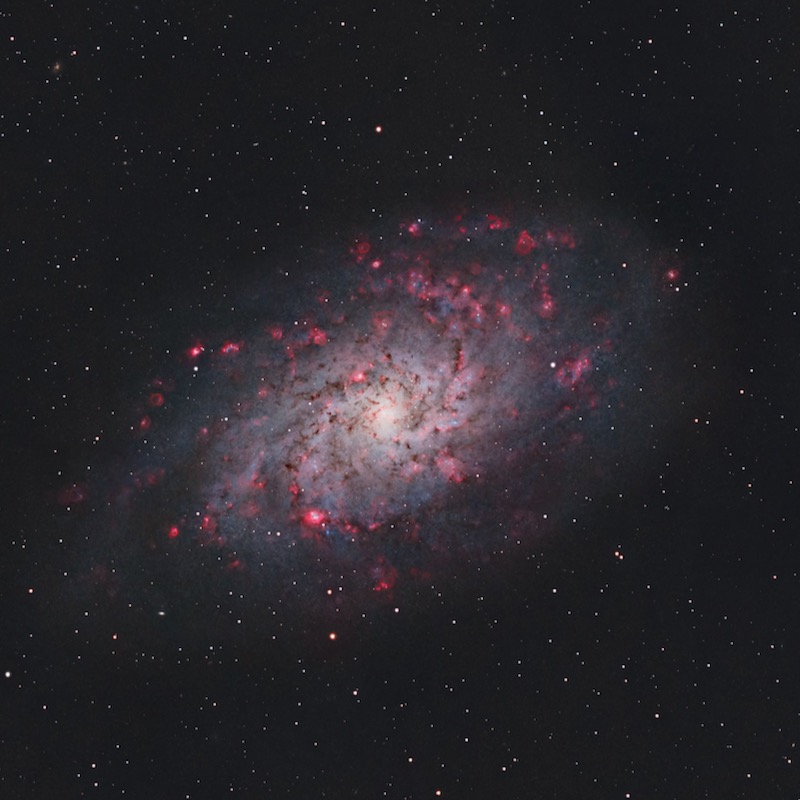
The Triangulum galaxy, also referred to as Messier 33 (M33), is theoretically the farthest object seen with the unaided eye. However, in observe, you’ll want good dark sky circumstances – and good eyesight – to see it with the attention alone. Even with binoculars and a telescope, this pinwheel-shaped spiral galaxy is a problem to identify. It’s comparatively close by. But it surely’s turned face-on to us, so it has a low surface brightness in our sky.
The Triangulum galaxy, named for its location within the constellation Triangulum, is the 2nd-nearest spiral galaxy to our Milky Way, after the Andromeda galaxy (M31). If you happen to do handle to glimpse it, you’re trying throughout a distance of 2.7 million light-years.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Learn how to discover the Triangulum Galaxy
Have you ever ever seen the Andromeda galaxy (Messier 31), closest spiral galaxy to our Milky Way? It’s about 2.2 million light-years away, and seems edge-on to us. It’s a lot simpler to see. Strive discovering the Andromeda galaxy earlier than you tackle the Triangulum galaxy. Listed below are two methods to search out the Andromeda galaxy:
Use constellation Cassiopeia to find Andromeda galaxy
Use Great Square of Pegasus to find Andromeda galaxy
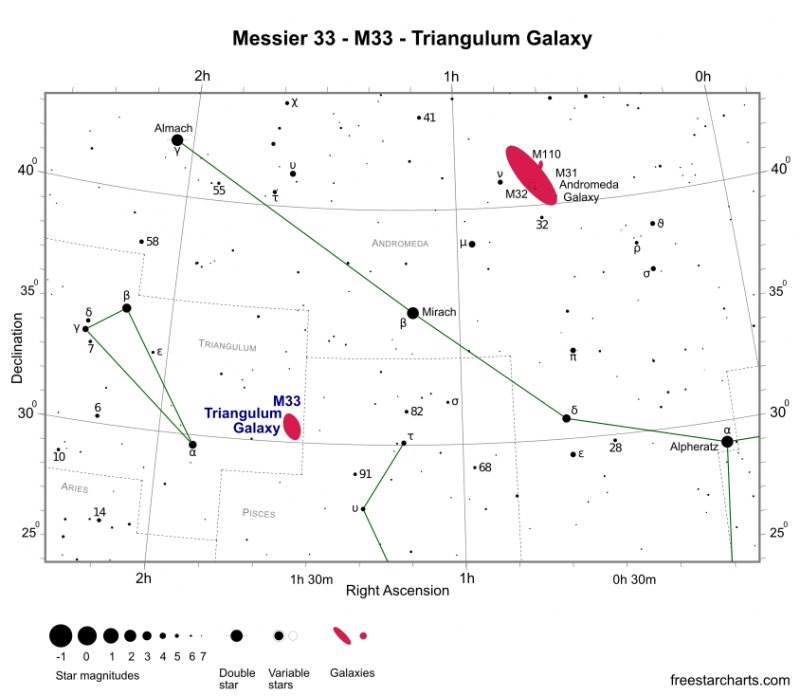
The Andromeda galaxy shines eight occasions extra brightly in our sky than the Triangulum galaxy. The Triangulum and Andromeda galaxies are comparatively shut collectively in our sky, solely 15 degrees aside. For reference, a fist-width at arm’s size approximates 10 levels.
Seeing M33
Star-hop to the Andromeda galaxy to orient your self to the Triangulum galaxy. As seen on the sky chart, the star Mirach stands about halfway between the 2 galaxies. As soon as you discover Mirach and the Andromeda galaxy, you’ll be able to draw a line between them to level within the common route of the Triangulum galaxy.
Now for a phrase of warning: even for those who’re staring proper on the Triangulum galaxy, it’s nonetheless doable to overlook it. You gained’t see the galaxy’s stars in any respect. Typically, this galaxy seems nearly clear, like a water spot on a window. The small blob in your binocular area may resemble an unwashed spot on an in any other case clear window.
