Rigel is considered one of a number of good stars that grace our night time sky in January. It’s additionally the brightest star in one of the crucial beloved of constellations, Orion the Hunter. Rigel seems blue-white to the attention. It’s a surprising distinction to purple Betelgeuse, Orion’s second-brightest star. Categorised as a blue supergiant, Rigel is within the latter levels of its stellar lifetime and can sometime develop into a supernova. Hidden in Rigel’s brilliance are at the very least three different fainter companion stars that may solely be detected utilizing massive telescopes.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best New Year’s gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Easy methods to discover Rigel
At magnitude 0.13, Rigel is the Seventh-brightest star within the heavens, and the Fifth-brightest as seen from North America. It seems at a decrease nook of Orion the Hunter, one of many sky’s best-known constellations. It’s simple to identify due to its brightness and likewise due to its distinctive blue-white shade.
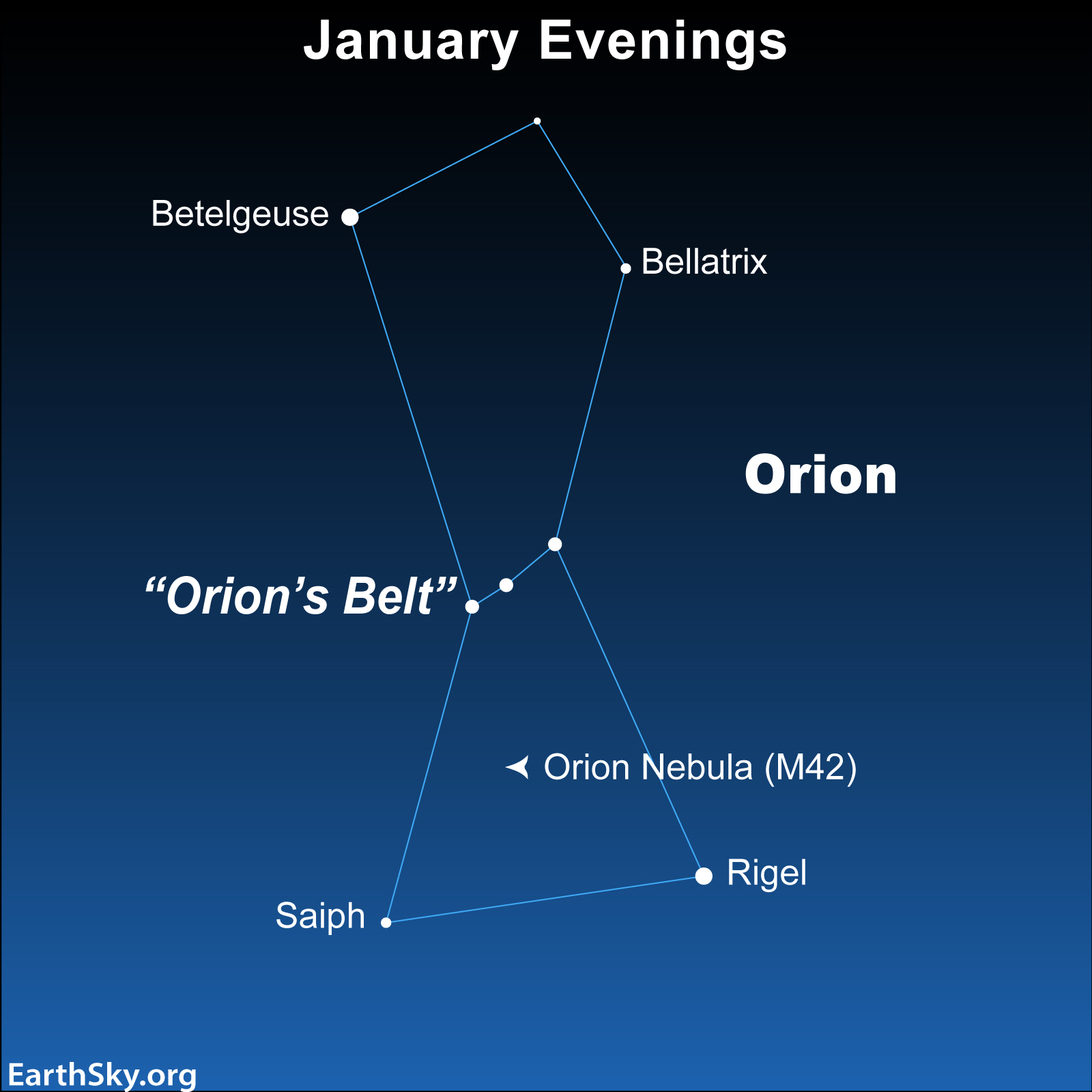
You’ll be able to catch Orion within the east earlier than daybreak in the course of the late Northern Hemisphere summer time. On January evenings, Orion shines prominently within the mid-evening sky. Search for Orion excessive within the south on northern winter (southern summer time) evenings. By early March, as quickly because the sun units, Orion is at its highest within the sky. By early Could, as seen from across the globe, Orion units earlier than the sky has an opportunity to get actually darkish.
