The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy round 13.6 billion years outdated with massive pivoting arms stretching out throughout the cosmos.
Milky Way fast info:
– Galaxy sort: Barred spiral
– Age: 13.6 billion years (and counting)
– Dimension: 100,000 light-years throughout
– Variety of stars: about 200 billion
– Rotation time: 250 million years
Our residence galaxy’s disk is about 100,000 light-years in diameter and simply 1000 light-years thick, in line with Las Cumbres Observatory (opens in new tab).
Simply as Earth orbits the sun, the solar system orbits the middle of the Milky Way. Regardless of hurtling by space at speeds of round 515,000mph (828,000kmph) our solar system takes roughly 250 million years to finish a single revolution, in line with Interesting Engineering (opens in new tab). The final time our planet was on this place, dinosaurs had been simply rising and mammals had been but to evolve.
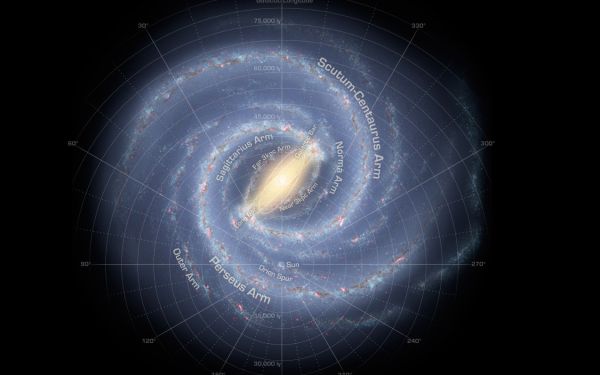
If the middle of the Milky Way had been a metropolis, we might be residing in suburbia, about 25,000 to 30,000 light-years from town heart. Life within the outskirts is sweet; we discover ourselves nestled in one of many smaller neighborhoods, the Orion-Cygnus Arm, sandwiched between bigger Perseus and Carina-Sagittarius arms. If we had been to journey inwards in the direction of town heart, we might discover the Scutum-Centaurus and Norma arms.
Associated: How to photograph the Milky Way: A guide for beginners and enthusiasts
On a transparent evening, void of sunshine air pollution, we will catch a glimpse of the intense lights of the galactic metropolis streaking throughout the evening sky. Our window into the universe, this milky white band of stars, dust and gasoline is the place our galaxy will get its identify.
Mendacity on the very coronary heart of the Milky Way is a supermassive black hole referred to as Sagittarius A*. About 4 million occasions the mass of the sun, this beast consumes something that strays too shut, gorging on an ample provide of stellar materials enabling it to develop into an enormous. In 2022, we imaged this glutton at the core of our galaxy for the very first time, by an revolutionary approach permitting us to view the shadow of the black hole.
Why is our galaxy referred to as the Milky Way?
In response to the American Museum of Natural History (opens in new tab) (AMNH), our galactic residence is known as the Milky Way after its obvious milky white look because it stretches throughout the evening sky. In Greek mythology, this milky band appeared as a result of the goddess Hera sprayed milk throughout the sky.
All over the world, the Milky Way is understood by totally different names. For instance in China it’s referred to as “Silver River” and within the Kalahari Desert in South Africa it is referred to as the “Spine of Night time”.
Milky Way galaxy sort and the nice debate of 1920
(opens in new tab)
We’re consistently constructing on our wealth of data of the Milky Way, although up till comparatively just lately astronomers believed that each one the celebs within the sky belonged to our galaxy.
“The Nice Debate” in 1920 noticed astronomers Herber Curtis and Harlow Shapley argue the size of the universe and the prospect of “island universes” (galaxies), in line with the National Academy of Sciences (opens in new tab).
On one aspect of the controversy, Shapley believed the Milky Way was a lot bigger than earlier estimates and that we weren’t on the heart. He additionally claimed that “spiral nebulae” comparable to Andromeda had been part of the Milky Way. On the opposite aspect of the controversy, Curtis didn’t dispute Shapley’s claims of a far bigger Milky Way, he did nevertheless argue that there have been massive island universes (galaxies) comparable to Andromeda, that lay past the boundaries of the Milky Way.
The dispute was resolved when Edwin Hubble’s measurements of Cepheid variable stars proved Andromeda was positioned far outdoors the Milky Way. Trendy estimates recommend the Andromeda galaxy, our nearest galaxy neighbor is 2.5 million light-years away.
Extra just lately, astronomers have been attempting to determine what sort of galaxy the Milky Way is. Our greatest estimates as of late recommend that it’s a barred spiral, which means that there’s a bar construction throughout the middle. Astronomers can estimate the form of the Milky Way by taking a look at its inhabitants of stars, in addition to their actions throughout the sky.
