It seems two volcanoes erupted within the early Nineties. This provides to the 2023 discovery of a special energetic volcano in Magellan knowledge.
Read more: Active volcanoes on Venus found in Magellan data