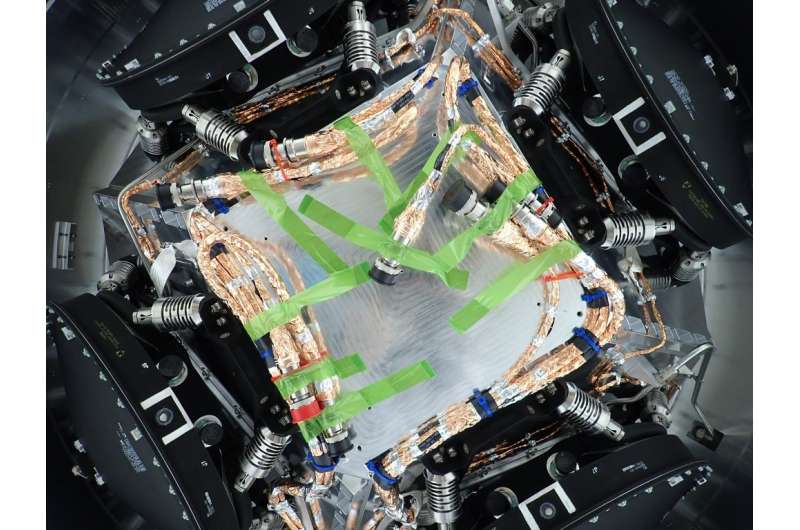
The large spacecraft that may head to Jupiter’s moon Europa makes use of 4 giant response wheels to assist hold it oriented.
Simply as NASA’s Mars rovers depend on strong wheels to roam the Pink Planet and conduct science, some orbiters depend on wheels, too—on this case, reaction wheels—to remain pointed in the precise course. Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California not too long ago put in 4 response wheels on Europa Clipper, which can depend on them throughout its journey at Jupiter’s icy moon Europa.
When NASA’s spacecraft heads via deep space, slips into orbit round Jupiter, and collects science observations whereas flying dozens of occasions by Europa, the wheels rotate the orbiter in order that its antennas can talk with Earth and its science devices, together with cameras, can keep oriented.
Two toes extensive and product of metal, aluminum, and titanium, the wheels spin quickly to create torque that causes the orbiter to rotate in the other way. Isaac Newton’s third legislation of movement additionally applies in deep space and explains the underlying phenomenon: For each motion, there may be an equal and reverse response. The response wheels trigger the spacecraft to react to the spinning motion of the wheels.
Here is one option to visualize how response wheels work: Think about you’re sitting in a swivel chair and raise your toes off the ground so that you’re free to rotate. When you jerk your torso one course, the chair and your legs will rotate the other way. The response wheels work the identical approach: Because the response wheel’s motor accelerates the steel wheel in a single course, the spacecraft experiences an acceleration in the other way.
With out these response wheels, Europa Clipper would not be capable to do its science investigations when it arrives on the Jupiter system in 2030 after its 2024 launch. Scientists consider Europa harbors an enormous inside ocean which will have circumstances appropriate for supporting life. The spacecraft will collect information on the moon’s ambiance, floor, and inside—info that may assist scientists study extra concerning the ocean, the ice crust, and potential plumes which may be venting subsurface water into space.

Throughout its orbits round Jupiter, Europa Clipper will depend on response wheels to assist it carry out 1000’s of turns, or “slews.” Though the spacecraft may carry out a few of these maneuvers with thrusters, its thrusters want gas—a finite useful resource aboard the orbiter. The response wheels will run on electrical energy supplied by the spacecraft’s huge solar arrays.
The trade-off is that the response wheels work slowly. Europa Clipper’s response wheels will take about 90 minutes to rotate the craft 180 levels—a motion so gradual that from a distance, it will be imperceptible to the human eye. The rotation of the spacecraft might be 3 times slower than the minute hand on a clock.
Additionally, they’ll put on out over time. It occurred on NASA’s Daybreak spacecraft, requiring engineers to determine the best way to rotate utilizing thrusters with the out there gas. To handle this, engineers have put in 4 wheels on Europa Clipper although solely three are wanted to maneuver. They alternate which three wheels are in operation to even the wear and tear. That leaves them with a “spare” wheel if one of many others fails.
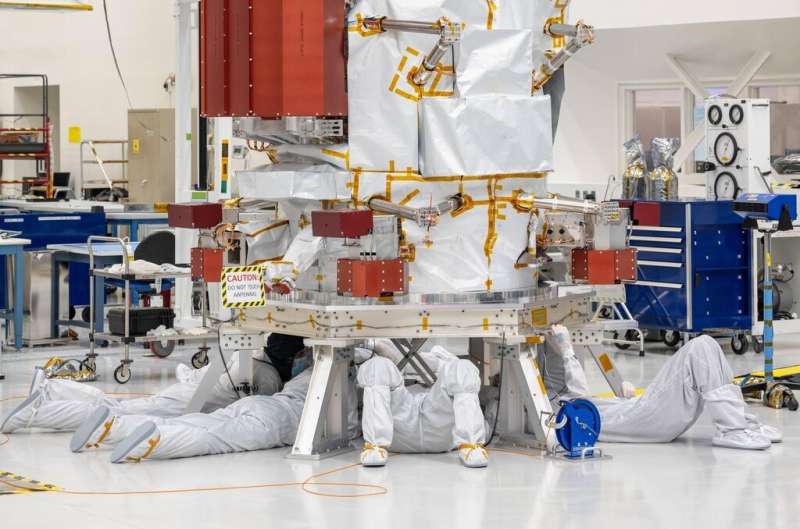
Putting in the wheels was one of the latest steps of the phase often known as meeting, check, and launch operations. Science devices proceed to reach at JPL to be added to the spacecraft. Subsequent, quite a lot of checks might be performed, because the spacecraft strikes towards its October 2024 launch interval. After touring over 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion kilometers), Europa Clipper might be set to start unlocking the secrets and techniques of this icy world.
Quotation:
NASA’s Europa Clipper will get its wheels for touring in deep space (2022, November 23)
retrieved 23 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-nasa-europa-clipper-wheels-deep.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