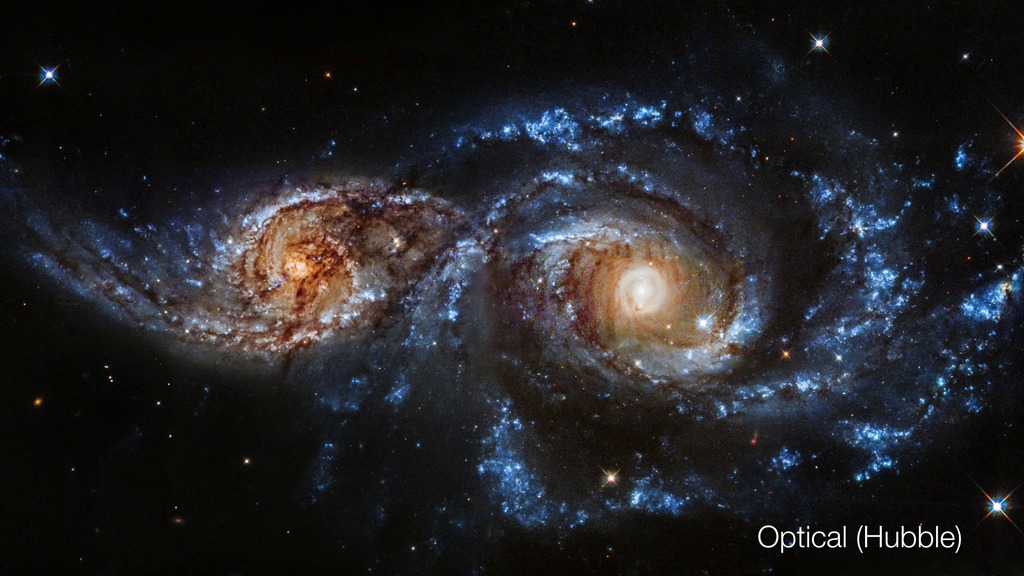
A future collision of galactic proportions

(opens in new tab)
We now know that the Milky Way resides throughout the Native Group of galaxies, made up of over 30 galaxies together with Andromeda, Triangulum and Leo I to call however just a few. It seems that it is fairly good to know who your neighbors are, as they might be nearer than you suppose. The Milky Way is at present hurtling in the direction of Andromeda at 250,000mph (400,000 km/h). Although there isn’t a want to fret simply but, this crash of cosmic proportions isn’t due for one more 4 billion years.
NASA and different space entities have been observing distant galaxy collisions for many years now to get a way of what we is likely to be going through when Andromeda and the Milky Way collide. The quick story is there’s little to fret about; the longer story is the method is an fascinating one because it exhibits how galaxies might evolve.
For instance, observations of a three-way galactic collision in 2022 utilizing the famed Hubble Space Telescope gave some intriguing insights. The biggest of the group, because it received into a decent orbit with the opposite two, snagged some materials with its comparatively stronger gravity. This created an intriguing streak of gasoline, dust and different supplies flowing into the bigger galaxy, seen even from Earth.
Whereas the arms of the Milky Way will certainly be ripped up by this course of, particular person stars are comparatively secure because the areas between them are fairly massive. In different phrases, do not search for star collisions, as they are going to be virtually non-existent. Starbirth, nevertheless, will speed up because of the quantity of gasoline being pumped into our galaxy, inflicting our galaxy to brighten and for its inhabitants to broaden within the coming thousands and thousands of years following the collision.
Our personal solar system, due to this fact, ought to be comparatively secure because of the low danger of star collision. That mentioned, we might discover ourselves thrown into a very totally different path across the new galactic heart because the merger pushes by.
One sensible impact is that the constellations we observe from Earth might change as star orbits alter or new stars are added into the combination; that mentioned, the collision is occurring to this point sooner or later that the constellations we see as we speak could also be altered in any case, attributable to pure starbirth and star dying outdoors of the collision. This Milky Way timelapse exhibits how the evening sky will shift over time.
The Milky Way: Dimension, construction and mass

(opens in new tab)
Finding out the Milky Way was once notoriously troublesome. Astronomers typically evaluate the hassle to trying to explain the dimensions and construction of a forest whereas being misplaced in the midst of it. From our place on Earth, we merely lack an summary. However two ground-breaking space telescopes launched because the Nineties have helped usher within the golden age of Milky Way analysis. Main strides have been made, particularly because the 2013 launch of the European Area Company’s (ESA) Gaia mission.
Telescopes enabled astronomers to tell apart the fundamental form and construction of among the closest galaxies earlier than they knew they had been taking a look at galaxies. However reconstructing the form and construction of our personal galactic residence was gradual and tedious. The method concerned constructing catalogs of stars, charting their positions within the sky and figuring out how removed from Earth they’re.
Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, typically dubbed the grasp of the galactic system, was the primary to appreciate that the Milky Way is not immobile however rotates, and he calculated speeds at which stars at varied distances orbit across the galactic heart. It additionally was Oort who decided the place of our sun within the huge galaxy. (The Oort Cloud, a repository of trillions of comets removed from the sun, was named after him.)
(opens in new tab)
Progressively, a posh image emerged of a spiral galaxy that seems fairly strange.
