From time to time there’s a vivid radio flash someplace within the sky. It will probably final wherever from a number of milliseconds to a couple seconds. They seem considerably at random, and we nonetheless aren’t positive what they’re. We name them quick radio bursts (FRBs). Proper now the main idea is that they’re attributable to extremely magnetic neutron stars referred to as magnetars. With observatories resembling CHIME we are actually capable of see numerous them, which might give astronomers a brand new strategy to measure the speed of cosmic growth.
The speed of cosmic growth is described by the Hubble parameter, which we are able to measure to inside a number of %. Sadly, our numerous strategies of measure are actually so exact their uncertainties do not overlap. This contradiction in values is named the Hubble pressure. A number of re-evaluations of our strategies have dominated out systematic error, so astronomers look to new impartial methods to measure the Hubble parameter, which is the place a brand new examine is available in.
The paper, posted to the arXiv preprint server, seems to be at utilizing FRBs as a Hubble measure. For gentle from an FRB to achieve us, it must journey thousands and thousands of light-years by means of the diffuse intergalactic and interstellar medium. This causes the frequency of the sunshine to unfold out. The quantity of spectral spreading is named the Dispersion Measure (DM), and the better the DM the better the gap. So we all know the gap to FRBs. However to measure cosmic growth, we additionally want a second distance measure, and right here the paper proposes utilizing gravitational lensing.
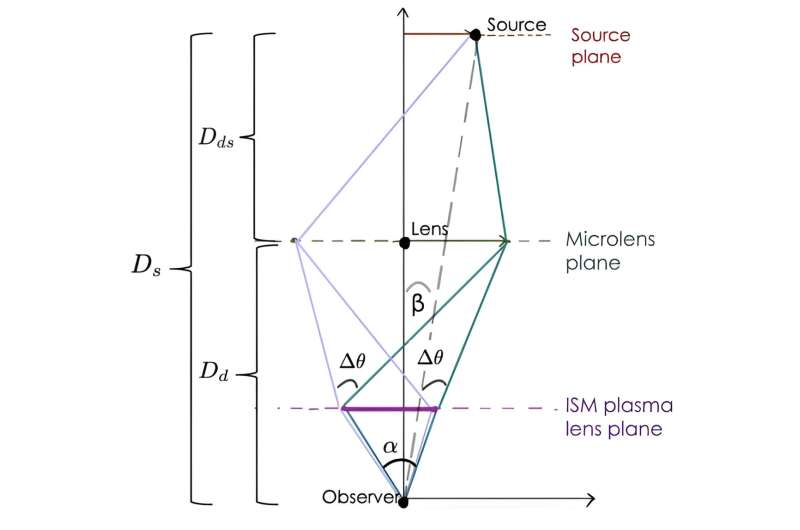
If the FRB gentle path passes comparatively shut to an enormous object resembling a star, the sunshine might be gravitationally lensed across the object. From the width of the lensing, now we have an concept of its relative distance to the FRB supply. When the FRB gentle passes from the intergalactic medium to the extra dense interstellar medium of our galaxy, there’s a brightening impact referred to as scintillation, which provides us one other distance measure A little bit of geometry then permits us to calculate the Hubble parameter.
Based mostly on their calculations, the authors estimate {that a} single lensed FRB statement would permit them to pin down the Hubble parameter to inside 6% accuracy. With 30 or extra occasions, they need to be capable to improve their precision to a fraction of a % uncertainty. This might put it on par with different strategies. This must be achievable given present and deliberate FRB telescopes.
New statement strategies resembling this are the one approach we’re going to resolve the Hubble pressure. Hopefully, we are going to resolve this thriller, and maybe it can level us to a radically new understanding of cosmic evolution.
Extra info:
Anna Tsai et al, Scintillated microlensing: measuring cosmic distances with quick radio bursts, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2308.10830
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Measuring distances within the universe with quick radio bursts (2024, February 13)
retrieved 14 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-distances-universe-fast-radio.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