Science of the Triangulum galaxy
The Triangulum galaxy – at 2.7 million light-years from our Milky Way – is a spiral galaxy. Its face-on orientation has given it the nickname the Pinwheel (one other face-on spiral, Messier 101, additionally has this nickname).
The Triangulum galaxy is the Third-largest member of our Local Group of galaxies. Our Native Group consists of a number of dozen galaxies. Our Milky Way, the Andromeda galaxy and the Triangulum galaxy are the most important members.
The Triangulum galaxy’s diameter is about 60,000 light-years, or about 60% that of our Milky Way. It’s thought to include some 40 billion stars. In distinction, there are 100-400 billion stars within the Milky Way and a trillion (1,000 billion) stars within the Andromeda galaxy.
In 2004, astronomers discovered evidence for a clumpy stream of hydrogen gasoline linking the Triangulum galaxy with the close by Andromeda galaxy. A 12 months later, astronomers have been in a position to estimate the correct movement – or sideways movement on our sky’s dome – of the Triangulum Galaxy for the primary time. They discovered that this galaxy is transferring in direction of the Andromeda galaxy. Afterwards, some astronomers steered the Triangulum galaxy may be a satellite of the Andromeda galaxy. In different phrases, over a timescale so huge we haven’t but comprehended it, the Triangulum galaxy may orbit across the Andromeda galaxy.
The destiny of the Triangulum galaxy
It’s well-known that the Andromeda galaxy is transferring towards our Milky Way and that a collision between the two galaxies will occur some 4 billion years from now.
In the meantime, the destiny of the Triangulum galaxy isn’t identified for sure. It would sometime be torn aside and absorbed by the Andromeda galaxy. It would take part within the collision between the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies. Two different potentialities are a collision with the Milky Way earlier than Andromeda arrives or an ejection from the Native Group.
It’s secure to say that the destiny of those nice galaxies is past human information right now!
Backside line: The Triangulum Galaxy, aka M33, is the farthest object you’ll be able to see with the unaided eye, if actually you’ll be able to see it. However seeing it’s a problem.