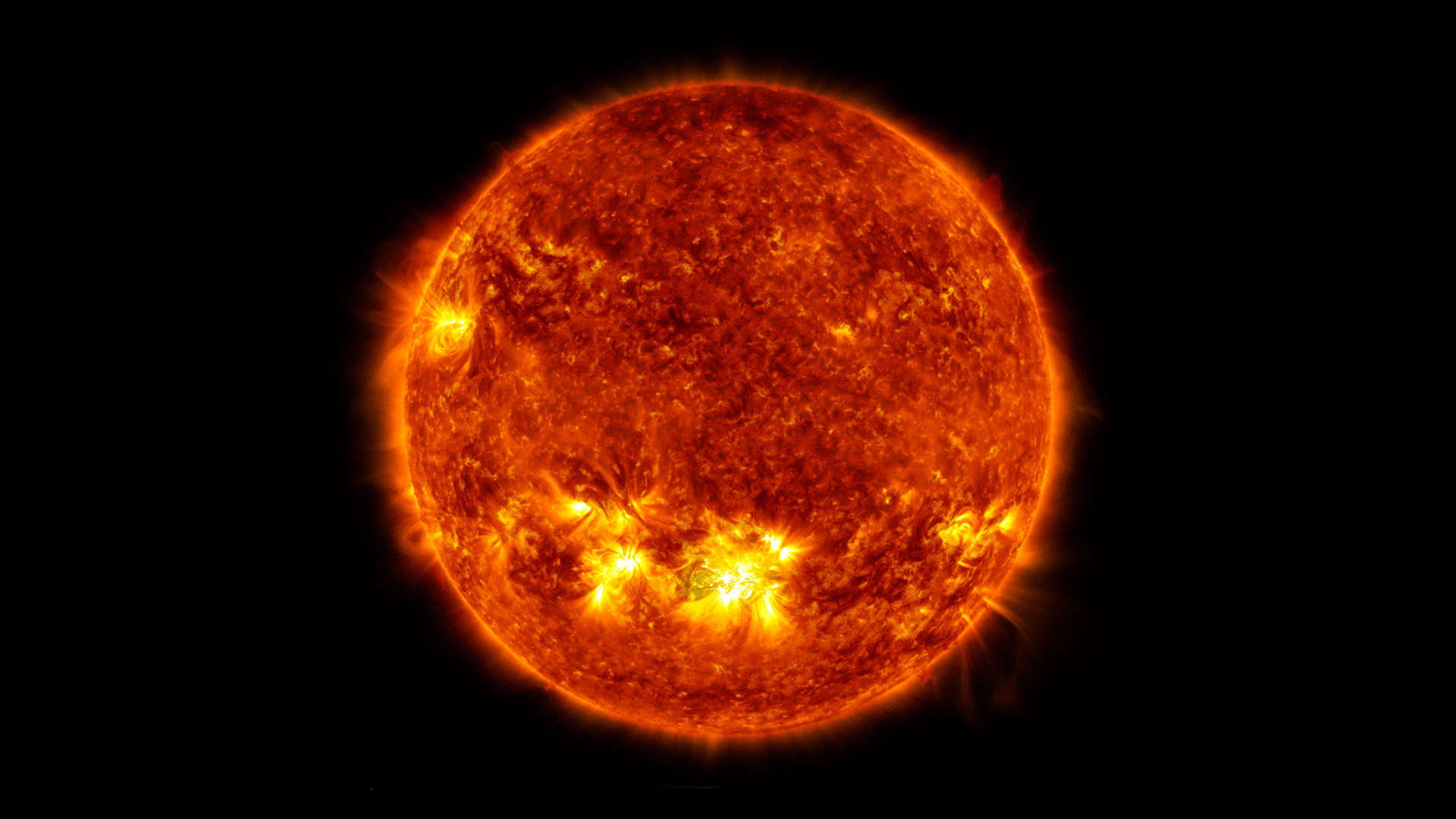
On the heart of the Milky Way sits a supermassive black hole referred to as Sagittarius A*. With a mass equal to that of 4 million suns, the black hole, found in 1974, might be noticed within the sky with radio telescopes near the constellation Sagittarius.
The whole lot else within the galaxy revolves round this highly effective gateway to nothingness. In its quick environment is a tightly packed area of dust, gasoline and stars referred to as the galactic bulge. Within the case of the Milky Way, this bulge is peanut-shaped, measuring 10,000 light-years throughout, according to ESA. It harbors 10 billion stars (out of the Milky Way’s total of about 200 billion), principally outdated red giants, which shaped within the early levels of the galaxy’s evolution.
Associated: ‘Weird signal’ hails from the Milky Way. What’s causing it?
Past the bulge extends the galactic disk. This function is 100,000 light-years throughout and 1,000 light-years thick, and it is residence to the vast majority of the galaxy’s stars, together with our sun. Stars within the disk are dispersed in clouds of stellar dust and gasoline. Once we look as much as the sky at evening, it is the edge-on view of this disk extending towards the galactic heart that takes our breath away.
