A brand new scale for atmospheric rivers
Atmospheric rivers aren’t new. However they’re coming into the general public consciousness now, as they grow to be extra intense and frequent with world warming. A pair of atmospheric rivers are placing California now, for instance, inflicting widespread flooding that’s anticipated to proceed via Tuesday, March 14, 2023. In the meantime, the American Geophysical Union (AGU) has launched phrase of a brand new study that demonstrates the worth of a just lately developed depth scale for atmospheric rivers.
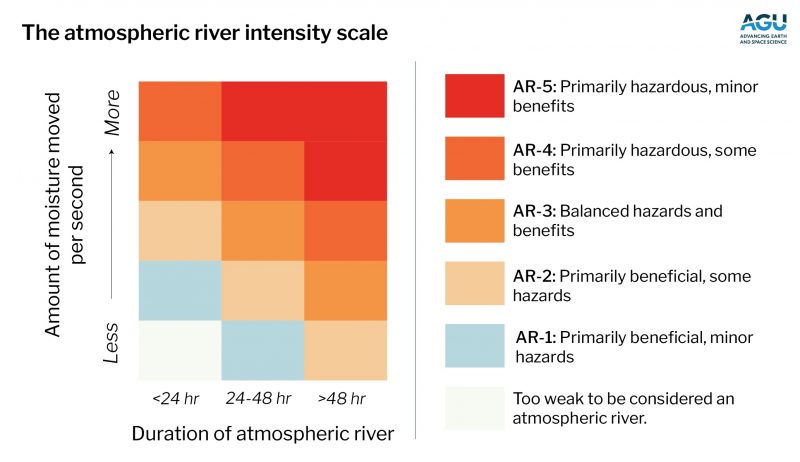
It’s very like the Saffir–Simpson scale that slots hurricanes into 5 classes: 1 (weakest) to five (strongest). The hurricane scale relies on sustained winds. The brand new atmospheric river scale additionally has 5 classes: AR-1 (weakest) to AR-5 (strongest).
It’s primarily based on how lengthy the atmospheric river lasts, and the way a lot moisture it transports.
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
Never-ending rain and harmful flooding
The AGU’s peer-reviewed Journal of Geophysical Analysis: Atmospheres published the brand new research earlier this yr (January 2023). The scientists’ statement defined:
Partially as a result of some West Coast weather outlets are utilizing the depth scale, ‘atmospheric river’ is now not an obscure meteorological time period. As an alternative, it brings sharply to thoughts endless rain and harmful flooding …
The string of atmospheric rivers that hit California in December and January, for example, at occasions reached AR-4. Earlier in 2022, the atmospheric river that contributed to disastrous flooding in Pakistan was an AR-5, probably the most damaging, most intense atmospheric river ranking.
The dimensions helps communities know whether or not an atmospheric river will convey profit or trigger chaos. The storms can ship much-needed rain or snow. But when they’re too intense, they’ll trigger flooding, landslides and energy outages, as California and Pakistan skilled.
Probably the most extreme atmospheric rivers could cause tons of of thousands and thousands of {dollars} of injury in days within the western U.S.; harm in different areas has but to be comprehensively assessed.
Striving for situational consciousness
F. Martin Ralph is an atmospheric scientist at Scripps Establishment of Oceanography at UC San Diego and a co-author on the brand new research. He stated:
Atmospheric rivers are the hurricanes of the West Coast relating to the general public’s situational consciousness. Individuals must know after they’re coming, have a way for the way excessive the storm can be, and know methods to put together.
This scale is designed to assist reply all these questions.
Ralph and his colleagues initially developed the dimensions for the U.S. West Coast. They stated their new study demonstrates that atmospheric river occasions could be immediately in contrast globally utilizing the depth scale.
How they did the research
The researchers used local weather knowledge and their previously developed algorithm for figuring out and monitoring atmospheric rivers to construct a database of intensity-ranked atmospheric river occasions across the globe over 40 years (1979/1980 to 2019/2020). Atmospheric scientist Bin Guan, who’s affiliated with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, led the research. He commented:
This research is a primary step towards making the atmospheric river scale a globally great tool for meteorologists and metropolis planners. By mapping out the footprints of every atmospheric river rank globally, we will begin to higher perceive the societal impacts of those occasions in many various areas.
Extra research outcomes
The authors additionally discovered that extra intense atmospheric rivers (AR-4 and AR-5) are much less widespread than weaker occasions. And that AR-5 occasions happen solely as soon as each two to a few years when globally averaged.
Probably the most intense atmospheric rivers are additionally much less prone to make landfall, and after they do, they’re unlikely to keep up their energy for lengthy and penetrate farther inland. Guan stated:
They have an inclination to dissipate quickly after landfall, leaving their impacts most felt in coastal areas.
The research discovered 4 “facilities,” or hotspots, of the place AR-5s are likely to die, within the extratropical North Pacific and Atlantic, Southeast Pacific, and Southeast Atlantic. Cities on the coasts inside these hotspots, similar to San Francisco and Lisbon, are almost certainly to see intense AR-5s make landfall.
Midlatitudes usually are the almost certainly areas to have atmospheric rivers of any rank.
Sturdy El Niño years usually tend to have extra atmospheric rivers, and stronger ones at that, which is noteworthy as a result of NOAA just lately forecasted that an El Niño situation is prone to develop by the tip of the summer season this yr.
Will TV meteorologists undertake the dimensions for atmospheric rivers?
Whereas native meteorologists, news outlets and different West Coasters could have integrated “atmospheric river” and the depth scale into their lives, adoption has been slower elsewhere, Ralph stated.
He hopes to see, inside 5 years or so, meteorologists on TV all over the world incorporating the atmospheric river depth scale into their forecasts, telling folks whether or not the atmospheric river can be helpful or if they should put together for a critical storm.
Backside line: Scientists are pushing an depth scale for atmospheric rivers, very like the hurricane depth scale. They assume it’ll assist hold folks safer.