A world crew of astronomers at present introduced the invention of the 2 earliest and most distant galaxies ever seen, relationship again to solely 300 million years after the Large Bang. These outcomes, utilizing NASA’s James Webb House Telescope (JWST), mark a significant milestone within the examine of the early universe.
The discoveries had been made by the JWST Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) crew. Daniel Eisenstein from the Heart for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA) is without doubt one of the crew leaders of JADES and Principal Investigator of the observing program that exposed these galaxies. Ben Johnson and Phillip Cargile, each Analysis Scientists at CfA, and Zihao Wu, a Harvard Ph.D. scholar at CfA, additionally performed vital roles.
Due to the enlargement of the universe, the sunshine from distant galaxies stretches to longer wavelengths because it travels. This impact is so excessive for these two galaxies that their ultraviolet light is shifted to infrared wavelengths the place solely JWST can see it. As a result of gentle takes time to journey, extra distant galaxies are additionally seen as they had been earlier in time.
The 2 record-breaking galaxies are known as JADES-GS-z14-0 and JADES-GS-z14-1, the previous being the extra distant of the 2. Along with being the brand new distance file holder, JADES-GS-z14-0 is outstanding for a way huge and shiny it’s.
“The scale of the galaxy clearly proves that many of the gentle is being produced by massive numbers of young stars,” mentioned Eisenstein, a Harvard professor and chair of the astronomy division, “moderately than materials falling onto a supermassive black hole within the galaxy’s middle, which would seem a lot smaller.”
The mixture of the acute brightness and the truth that younger stars are fueling this excessive luminosity makes JADES-GS-z14-0 probably the most placing proof but discovered for the speedy formation of huge, large galaxies within the early universe.
“JADES-GS-z14-0 now turns into the archetype of this phenomenon,” says Dr. Stefano Carniani of the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, lead writer on the discovery paper. “It’s gorgeous that the universe could make such a galaxy in solely 300 million years.”
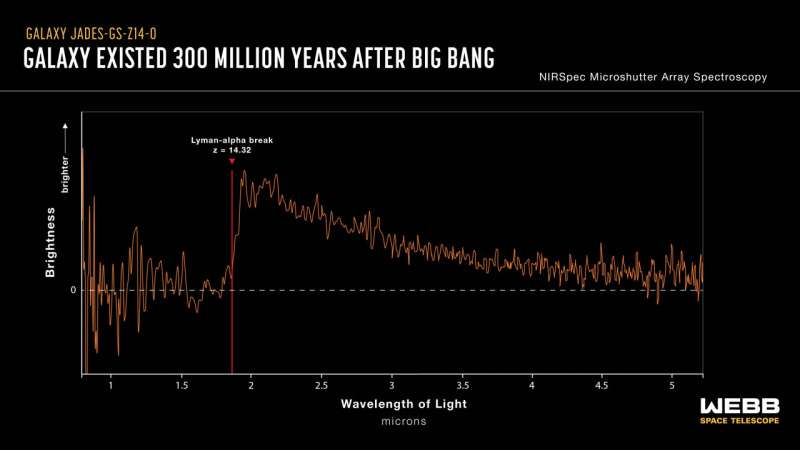
Proof for surprisingly vigorous early galaxies appeared even within the first JWST photographs and has been mounting within the first two years of the mission. This pattern runs counter to expectations that almost all astronomers had earlier than the launch of JWST of theories of galaxy formation.
JADES-GS-z14-0 was a puzzle for the JADES crew once they first noticed it over a yr in the past, because it seems shut sufficient on the sky to a foreground galaxy that the crew couldn’t ensure that the 2 weren’t neighbors. However in October 2023, the JADES crew carried out even deeper imaging—5 full days with the JWST Close to-Infrared Digicam on only one subject—and used filters designed to raised isolate the earliest galaxies.
“We simply could not see any believable option to clarify this galaxy as being merely a neighbor of the extra close by galaxy,” says Dr. Kevin Hainline, analysis professor on the College of Arizona.
The galaxy is situated in a subject the place the JWST Mid-Infrared Instrument had carried out an ultra-deep remark. Its brightness at intermediate infrared wavelengths is an indication of emission from hydrogen and even oxygen atoms within the early universe.
“Regardless of being so younger, the galaxy is already onerous at work creating the weather acquainted to us on Earth,” mentioned Zihao Wu, a co-author on a second paper about this discovering, led by Jakob Helton, a graduate scholar on the College of Arizona.
Emboldened, the crew then obtained a spectrum of every galaxy, and confirmed their hopes that JADES-GS-z14-0 was certainly a record-breaking galaxy and that the fainter candidate, JADES-GS-z14-1, was almost as far-off.
A third paper led by Brant Robertson, professor on the College of California-Santa Cruz, and Ben Johnson, research the evolution of this early inhabitants of galaxies.
“This superb object exhibits that galaxy formation within the early universe may be very speedy and intense,” mentioned Johnson, “and JWST will enable us to seek out extra of those galaxies, maybe when the universe was even youthful. It’s a marvelous alternative to review how galaxies get began.”
All three papers are at the moment obtainable on the arXiv preprint server.
Extra info:
A shining cosmic daybreak: spectroscopic affirmation of two luminous galaxies at z∼14, arXiv:2405.18485 [astro-ph.GA] arxiv.org/abs/2405.18485
JWST/MIRI photometric detection at 7.7 μm of the stellar continuum and nebular emission in a galaxy at z>14, arXiv:2405.18462 [astro-ph.GA] arxiv.org/abs/2405.18462
Brant Robertson et al, Earliest Galaxies within the JADES Origins Discipline: Luminosity Perform and Cosmic Star-Formation Charge Density 300 Myr after the Large Bang, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2312.10033
Journal info:
arXiv
Supplied by
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
Quotation:
Astronomers assist discover most distant galaxy utilizing James Webb House Telescope (2024, Might 30)
retrieved 30 Might 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-astronomers-distant-galaxy-james-webb.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




