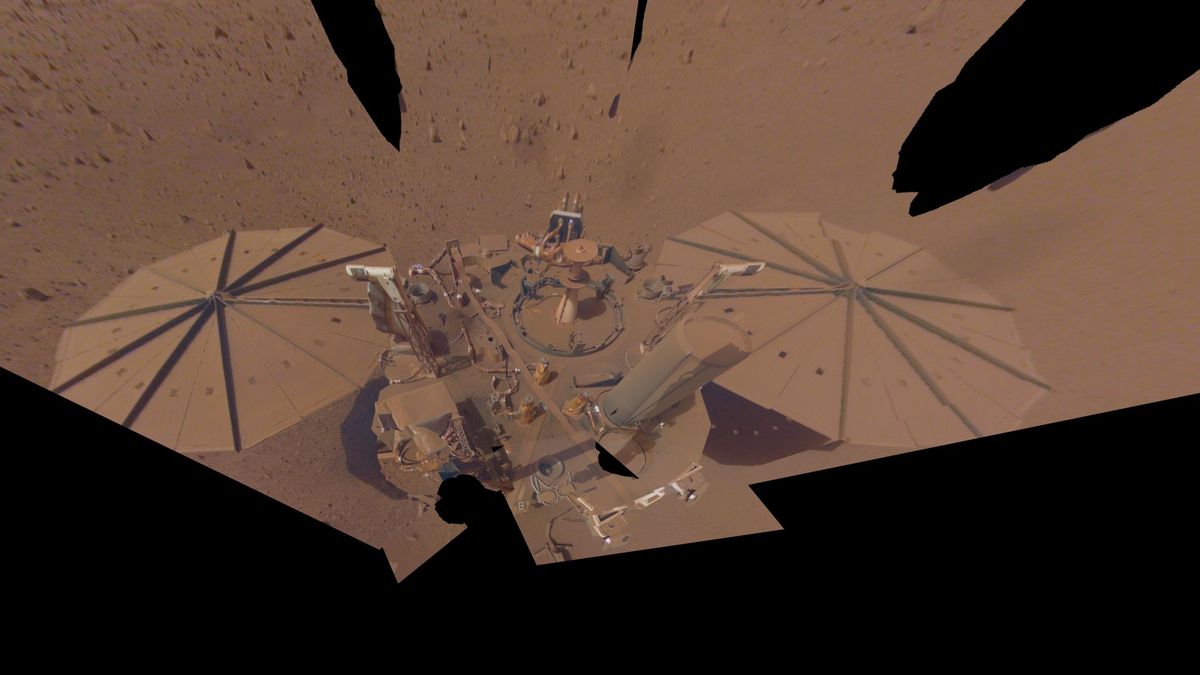
The Purple Planet’s harsh dust has claimed one other spacecraft.
NASA introduced Wednesday (Dec. 21) that its InSight lander, designed to know the geologic life story of Mars, has accomplished its mission on the Purple Planet. The spacecraft relied on solar energy, and after 4 years on Mars, its sunlight-collecting panels have constructed up an excessive amount of dust to generate sufficient energy to run the lander. For months now, the InSight staff have been anticipating the lander to fall silent. Now, the robotic has missed two calls dwelling; scientists final heard from the robotic on Dec. 15. NASA will maintain listening, however would not count on to listen to something extra from the lander.
“We have truly been in a position to do an entire lot greater than what we claimed and promised to do,” Bruce Banerdt, a planetary scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California and principal investigator of the InSight mission, informed Area.com earlier this yr. “I really feel like, wanting again, this has been an enormously profitable mission.”
Associated: NASA’s Mars InSight lander snaps dusty ‘final selfie’ as power dwindles
InSight launched in Could 2018 and landed six months later; for 4 years, the $814 million robotic quietly listened to the Purple Planet’s rumblings.
Not like its rover siblings Curiosity and Perseverance, which give attention to evaluating the Purple Planet’s habitability over time, InSight was designed to look deep contained in the planet, measuring the layers from the floor all the way down to the molten core. The mission was additionally meant to trace present geologic exercise by feeling for marsquakes.
And InSight discovered success on each fronts, even when issues did not go exactly in accordance with plan.
“Mars itself has been shocking: It has been harder in some methods and it has been extra forthcoming in some methods,” Banerdt stated. “The locations that have been tough, we have been nonetheless in a position to eke out the data that we have been in search of by getting extra intelligent in regards to the evaluation and so forth. And the locations the place Mars was beneficiant to us, we had issues fall in our lap that we weren’t anticipating.”
