Many of the worlds of our solar system are pockmarked with impression craters. These bear testomony to the violence of the early days of the sun, when asteroids, comets and whole planets routinely collided with and annihilated one another.
Our personal moon was almost certainly shaped by certainly one of these collisions, and is itself dwelling to the biggest impression function within the solar system—the South Pole/Aitken Basin, some 2,500km throughout. Mars’ huge, flat northern deserts might too have shaped throughout a huge collision some 4 billion years in the past.
As we speak’s solar system is a way more peaceable place. However impacts from meteorites are nonetheless one of many dominant processes shaping planetary landscapes on most worlds aside from the Earth. Now our new examine of the biggest latest impact craters on Mars, published in Science, sheds new gentle on the crimson planet’s inside.
Inspecting impression craters can train us quite a bit—from understanding the composition and dimension of the asteroids or comets which created them, via to unearthing the properties of planetary surfaces and interiors. The interiors of craters can in truth be used to check in any other case inaccessible underground geology. The diploma of cratering on a floor can be used to estimate its age: the older it’s, the extra craters (normally).
Late final 12 months, Nasa’s InSight spacecraft, which is on the floor of Mars “listening” to seismic waves within the planet’s inside, detected two monumental “marsquakes” round 90 days aside—among the many largest we’ve got seen up to now throughout our analysis.
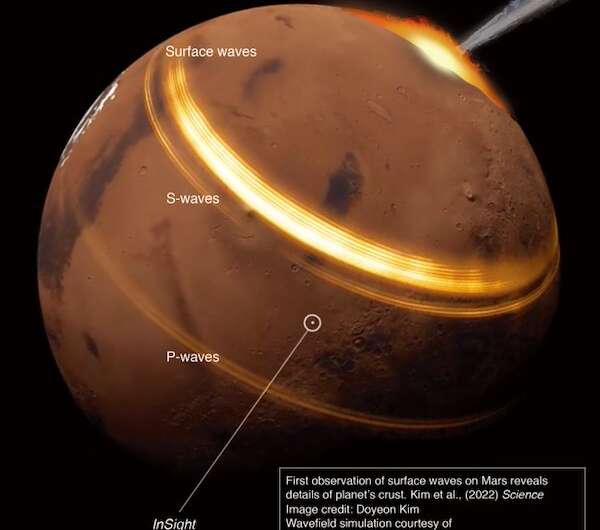
These marsquakes have been somewhat completely different to earlier ones recorded by InSight. For instance, they appeared to be what we name “floor waves”—that’s, seismic waves propagating within the outermost layers of the martian crust (its surface layer).
These types of waves are uncommon. They’re additionally notably thrilling as a result of they permit us to “map” the construction of Mars’ extremely uncommon crust, which is far flatter within the northern hemisphere and thicker and extra mountainous within the southern.
Martian detective work
We may inform the marsquakes in all probability had a shallow origin—doubtlessly produced by an unlimited impression occasion somewhat than originating from processes deeper throughout the planet’s inside. By analyzing the seismic waves that InSight recorded, we have been additionally in a position to work out the marsquakes’ approximate epicenter, or level of origin. As a result of these two quakes have been so uncommon, we requested follow-up observations from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft which orbits the planet.
The outcomes have been fairly outstanding. The epicenters of each marsquakes have been discovered to correlate with the positions of monumental black smudges on the planet’s floor—the blast zones of recent impression craters. Trying again at older, low decision photographs allowed the imaging workforce to pin down the precise dates for the formation of the craters, which coincided precisely with when the marsquakes have been detected by InSight.
The craters themselves have been monumental—round 130m and 150m in diameter respectively. The “blast zones”, created by the shockwaves from the meteors getting into the environment and impacting the floor, prolonged out for dozens of kilometers. These have been by far the most important recent craters we had ever seen kind anyplace within the solar system.
The bigger of the 2 craters was solely round thirty levels north of Mars’ equator—by Martian requirements, a semi-tropical latitude. On the backside of the crater have been chunks of what was recognized as ice (from water), excavated by the impacting physique because it broke via into an underground frozen layer. This was the closest to the equator that we might ever seen ice, and means that there’s probably extra water on Mars (albeit frozen) than beforehand thought. That is notably necessary if people are to at least one day settle there.
Because it turned out, the floor waves from one of many occasions have been so sturdy that that they had truly been recorded by InSight after going each methods across the planet—a primary for seismology.
By analyzing the surface waves, we have been additionally in a position to create a picture of the construction of the crust. Preliminary outcomes recommended that the variations between the northern and the southern hemisphere is likely to be extra superficial than beforehand believed. Particularly, it regarded like a number of the variations within the crust have been confined to the world very close to the floor somewhat than extending deeper down. Why the northern and southern hemispheres look so completely different, regardless of being very related at even shallow depths, stays a little bit of a thriller.
We additionally do not know why these two craters shaped so shut to one another in time—a lot nearer collectively than random statistics would recommend is probably going. One principle that we explored was whether or not an asteroid might have damaged up in orbit round Mars and the fragments slowly re-entered the environment over a interval of a number of months, creating completely different craters. However the lack of another equally sized craters or direct proof for this makes it difficult to show.
Sadly, the detection of those impression occasions is prone to have been one of many final outcomes of the InSight mission. The spacecraft’s solar panels are actually so dusty that it’s changing into unattainable to maintain the batteries charged sufficient to stay operational. Though we are going to maintain listening for so long as we will, it could be solely after the subsequent set of seismometers are despatched to Mars that we will discover a few of these unanswered questions on impression occasions on the crimson planet.
Offered by
The Conversation
This text is republished from The Conversation underneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the original article.![]()
Quotation:
Mars: How we found two big, uncommon impression craters, and the secrets and techniques they unveil (2022, November 21)
retrieved 21 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-mars-huge-unusual-impact-craters.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




