We’ve all seen the unimaginable photos of black holes, together with the first direct images of those mysterious objects, first launched in 2019. Now astronomers have obtained one other first: a picture exhibiting each a supermassive black hole on the heart of a distant galaxy, and its highly effective jet. The huge black hole is within the heart of galaxy Messier 87, which is 55 million light-years away. It’s the identical black hole imaged initially by the Occasion Horizon Telescope (EHT) in 2019. A world group of astronomers released the brand new picture on Wednesday, April 26, 2023.
The researchers published their related peer-reviewed paper in Nature on the identical day.
The Occasion Horizon Telescope took the earlier photos of this black hole. However this time, astronomers used a number of telescopes to acquire the brand new picture: the International mm-VLBI Array (GMVA), the Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Greenland Telescope (GLT). The European Southern Observatory (ESO) is a companion of ALMA.
The astronomers first carried out the observations in 2018. They’ve been combining the information from the a number of telescopes collectively since then.
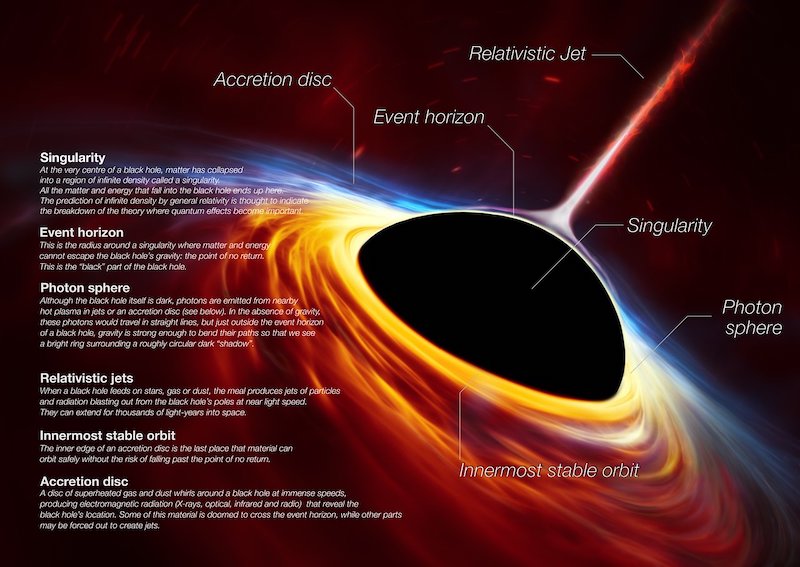
A black hole and its highly effective jet
That is the primary time that astronomers have captured each a black hole and its jet – known as a relativistic jet – in the identical picture. Scientists have lengthy recognized that black holes can emit these enormous jets. However how they kind nonetheless isn’t nicely understood. Ionized matter inside the jets strikes at near the pace of sunshine. As lead writer Ru-Sen Lu from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory in China stated:
We all know that jets are ejected from the area surrounding black holes. However we nonetheless don’t totally perceive how this really occurs. To review this straight we have to observe the origin of the jet as shut as doable to the black hole. Because of ALMA’s location and sensitivity, we might reveal the black hole shadow and see deeper into the emission of the jet on the similar time.
We consider black holes as highly effective objects that suck in materials that may by no means escape. Not even mild can depart a black hole. That’s principally true, however black holes also can have enormous rings of matter – known as accretion disks – that swirl round them. The brand new photos present the bottom of a jet linked to the ring surrounding the black hole. Co-author Jae-Young Kim, from the Kyungpook Nationwide College in South Korea and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany, stated:
This new picture completes the image by exhibiting the area across the black hole and the jet on the similar time.
New picture exhibits unprecedented element
The brand new picture exhibits particulars not beforehand seen collectively in any photographs of black holes. You may clearly see the jet expelled from the black hole. You can even see the ring of fabric and the black hole’s shadow. The shadow is a two-dimensional darkish zone brought on by the sturdy gravity of the black hole. It’s the pitch-black darkness within the heart of the accretion disk, within the singularity area. A singularity itself, nonetheless, isn’t a lot a place as it’s a situation, the place gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down.
The fabric within the ring turns into heated because it orbits the black hole. Because of this, it emits mild. That’s the reason we are able to see it, although the black hole itself is black and invisible. We see the matter orbiting the black hole as a hoop, as a result of the gravity of the black hole bends the sunshine. Within the shadow area, nonetheless, nothing is seen in any respect.
Beforehand, the Occasion Horizon Telescope imaged the black hole at a wavelength of 1.3 mm. However now, the brand new community of telescopes was in a position to receive a picture at an extended wavelength of three.5 mm. That permits extra particulars to be seen. Thomas Krichbaum of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy stated:
At this wavelength, we are able to see how the jet emerges from the ring of emission across the central supermassive black hole.
Bigger accretion disk
The dimensions of the accretion disk can also be bigger within the new picture. It seems to be about 50% bigger than it did within the earlier Occasion Horizon Telescope picture. The researchers say that’s as a result of the brand new picture is solely in a position to resolve extra of the fabric within the accretion disk. This additionally gives clues as to how the accretion disk shaped. As Keiichi Asada from the Academia Sinica in Taiwan famous:
To grasp the bodily origin of the larger and thicker ring, we had to make use of pc simulations to check totally different eventualities.
Future observations of the Messier 87 black hole
The researchers plan to make use of the identical community of telescopes to maintain observing the black hole. This could assist astronomers higher perceive how the highly effective jets originate. Eduardo Ros from the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy stated:
We plan to look at the area across the black hole on the heart of M87 at totally different radio wavelengths to additional research the emission of the jet. The approaching years can be thrilling, as we will be taught extra about what occurs close to some of the mysterious areas within the universe.
Backside line: For the first time, astronomers have taken a picture of a black hole that exhibits each the black hole and a strong jet of fabric being blasted away from it.
Source: A ring-like accretion structure in M87 connecting its black hole and jet




