NASA’s LRO (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter) has twice transmitted a laser pulse to a cookie-sized retroreflector aboard JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Company) SLIM lander on the moon and acquired a return sign.
As LRO handed 44 miles above SLIM (Good Lander for Investigating Moon) throughout two successive orbits on Could 24, 2024, it pinged the lander with its laser altimeter instrument because it had completed eight occasions earlier than. However, on these two makes an attempt, the sign bounced again to LRO’s detector.
This was an vital accomplishment for NASA as a result of the system shouldn’t be in an optimum place. Retroreflectors are sometimes secured to the highest of landers, giving LRO a 120-degree vary of angles to purpose towards when sending laser pulses to the approximate location of a retroreflector. Nonetheless, the SLIM lander had settled on the floor with its high dealing with sideways, limiting LRO’s vary.
To spice up the probabilities of reaching their goal, the LRO staff labored with JAXA to find out the precise location and orientation of SLIM. Then, NASA engineers predicted when LRO’s orbit trajectory would deliver it to coordinates that will give it the perfect probability of reaching SLIM’s retroreflector with the laser beams.
“LRO’s altimeter wasn’t constructed for this sort of software, so the probabilities of pinpointing a tiny retroreflector on the moon‘s floor are already low,” stated Xiaoli Solar, who led the staff that constructed SLIM’s retroreflector at NASA’s Goddard House Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland, as a part of a partnership between NASA and JAXA.
“For the LRO staff to have reached a retroreflector that faces sideways, as a substitute of the sky, exhibits that these little gadgets are extremely resilient,” Solar stated.
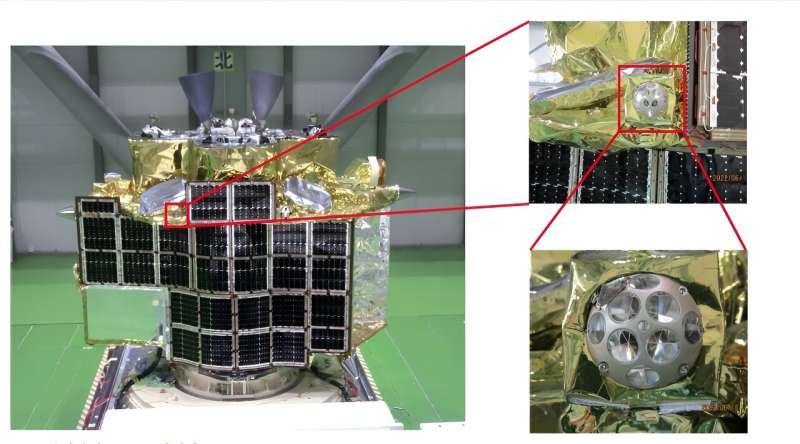
SLIM touched down on the moon’s floor on Jan 20. The retroreflector that hitched a experience with the lander, referred to as a Laser Retroreflector Array, is among the six NASA has despatched to the moon aboard personal and public landers, and the second to bounce sign again to LRO’s altimeter.
The primary time a laser beam was transmitted from LRO to a NASA retroreflector and again was on Dec. 12, 2023, when LRO pinged ISRO’s (Indian House Analysis Organisation) Vikram lander. LRO has since exchanged laser pings with Vikram three extra occasions.
NASA’s retroreflector has eight quartz corner-cube prisms set right into a dome-shaped aluminum body that’s 2 inches large. With no energy or upkeep required, retroreflectors can final on the moon’s floor for many years and thus present dependable beacons for future missions.
The retroreflectors may information Artemis astronauts to the floor at nighttime, for instance, or mark the places of spacecraft already on the floor to assist astronauts and uncrewed spacecraft land close to them.
LRO’s laser altimeter, the one laser instrument orbiting the moon for now, was designed to map the moon’s topography to organize for missions to the surface—to not level to inside 1/a centesimal of a level of a retroreflector, which is what LRO engineers are attempting to do with each ping.
Quotation:
NASA, JAXA bounce laser beam between moon’s floor and lunar orbit (2024, July 29)
retrieved 29 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-nasa-jaxa-laser-moon-surface.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