Unable to dig
Mars was notably difficult when it got here to the InSight instrument nicknamed “the mole,” formally generally known as the Warmth Circulation and Bodily Properties Bundle. The gadget was meant to hammer itself down 16 ft (5 meters) and measure how a lot warmth is rising up from the deep core of Mars. However it doesn’t matter what scientists tried, the mole could not get a grip on the soil at InSight’s touchdown web site, leaving it caught close to the floor.
The problem means that the bottom beneath InSight is totally different than at places NASA’s rovers have beforehand explored, in accordance with Sue Smrekar, a planetary scientist at JPL and deputy principal investigator for InSight.
“Based mostly on our understanding of what we noticed elsewhere, sure, it ought to have labored,” Smrekar informed Area.com earlier this yr. She stated she believes that the mole would have labored in a type of places and that an tailored model may work even the place InSight landed.
Even with out digging correctly, the mole nonetheless gathered restricted knowledge — however nothing like what scientists had hoped for. “It isn’t the warmth circulate that we have been actually after, the large prize, and that is been, for me personally, tremendous irritating,” Smrekar stated.
The InSight staff abandoned efforts to get the mole digging correctly in January 2021, after troubleshooting the difficulty for practically two years. “We knew from the start that this was a bit little bit of a difficult experiment,” Banerdt stated.
Shaking up science
However the place the mole’s patch of the Purple Planet stymied InSight, one other area of Mars was surprisingly beneficiant: Cerberus Fossae. The area, which is scarred by faults and lies about 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) away from InSight,, has produced far more of the marsquakes the lander has detected than some other area.
“So far as we perceive, there’s this one super-active space, and it defies the prediction of how chilly Mars is, how inactive Mars is,” Smrekar stated. “It permits us to see Mars as not a uniform and outdated and lifeless planet.”
InSight additionally gave scientists a greater view inside Mars than any earlier mission has managed, to nice impact. “Numerous issues are totally different than we imagined,” Smrekar stated. “Based mostly on the info that we had obtainable, we needed to make loads of assumptions in regards to the inside. Now now we have this tough knowledge, which provides us a a lot clearer image of what is going on on contained in the planet.”
InSight’s knowledge has informed scientists that the Martian crust, at the very least on the robotic’s near-equatorial touchdown web site, consists of two different layers: a prime layer about 6 miles (10 km) thick that has been battered by impacts atop a deeper layer about 25 miles (40 km) thick. “We actually did not have a transparent image about these a number of layers within the crust,” Smrekar stated. Even now, she and her colleagues aren’t positive whether or not the two-layer construction happens globally or solely particularly areas.
As well as, InSight discovered that the core of Mars is much larger than scientists had anticipated; the discovering additionally signifies that the core should include larger quantities of lighter parts than scientists thought — particularly, extra sulfur, maybe as a lot as 15% to twenty%, Banerdt stated.
“That is type of damaged our fashions of the core,” Banerdt stated. “While you do an experiment and get knowledge that breaks the fashions, that is an actual advance.”
(Nobody is gloomy to see the fashions go. “Planets are way more attention-grabbing than our fashions,” Smrekar stated; in any case, discovering the strengths and weaknesses of present fashions is the purpose of any space mission.)
Finish of the road
The InSight staff has spent current months eking as a lot knowledge out of the lander as doable. Because the robotic’s energy manufacturing fell, mission personnel organized for the seismometer to run in eight-hour chunks, buffered by time for the lander to recharge its battery.
“Each totally different type of marsquake, each extra quake, it simply provides one other piece of the story of what is going on on inside Mars,” Smrekar stated, noting that the lander caught its largest marsquake in early Could, simply two weeks earlier than NASA announced that the mission was nearing its finish. “It will be simply improbable if we may carry on.”
However no mission lasts ceaselessly — particularly not a solar-powered Mars mission. The Purple Planet’s dust is brutal for these spacecraft, piling up on solar panels and dramatically decreasing the arrays’ energy manufacturing. And the dust is a double whammy, because it additionally seasonally fills the skies, decreasing the quantity of daylight that reaches the Martian floor.
The mix equally did in NASA’s Opportunity rover in 2018, and now dust has ended InSight’s mission as effectively.
“It has been a tremendous spacecraft. It is carried out every little thing that we have requested it to do and extra,” Banerdt stated. “It is earned its retirement — I like to consider it as retiring and never dying. And it is going to sit on Mars and benefit from the Martian sunsets for some time after it stops speaking to us.”
Electronic mail Meghan Bartels at mbartels@space.com or observe her on Twitter @meghanbartels. Comply with us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.