Stars within the disk orbit across the galactic heart, forming swirling streams that seem to emanate like arms from the galactic bulge. Analysis into the mechanisms that drive the creation of spiral arms remains to be in its infancy, however the newest research recommend that these arms type and disperse inside comparatively quick intervals of as much as 100 million years (out of the galaxy’s 13 billion years of evolution).
Inside these arms, stars, dust and gasoline are extra tightly packed than within the extra loosely crammed areas of the galactic disk, and this elevated density triggers extra intense star formation. Consequently, stars within the galactic disk are usually a lot youthful than these within the bulge.
“Spiral arms are like site visitors jams in that the gasoline and stars crowd collectively and transfer extra slowly within the arms. As materials passes by the dense spiral arms, it’s compressed and this triggers extra star formation,” Denilso Camargo, of the Federal College of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, mentioned in a statement (opens in new tab).
The Milky Way at present has 4 spiral arms, in line with the National Science Foundation (opens in new tab) (NSF). There are two most important arms — Perseus and Scutum-Centaurus — and the Sagittarius and Native Arm, that are much less pronounced. Scientists nonetheless focus on the precise place and form of those arms utilizing Gaia information.
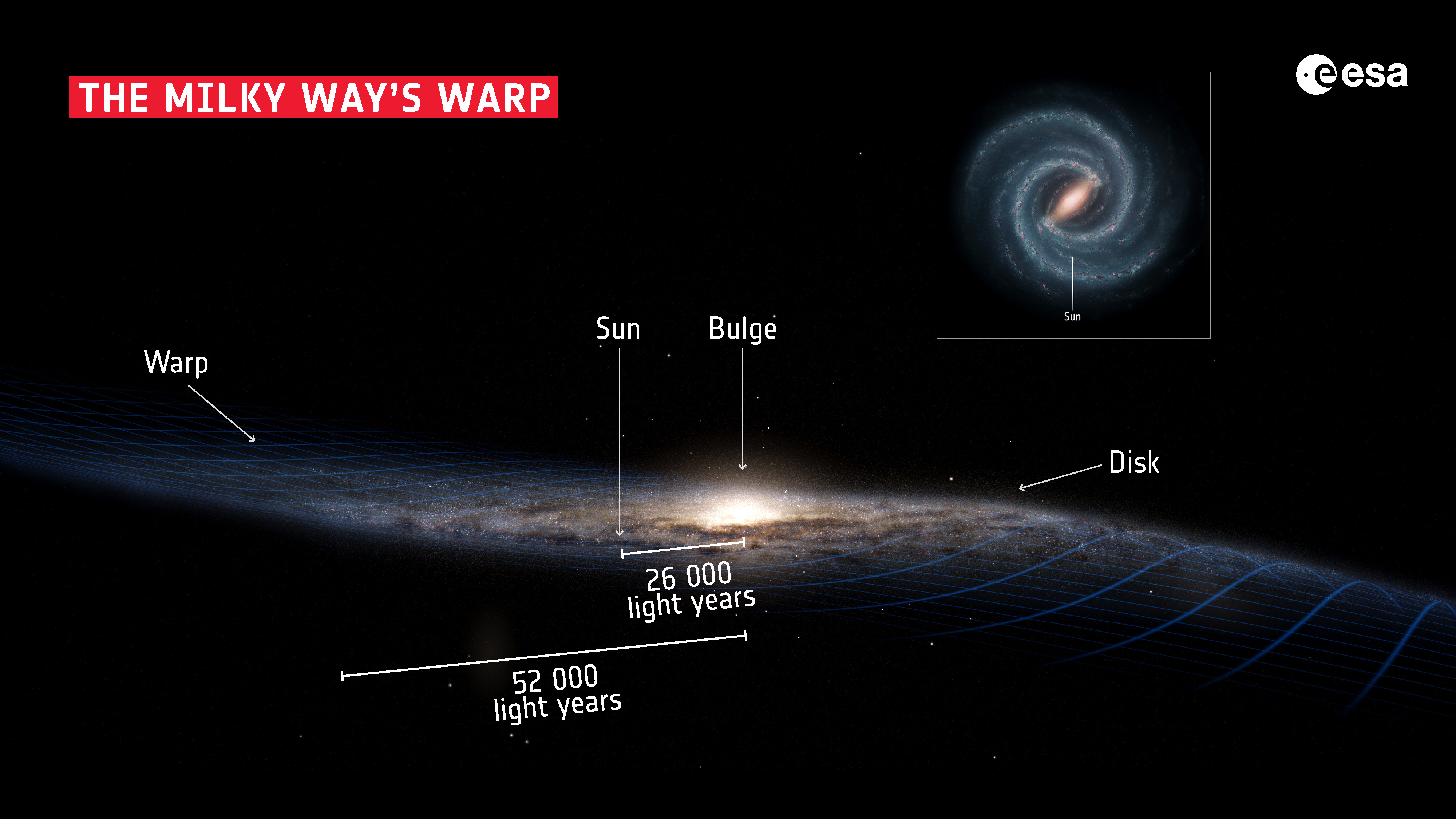
The Milky Way disk is not flat but warped (opens in new tab), in line with ESA. Because it rotates, it precesses like a wobbling spinning high. This wobble, basically an enormous ripple, circles the galactic heart rather more slowly than the celebs within the disk, finishing a full rotation in about 600 to 700 million years. Astronomers suppose this ripple could also be a results of a previous collision with one other galaxy.