Search for Orion
To search out Rigel, first search for its constellation, Orion. You’ll discover three stars in a brief, straight line. These stars mark Orion’s Belt. An imaginary line within the sky, heading typically southward – that’s at a proper or 90-degree angle from Orion’s Belt – takes you to Rigel. (In the event you as a substitute draw within the different course, you’d come to Betelgeuse, with its distinctive reddish tinge.)
Don’t confuse Rigel with Sirius, which is farther to the east and farther south. Sirius is comparable in look, however considerably brighter than Rigel.
The science of Rigel
We couldn’t dwell as near Rigel as we do to our sun. That’s as a result of its floor temperature is far hotter, about 21,000 levels Fahrenheit (11,600 levels Celsius) in distinction to about 10,000 F (5,500 C) for the sun.
Counting all its radiation (not simply seen mild, however infrared, ultraviolet and so forth), Rigel emits about 120,000 instances extra vitality than the sun. Astronomers calculate this luminosity based mostly on a distance of 860 light-years, a distance derived from knowledge collected by the Hipparcos space telescope. With such monumental vitality, you may be shocked to seek out that Rigel has solely 21 instances extra mass, and is greater than 70 instances the diameter of our sun.
Rigel is a blue supergiant star, designated as type B8 Ia. In response to stellar evolution idea, it’s a huge star coming into the latter a part of its life, having exhausted many of the hydrogen gas in its core. It’s additionally a variable star that exhibits slight irregular fluctuations in brightness. Sometime, it would explode as a supernova.
But Rigel shouldn’t be one of many galaxy’s largest stars, because the video under – from the European Southern Observatory – exhibits.
A bit of-known reality about Rigel: it’s the largest star in a multiple star system. There’s a shut companion about 400 instances fainter than Rigel. That “companion” is definitely two stars that may solely be resolved by massive telescopes. And a type of two companion stars is what’s referred to as a spectroscopic binary: two stars so shut they are often distinguished as two distinct entities solely through spectroscopic observations.
In different phrases, the Rigel system has 4 identified stars!
Historical past and mythology
Traditionally, the brightest star in a constellation receives the designation Alpha, the second-brightest is Beta, and so forth. This method isn’t used for Orion’s stars, nonetheless. As a substitute, the purple star Betelgeuse is Alpha Orionis, and Rigel is Beta. However Rigel is the brightest star in Orion.
This deviation from customary stellar designations may be as a result of Betelgeuse is a variable star and has been identified to at the very least method Rigel in brilliance. The German astronomer Johann Bayer utilized the designation Beta Orionis to Rigel within the early 1600s. He sought to systematize stellar naming conventions. It’s doable Betelgeuse was brighter round this time. These days, Rigel outshines Betelgeuse.
The identify Rigel comes from an Arabic phrase steadily translated as “The Left Foot of the Central One.” Though Orion was depicted as a large or warrior in lots of cultures, within the authentic Arabic it may need been a reference to a black sheep with a white spot or spots. Thus within the authentic kind, Rigel may need designated the left foot of a sheep! Now, nonetheless, many individuals realize it because the left foot of Orion the Hunter.
Aurvandill’s large toe
The mythology associated to Rigel is sparse and unclear. Maybe essentially the most fascinating connection is in Norse mythology, which typically recognized Orion with Aurvandill (additionally Orwandil, Earendel and others). In response to some, Aurvandill was touring together with his companion, the god Thor, when his large toe froze in an unlucky river-crossing incident. Thor broke off the frozen digit and threw it into the sky, the place it grew to become the star we see as Rigel. In some variations, Aurvandill’s different large toe grew to become faint Alcor in Ursa Major.
Rigel’s place is RA: 05h 14m 32.3s, Dec: -08° 12′ 05.9”.
Backside line: Rigel, the brightest star within the constellation Orion the Hunter, shines an excellent bluish-white shade. It’s a lot hotter and extra huge than our sun, and sometime, Rigel will explode as a supernova.