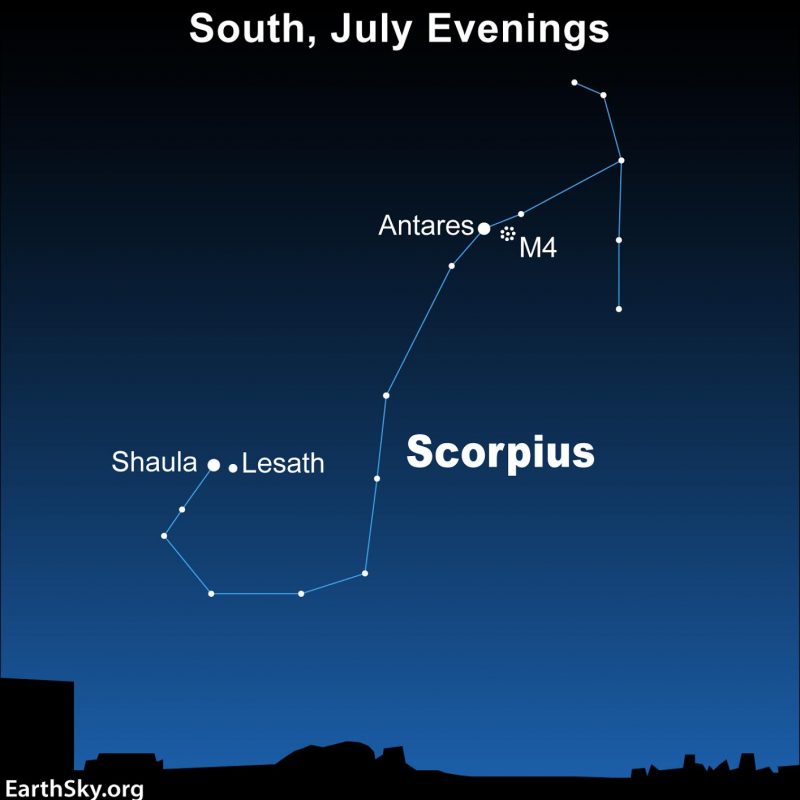
Shiny pink Antares is simple to search out within the distinguished zodiacal constellation Scorpius the Scorpion. And in the event you look simply barely west of it via binoculars, you’ll see a small faint diffuse ball of sunshine. Via a moderate-sized telescope, that fuzzy ball resolves into a decent assortment of faint stars suspended within the darkness. That’s Messier 4, referred to as M4 for brief. It’s a globular star cluster, an historical member of our Milky Way galaxy. M4 shines at magnitude +5.9, so it could be seen as a smudge on the sky below very dark skies.
Discover M4 in binoculars first
In case you’ve by no means discovered a deep-sky object by yourself earlier than, M4 is a grand place to start out. Northern Hemisphere summer time evenings – or Southern Hemisphere winter evenings – are most likely your greatest guess for catching M4. The M4 globular star cluster is simple to search out, as a result of it’s proper subsequent to the first-magnitude star Antares, the brightest star within the constellation Scorpius the Scorpion.
In early June, Antares is highest within the sky round midnight your native time (1 a.m. daylight saving time). Meaning it’s excessive within the south for Northern Hemisphere viewers, and overhead for Southern Hemisphere viewers. The celebrities return to the identical place within the sky some two hours earlier each month. So, Antares is highest up round 10 p.m. (11 p.m. daylight saving time) in early July, and eight p.m. (9 p.m. daylight saving time) in early August.
Antares and M4 match inside the identical binocular discipline of view, with M4 showing a bit greater than 1 degree to the west of Antares. For reference, a typical binocular discipline has a diameter of 5 to six levels. M4 seems like a fairly dim, hazy star in binoculars.
As soon as you see it, you may start eager for a telescope to have the ability to resolve this fuzzy cluster right into a clump of starry pinpoints.
Historical past of Messier 4
Swiss astronomer Jean-Philippe Loys de Chéseaux found M4 in 1746. Nonetheless, it’s named after comet hunter Charles Messier (1730-1817). He listed M4 as object #4 in his well-known Messier catalog. The catalog listed over 100 deep-sky objects that appear like comets however actually aren’t. Charles Messier needed to steer comet hunters away from these faint fuzzies that masquerade as comets.
Science of M4
Right this moment, we all know that M4 is a globular star cluster, a globe-shape stellar metropolis filled with maybe 100 thousand stars. At about 6,000 light-years from Earth, M4 is the closest globular cluster to us. Compared, most globulars in our galaxy reside tens of hundreds of light-years away. The farthest globular cluster, M54, is about 87,000 light-years in distance.
In contrast to open star clusters – such because the Pleiades and the Hyades – the Milky Way galaxy’s 150 or so identified globular star clusters will not be a part of the galactic disk. As a substitute, globular clusters populate the galactic halo, the sphere-shaped area of the Milky Way circling above and under the galactic disk. There are possible extra globular clusters hidden from view by the Milky Way’s central bulge and by clouds of dust and fuel.
Distinction between globular and open clusters
Globular clusters are tightly filled with tens to a whole bunch of hundreds of stars, whereas open clusters are loosely-bound stellar teams with only some hundred to a thousand stars. Globular clusters include primitive stars which might be billions of years outdated and nearly as outdated because the universe itself. However, open clusters encompass younger, sizzling stars that are inclined to disperse after a whole bunch of thousands and thousands of years.
In case you had a telescope like Hubble, it could mean you can see these historical stars as proven on this animation.
M4’s place is at Proper Ascension: 16h 23m 35s; Declination: -26° 31′ 33″
Backside line: Discover M4, one of many best globular star clusters for inexperienced persons to identify, situated simply subsequent to reddish Antares, the brightest star in Scorpius the Scorpion.