(opens in new tab)
Sprinkled across the disk and the bulge are globular clusters, collections of historical stars, in addition to roughly 40 dwarf galaxies which might be both orbiting or colliding with the bigger Milky Way in line with a statement from ESA (opens in new tab).
All of that’s surrounded by a spherical halo of dust and gasoline, which is twice as broad because the disk. Astronomers consider that all the galaxy is embedded in a good bigger halo of invisible dark matter. Since dark matter would not emit any mild, its presence can solely be inferred not directly by its gravitational results on the motions of stars within the galaxy. Calculations recommend that this puzzling stuff makes as much as 90% of the galaxy’s mass.
The mass of the Milky Way, dark matter included, equals 1.5 trillion solar lots, in line with recent NASA estimates (opens in new tab). The galaxy’s seen matter is distributed between its 200 billion stars, their planets and the large clouds of dust and gasoline that fill the interstellar space. Astronomers aren’t fairly positive what number of planets are within the Milky Way, given we’ve solely discovered just a few thousand all informed, however one NASA estimate suggests it is more than 100 billion planets. What number of solar methods there are within the Milky Way can also be a thriller, as we’re nonetheless searching for the planets.
The place is the sun within the Milky Way?

(opens in new tab)
The sun orbits about 26,000 light-years from the black hole Sagittarius A*, roughly in the midst of the galactic disk. Touring on the velocity of 515,000 mph (828,000 kph), the sun takes 230 million years to finish a full orbit across the galactic heart.
The sun sits close to the sting of the Native Arm of the Milky Way, one of many two smaller spiral arms of the galaxy. In 2019, using data from the Gaia mission, astronomers discovered that the sun is basically browsing a wave of interstellar gasoline that is 9,000 light-years lengthy, 400 light-years broad and undulates 500 light-years above and beneath the galactic disk in line with ESA.
Planets of the solar system don’t orbit within the aircraft of the galaxy however are tipped by about 63 levels.
“It is nearly like we’re crusing by the galaxy sideways,” Merav Opher, an astrophysicist at George Mason College in Virginia, informed Area.com.
What’s the black hole within the Milky Way?
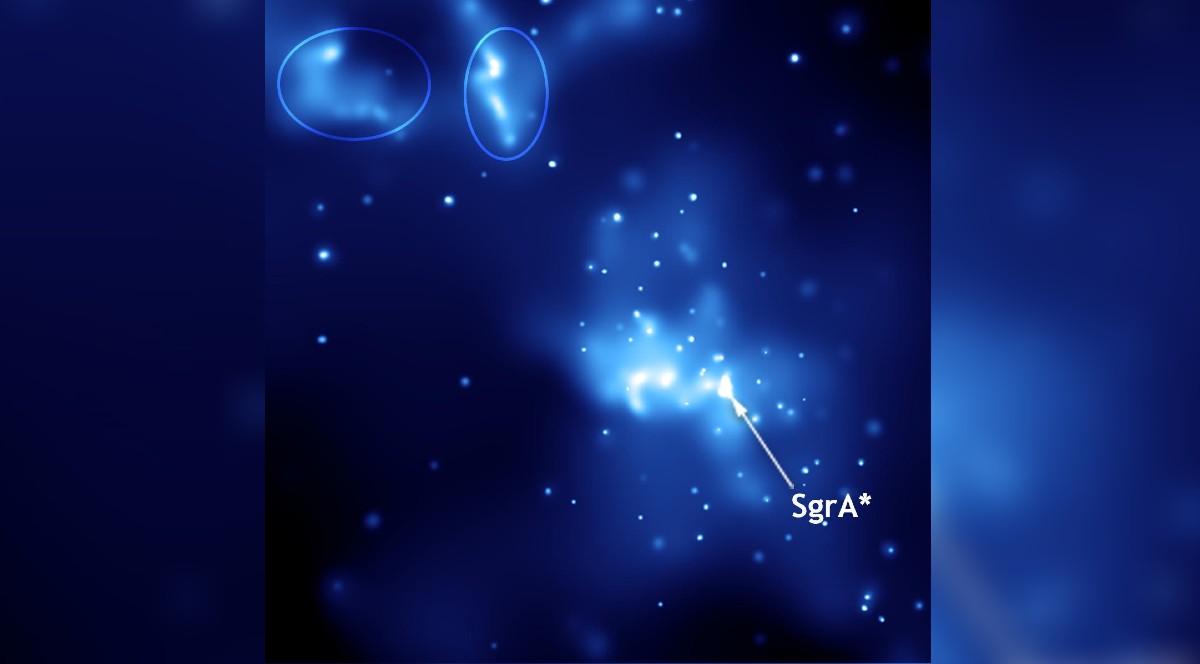

(opens in new tab)
The black hole within the Milky Way is known as Sagittarius A*. The black hole is usually dormant, which makes it very difficult to watch. Sagittarius A* has a mass 4.3 million occasions that of the sun, astronomers Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez found it in 2008. The approximate diameter is 14.6 million miles (23.5 million kilometers) . By comparability, the Milky Way itself is roughly 100,000 light-years broad and 1,000 light-years thick.
