Many moons within the outer solar system have outer crusts of stable ice. However some options on these moons nonetheless puzzle scientists. Think about the reddish cracks on Jupiter’s moon Europa. Scientists say the purple coloration doubtless comes from an unknown combination of ice and salts, from throughout the moon. Now a global group of researchers has announced a potential motive: a newly found type of salty ice.
Researchers from the College of Washington led the brand new research and introduced it on February 21, 2023. The Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences of the US of America (PNAS) published the peer-reviewed findings on February 21, 2023.
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
New sort of salty ice could exist on icy moons
Proper now, scientists have solely seen the newly found type of salty ice within the lab. The researchers created it by simulating the chilly and high-pressure situations discovered beneath the ice crust on the icy moons. However it could simply be the reply that they’ve been on the lookout for. It may clarify the weird streaks on Europa and options on different icy moons as effectively, if it does exist there.
The recipe for the substance is straightforward: sodium chloride, generally known as desk salt (in its edible kind), and water. Each are widespread, however the distinctive situations contained in the icy moons may produce a extra unique type of salty ice. Lead writer Baptiste Journaux on the College of Washington explained:
It’s uncommon these days to have basic discoveries in science. Salt and water are very well-known at Earth situations. However past that, we’re completely at midnight. And now we’ve got these planetary objects that most likely have compounds which are very acquainted to us, however at very unique situations. We’ve got to redo all the elemental mineralogical science that individuals did within the 1800s, however at excessive strain and low temperature. It’s an thrilling time.
New sorts of sodium chloride hydrates
The unique nature of the salty ice has to do with the meeting of its molecules. Sometimes, water and salts mix in chilly temperatures to kind a inflexible, salty and icy lattice generally known as a hydrate. Hydrogen bonds maintain that lattice collectively. Beforehand, scientists knew of just one different sort of hydrate for sodium chloride. That one consists of 1 salt molecule for each two water molecules. However now, the lab simulations have produced two new sorts of sodium chloride hydrates.
Whereas each hydrates are considerably completely different from what scientists usually see in nature (no less than on Earth), they’re additionally completely different from one another. One has two sodium chlorides for each 17 water molecules, however the different has one sodium chloride for each 13 water molecules. Might they clarify the odd options on Europa and different icy moons? Journaux mentioned:
It has the construction that planetary scientists have been ready for.
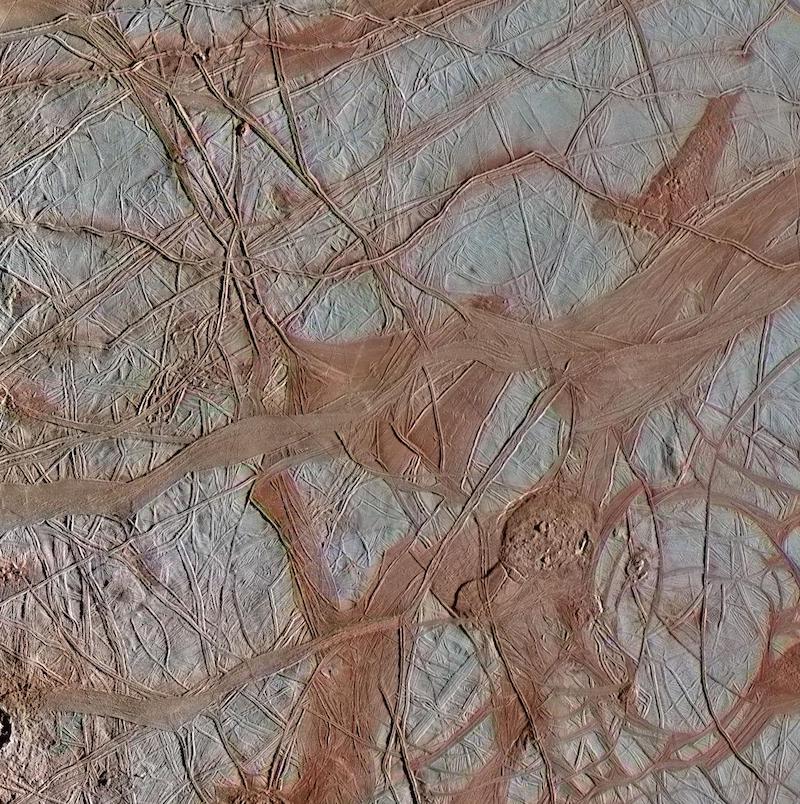
Lab-created situations widespread on icy moons
So, how did the researchers create the brand new salty ice? At synchrotron radiation facilities in France, Germany and the U.S., they compressed tiny quantities of salty water between two diamonds. The diamonds had been additionally tiny, every concerning the measurement of a grain of sand. Extremely, even in such a small space, the researchers had been capable of squeeze the salty water as much as 25,000 instances the usual strain of Earth’s environment. Journaux mentioned:
We had been making an attempt to measure how including salt would change the quantity of ice we may get, since salt acts as an antifreeze. Surprisingly, once we put the strain on, what we noticed is that these crystals that we weren’t anticipating began rising. It was a really serendipitous discovery.
What makes the simulated situations within the lab so intriguing is that these situations – excessive chilly and high-pressure – are widespread on icy moons. The newly found sorts of salty ice ought to have the ability to kind fairly simply in these environments. The hidden oceans on these moons are not like Earth’s open oceans. These oceans could also be as much as lots of of miles deep, with three to 6 miles (5 to 10 km) of ice on prime of them. As Journaux famous:
Stress simply will get the molecules nearer collectively, so their interplay modifications; that’s the essential engine for range within the crystal buildings we discovered.

Hydrates stay steady
Furthermore, the brand new hydrates remained steady even after the scientists lessened the strain. This reveals that they might be current for lengthy intervals of time on icy moons. Journaux added:
We decided that it stays steady at normal strain as much as about -50 C. So in case you have a really briny lake, for instance in Antarctica, that might be uncovered to those temperatures, this newly found hydrate might be current there.
Different purposes for the salty ice
In addition to serving to to clarify mysteries on faraway moons, the salty ice could have purposes proper right here on Earth. This might embrace bodily chemistry and vitality analysis, which makes use of hydrates for vitality storage (a sort of thermal energy storage).
Salt hydrate expertise makes use of the response vitality created when salts are hydrated or dehydrated. Since 2016, researchers in a number of international locations have been conducting experiments to find out one of the best sort of salt or salt combination to make use of.
NASA’s Europa Clipper mission, scheduled to launch in October 2024, will have the ability to take a more in-depth look. With its a number of science devices, it could possibly conduct new evaluation of the options on Europa the place this salty ice could also be current. Or, it may discover one thing utterly new! We’ll simply have to attend to seek out out.
Backside line: Researchers on the College of Washington have created new types of salty ice hydrates. They could clarify uncommon floor markings on icy moons like Europa.




