NASA initially posted this article on March 7, 2023. Edits by EarthSky.
A NASA Earth-observing satellite has helped researchers observe carbon dioxide emissions for greater than 100 international locations around the globe. The pilot venture provides a strong new take a look at the carbon dioxide being emitted in these international locations and the way a lot of it’s faraway from the environment by forests and different carbon-absorbing “sinks” inside their borders. The findings exhibit how space-based instruments can help insights on Earth as nations work to attain local weather targets.
The worldwide study, carried out by greater than 60 researchers, used measurements made by NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) mission, in addition to a community of surface-based observations, to quantify will increase and reduces in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations from 2015 to 2020. Utilizing this measurement-based (or “top-down”) method, the researchers had been then capable of infer the stability of how a lot carbon dioxide was emitted and eliminated.
Though the OCO-2 mission was not particularly designed to estimate emissions from particular person nations, the findings from the 100-plus international locations come at an opportune time. The primary Global Stocktake – a course of to evaluate the world’s collective progress towards limiting world warming, as specified within the 2015 Paris Agreement – takes place in 2023.
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
Growing a database of emissions
Karen St. Germain, director of NASA’s Earth Science Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, stated:
NASA is targeted on delivering Earth science information that addresses actual world local weather challenges, like serving to governments around the globe measure the impression of their carbon mitigation efforts. That is one instance of how NASA is creating and enhancing efforts to measure carbon emissions in a manner that meets consumer wants.
Conventional activity-based (or “bottom-up”) approaches to carbon measurement depend on tallying and estimating how a lot carbon dioxide is being emitted throughout all sectors of an financial system, corresponding to transportation and agriculture. Backside-up carbon inventories are essential for assessing progress towards emission-reduction efforts, however compiling them requires appreciable assets, experience, and data of the extent of the related actions.
Because of this creating a database of emissions and removals by way of a top-down method may very well be particularly useful for nations that lack conventional assets for stock growth, the examine authors assert. Actually, the scientists’ findings embrace information for greater than 50 international locations that haven’t reported emissions for a minimum of the previous 10 years.
Monitoring fluctuations in carbon dioxide emissions
The examine gives a brand new perspective by monitoring each fossil gas emissions and the total carbon “inventory” modifications in ecosystems, together with bushes, shrubs, and soils. The information is especially helpful for monitoring carbon dioxide fluctuations associated to land cowl change. Emissions from deforestation alone make up a disproportionate quantity of total carbon output within the Global South, which encompasses areas of Latin America, Asia, Africa, and Oceania. In different elements of the world, the findings point out some reductions in atmospheric carbon concentrations by way of improved land stewardship and reforestation.
The authors stated that bottom-up strategies for estimating carbon dioxide emissions and removals from ecosystems are important. Nevertheless, these strategies are weak to uncertainty when information is missing or the web results of particular actions, corresponding to logging, aren’t absolutely identified.
Philippe Ciais, a examine creator and analysis director on the Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement in France, stated:
Our top-down estimates present an unbiased estimate of those emissions and removals, so though they can not substitute the detailed course of understanding of conventional bottom-up strategies, we are able to verify each approaches for consistency.
Carbon dioxide emissions vs. storage
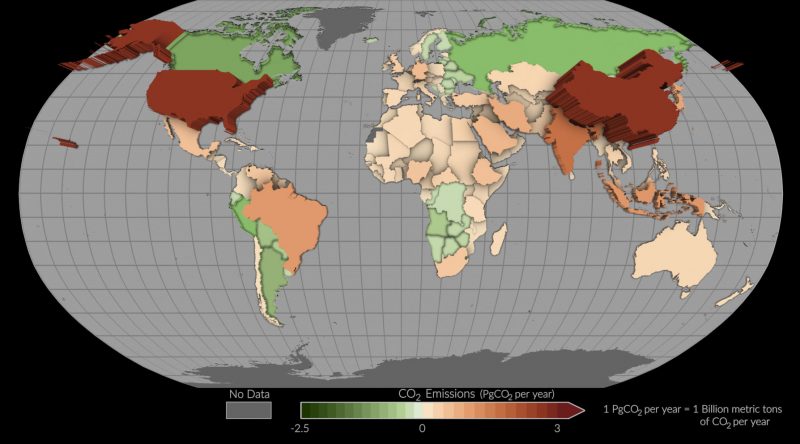
The animation beneath from NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio exhibits yearly fossil gas emissions by greater than 100 international locations from 2015 to 2020. International locations with excessive emissions, together with the U.S. and China (seen right here in darkish crimson), seem to pop from the web page, in comparison with these with decrease emissions.
The map beneath illustrates modifications within the quantity of carbon saved in natural matter on land, referred to as terrestrial carbon inventory modifications, from 2015 to 2020. Actions corresponding to improved land stewardship and deforestation, which is extra intensive within the tropics than different areas, have an effect on these inventory modifications.
Nationwide inventories
The examine provides a fancy image of carbon shifting by Earth’s land, ocean, and environment.
Along with direct human impacts accounted for by nationwide inventories, unmanaged ecosystems like some tropical and boreal forests – the place people have a minimal footprint – can sequester carbon from the environment, thus lowering potential world warming.
Examine creator Noel Cressie, a professor on the College of Wollongong in Australia, stated:
Nationwide inventories are supposed to trace how administration insurance policies impression emissions and removals of CO2. Nevertheless, the environment doesn’t care whether or not CO2 is being emitted from deforestation within the Amazon or wildfires within the Canadian Arctic. Each processes will enhance the focus of atmospheric CO2 and drive local weather change. Due to this fact, it’s essential to watch the carbon stability of unmanaged ecosystems and determine any modifications in carbon uptake.
Wanting towards the longer term
Wanting ahead, the researchers stated their pilot venture will be additional refined to grasp how emissions from particular person nations are altering.
Lead creator Brendan Byrne, a scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, stated:
Sustained, high-quality observations are essential for these top-down estimates. Continued observations from OCO-2 and floor websites will permit us to trace how these emissions and removals change because the Paris Settlement is carried out. Future worldwide missions that present expanded mapping of CO2 concentrations throughout the globe will permit us to refine these top-down estimates and provides extra exact estimates of nations’ emissions and removals.
Launched in 2014, the OCO-2 satellite maps pure and human-made carbon dioxide concentrations with the assistance of three camera-like spectrometers. These gadgets can detect the distinctive spectra, or mild signature, of carbon dioxide. They measure the fuel not directly by how a lot mirrored daylight it absorbs in a given column of air.
Backside line: A brand new examine breaks down carbon dioxide emissions by nation, revealing a map of which nations contribute the many of the greenhouse-warming fuel and which international locations present a carbon sink.
Read more: Why carbon dioxide has such outsized influence on Earth’s climate