An enormous disk of gasoline round Sagittarius A* billows out so far as 5 to 30 light-years from the supermassive black hole. It’s this large, however tenuous, space of gasoline that provides a bit of fabric for Sagittarius A* exercise. The area is understood to emit X-rays attributable to feeding on the gasoline, or due to friction throughout the disk as temperatures soar to as a lot as 18 million levels Fahrenheit (10 million levels Celsius).
Scientists would like to have extra details about this supermassive black hole to determine extra about the way it was shaped and the situations that made its development potential. A few potentialities embrace smaller black holes getting fairly massive as they eat up dust and gasoline within the surroundings close by; alternatively, smaller black holes might merge collectively and create one thing extra monstrous.
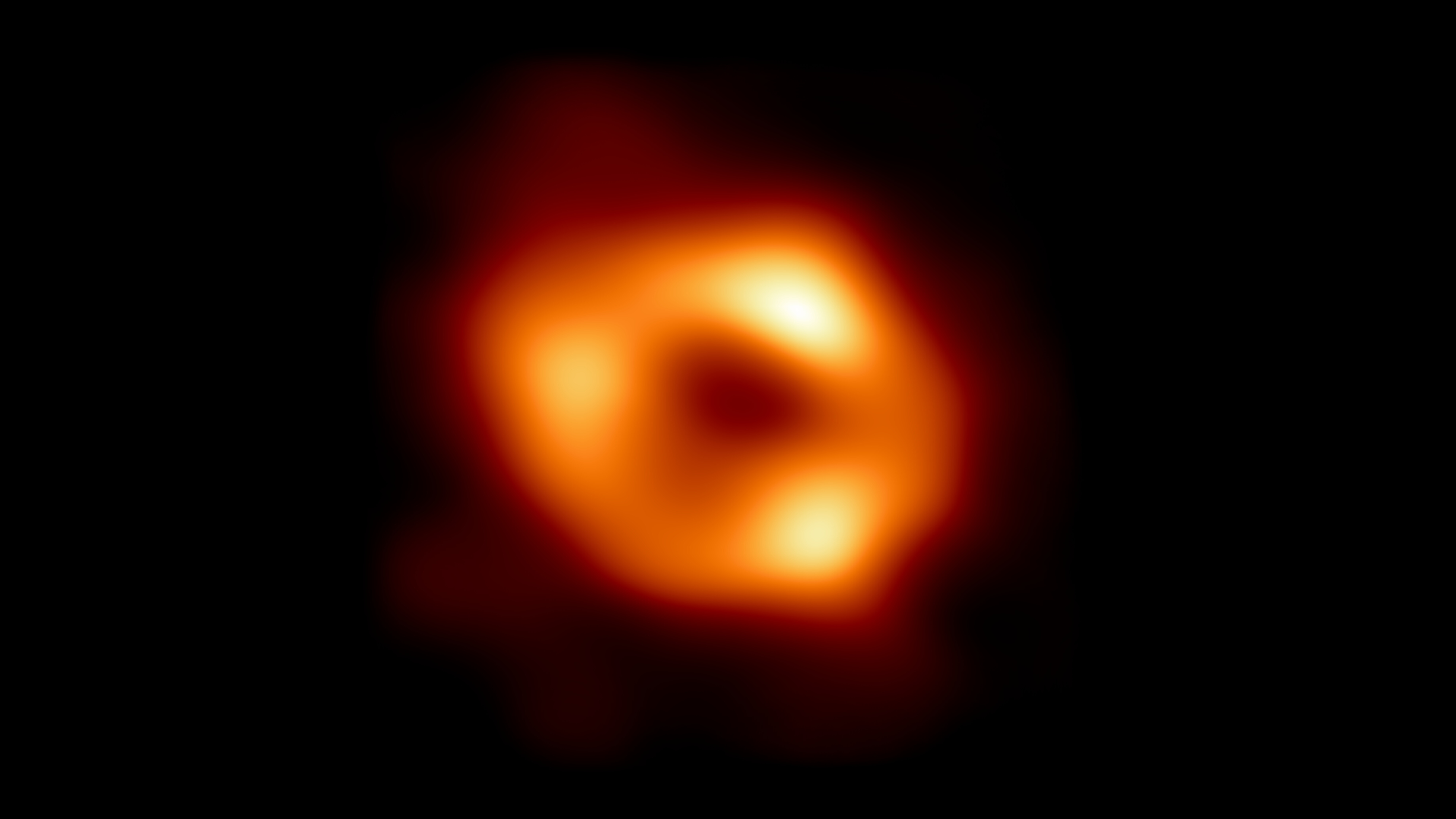

(opens in new tab)
Typically, scientists do have enhancing fashions for stellar-mass black holes and intermediate-mass black holes. These objects type when large stars, many occasions the mass of our sun, collapse after stopping nuclear fusion. Since they’re not capable of cease the gravitational collapse, they shrink to a gravitationally highly effective object that may warp time and space round it a lot that mild not can escape.
We’re steadily studying extra about Sagittarius A* by efforts such because the first-ever image of the black hole, which was obtained on Could 12, 2022. The picture captured faint quantities of sunshine brought on by heated matter transferring super-fast in the direction of the middle of the black hole; the picture is a high-definition shadow. This imaging required an enormous set of observatories all over the world, roughly the dimensions of Earth — which was potential by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT).
Associated: Here’s How Scientists Turned the World Into a Telescope (to See a Black Hole)
Mapping the Milky Way’s historical past
The evolution of the Milky Way started when clouds of gasoline and dust began collapsing, pushed collectively by gravity. First stars sprung up from the collapsed clouds, people who we see as we speak within the globular clusters. The spherical halo emerged quickly after, adopted by the flat galactic disk. The galaxy began small and grew because the inescapable drive of gravity pulled every little thing collectively.

(opens in new tab)
The galaxy’s evolution is, nevertheless, nonetheless shrouded in thriller. A self-discipline referred to as galactic archaeology is slowly unraveling among the puzzles of the Milky Way’s life because of the Gaia mission, which launched its first catalog of data (opens in new tab)in 2018.
Gaia measures (opens in new tab) the precise positions and distances of greater than 1 billion stars, in addition to their mild spectra, which permits scientists to grasp the celebs’ composition and age, in line with ESA. The place information enable astronomers to find out the speeds and instructions wherein the celebs transfer in space. As issues in space observe predictable trajectories, astronomers can reconstruct the paths of the celebs billions of years into the previous and future. Combining these reconstructed trajectories into one stellar film captures the evolution of the galaxy over eons.
There may be additionally evidence (opens in new tab) that the Milky Way collided with a number of smaller galaxies throughout its evolution. In 2018, a crew of Dutch astronomers discovered a group of 30,000 stars (opens in new tab) transferring in sync by the sun’s neighborhood in the wrong way to the remainder of the celebs within the information set. The movement sample matched what scientists had beforehand seen in laptop simulations of galactic collisions. These stars additionally differed in coloration and brightness, which urged they got here from a special galaxy.
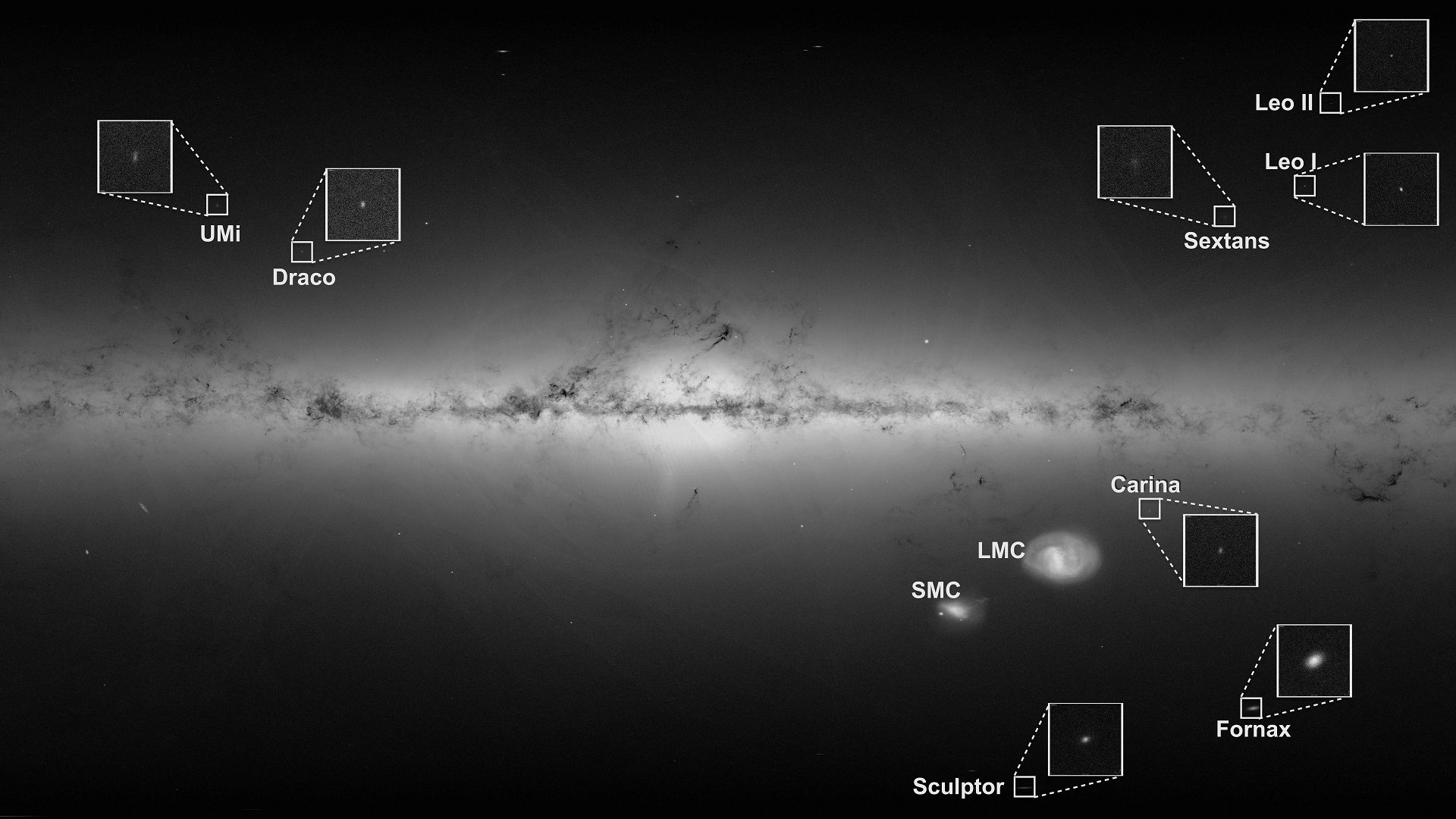

(opens in new tab)
Remnants of one other, barely youthful, collision had been noticed a 12 months later. The Milky Way continues devouring smaller galaxies to this day. A galaxy referred to as Sagittarius (to not be mistaken with the black hole) at present orbits near the Milky Way and has probably smashed through its disk several times (opens in new tab) previously 7 billion years. Utilizing Gaia information, scientists discovered that these collisions triggered intervals of intense star formation within the Milky Way and will even have one thing to do with the galaxy’s trademark spiral form. The examine means that our sun was born throughout a kind of intervals some 4.6 billion years in the past.
Photographing the Milky Way

(opens in new tab)
Photographing the Milky Way requires a darkish sky, a great “season” (typically between February and October), a long way from mild air pollution, and the power to make use of photographic gear to catch its faint mild. Fortunately, the Milky Way is seen in each the northern and southern hemispheres and it’s potential to seize it utilizing commonplace newbie pictures objects.
When you can, get to your web site within the daytime as you’ll probably wish to scout the realm for the perfect angles. Good Milky Way pictures have a tendency to utilize the panorama in artistic methods, so search for fascinating and outstanding pure options like mountains, boulders or rock shapes.
Subsequent comes the picture shoot. Typically talking, use a tripod, set your gear for a timelapse mode and be ready to experiment with totally different focuses and totally different lenses. For newbies, we even have a full information on how to photograph the Milky Way (opens in new tab).
The way forward for the Milky Way analysis
Because the starting of its operations, the Gaia mission has supplied three updates to its large stellar catalog. Astronomers from all around the world proceed analyzing the information searching for new patterns and revelations.
Gaia information at present generates extra analysis papers than even the well-known Hubble Space Telescope. Gaia will proceed charting the galaxy till not less than 2025, so long as the spacecraft stays in good well being, and the catalog it has compiled will maintain astronomers busy for many years to return.
Earlier than Gaia, the biggest dataset about positions and distances of stars within the Milky Way got here from a mission referred to as Hipparcos, after an historical Greek astronomer who started charting the evening sky 150 years earlier than Christ. Hipparcos solely noticed about 100,000 of the brightest stars within the sun’s neighborhood, in comparison with Gaia’s one billion. The information was additionally much less exact.
Though Gaia sees lower than 1% of stars within the galaxy, astronomers can broaden their findings and mannequin the conduct of all the Milky Way.
Further sources
Uncover extra concerning the Milky Way and different galaxies with this free studying materials from the Open University (opens in new tab). Discover the Milky Way in virtual reality (opens in new tab) with ESA’s Gaia mission. Tour the Milky Way with Gaia Sky (opens in new tab), a real-time, 3D, astronomy visualization software program that makes use of ESA’s Gaia mission information. Be taught why it was so troublesome to check the Milky Way earlier than Gaia on this article from ESA (opens in new tab).
Bibliography
Xiang, M., Rix, HW. “A time-resolved picture of our Milky Way’s early formation history (opens in new tab)“. Nature 603, 599–603 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04496-5
Robin, Annie C., et al. “A synthetic view on structure and evolution of the Milky Way. (opens in new tab)” Astronomy & Astrophysics 409.2 (2003): 523-540.
Dehnen, Walter, and James Binney. “Mass models of the Milky Way. (opens in new tab)” Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 294.3 (1998): 429-438.
Helmi, Amina. “Streams, substructures, and the early history of the Milky Way. (opens in new tab)” Annual Overview of Astronomy and Astrophysics 58 (2020): 205-256.




