by Beijing Institute of Expertise Press Co.
Touchdown stably is a precondition for exploring a small celestial physique in situ. The floor of a small celestial physique ceaselessly has weak gravity and is irregular, and the floor surroundings is unknown and unsure. The touchdown mechanism tends to rebound and switch over, and the touchdown stability time is lengthy. Nevertheless, whereas most touchdown efficiency analysis has centered on lunar touchdown, there are variations between the surfaces of the moon and Mars.
Subsequently, it vital to review touchdown efficiency in numerous circumstances as a way to analyze the touchdown stability boundary, and to suggest affordable touchdown ideas to help China’s small celestial physique exploration.
In a research article lately printed in House: Science & Expertise, researchers from Beijing Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering, Harbin Institute of Expertise, and Polytechnic College of Milan have established a simulation mannequin of a touchdown mechanism underneath completely different touchdown circumstances, analyzed the sensitivity of the important thing parameters affecting the touchdown efficiency, and verified correctness of the simulation through experimental tests, which may present steerage for a touchdown mechanism to land stably on a small celestial physique.
First, the authors briefly reproduce the touchdown mechanism and the touchdown simulation. The small celestial physique touchdown mechanism used within the simulation comprises a touchdown foot, touchdown legs, cardan ingredient, damping ingredient, gear base, and extra. In simulation, two eventualities are considered: the touchdown mechanism touchdown towards the touchdown slope with Vx > 0; and the touchdown mechanism touchdown away from the touchdown slope with Vx < 0.
In every situation, three touchdown modes are categorised in line with the contact order between the touchdown foot and the touchdown slope, i.e. (a) 1-2 touchdown mode, (b) 2-1 touchdown mode, and (c) 1-1-1 touchdown mode (with 30° yaw angle). For all touchdown modes in each simulation eventualities, the touchdown mechanism turnover is prevented by the retro-rocket, and there’s no sliding of the touchdown toes.
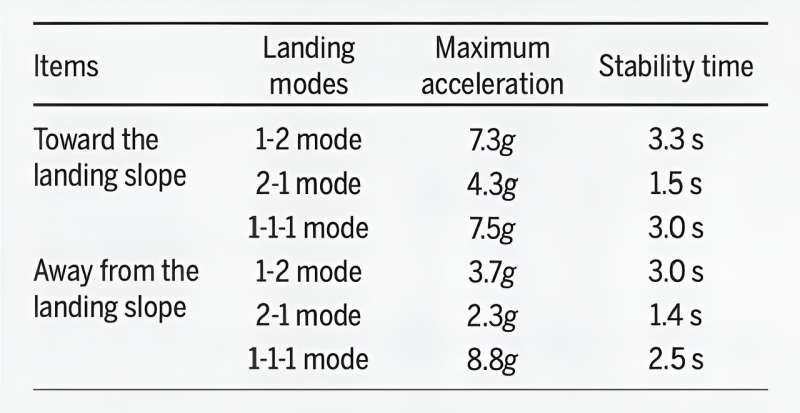
The utmost overloading acceleration of the gear base is lower than 10 g, and the touchdown stability time is lower than 4 seconds. This exhibits that the touchdown mechanism can land safely in numerous touchdown circumstances. Moreover, when Vx > 0, the analysis exhibits that the 2-1 mode has the perfect touchdown efficiency amongst three modes, and 1-2 and 1-1-1 modes’ touchdown performances are related. When Vx < 0, the touchdown efficiency of the 2-1 mode is the perfect, the 1-2 mode is normally, and the 1-1-1 mode is the worst.
Secondly, key elements affecting the touchdown efficiency are analyzed.
Cardan ingredient damping (c2)
The touchdown stabilization time is considerably shortened and the overloading acceleration is weakened when c2 is variable compared to fixed c2. The touchdown mechanism has higher touchdown efficiency when c2 is variable.
Foot anchors
The foot anchors have an effect on the friction coefficient between touchdown toes and the touchdown floor. Slipping induces the touchdown mechanism far-off from the touchdown level, which might have an effect on the anchorage of the anchoring system. Friction between the touchdown mechanism and the touchdown floor ought to be excessive to keep away from sliding of the touchdown mechanism. Overturning of touchdown mechanism attributable to excessive friction may be eradicated by retro-rocket thrust. Subsequently, it’s useful to design foot anchors on the touchdown mechanism, as it will possibly penetrate the touchdown floor and forestall or weaken sliding of the touchdown mechanism.
Retro-rocket thrust
Retro-rocket thrust can stop the touchdown mechanism from bouncing or turning; thus the retro-rocket thrust is useful for touchdown efficiently.
Touchdown slope
The bigger the slope angle is, the upper the turning angular velocity of touchdown legs is, and the longer the touchdown stabilization time is. The affect of slope angle on gear base overloading acceleration shouldn’t be apparent. Subsequently, the touchdown floor with smaller slope angle ought to be chosen to scale back the touchdown stabilization time.
Touchdown angle
When the touchdown mechanism lands in numerous touchdown attitudes inside the allowable touchdown velocity, the utmost overloading acceleration is lower than 10g and the touchdown stabilization time is lower than 5 seconds. Touchdown efficiency is nice. When the yaw angle is 60° (that’s, the 2-1 touchdown mode), the touchdown mechanism experiences the minimal overloading acceleration and the shortest touchdown stability time, and the touchdown efficiency is the perfect.
Then, the validity of the simulation mannequin is verified by assessments. These assessments are carried out on the air-floating platform. The touchdown accelerations are measured by acceleration sensors. Checks of touchdown on a 30° slope within the 1-2 mode, the 1-2 mode, and the 1-1-1 mode are performed individually. These touchdown modes and velocities are imported into the simulation mannequin. Touchdown performances between check and simulation are in contrast.
The overloading acceleration of the gear base obtained by simulation is near that obtained by check, and the simulation result’s barely bigger than the check. That is because of the mechanical flexibility of the touchdown mechanism, which can produce versatile deformation within the check and soak up a part of the influence load. The modifications of touchdown leg turnover angular velocity and turnover angle in simulation and check are comparatively constant.
However between about 0.7 seconds and a pair of.5 seconds within the 1-2 mode, about 0.5 and a pair of seconds within the 2-1 mode, and for the entire length of the 1-1-1 mode, the touchdown leg turnover angle in check is lower than that in simulation. The reason being that touchdown floor in check is tough wooden and the foot anchors fail to penetrate the arduous wooden, which leads to a slight slip of the touchdown mechanism. As well as, it’s discovered that the 2-1 touchdown mode has the shortest stability time, and there’s no apparent relationship between the overloading acceleration and the touchdown mode.
Lastly, authors come to the conclusion that the next strategies are useful to enhance touchdown efficiency:
- A 3-leg touchdown mechanism ought to preferentially select the 2-1 touchdown mode.
- Adjustable damping akin to touchdown circumstances is useful to enhance touchdown stability.
- Foot anchors can cut back touchdown slip and shorten touchdown stabilization time. A retro-rocket on high of the touchdown mechanism can weaken or stop rebounding when touchdown.
- The landing mechanism ought to preferentially land on flat areas.
Extra data:
Zhijun Zhao et al, A Legged Small Celestial Physique Touchdown Mechanism: Touchdown Simulation and Experimental Take a look at, House: Science & Expertise (2023). DOI: 10.34133/space.0066
Supplied by
Beijing Institute of Expertise Press Co.
Quotation:
Scientists develop a legged small celestial physique touchdown mechanism for touchdown simulation and experimental check (2023, November 1)
retrieved 1 November 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-11-scientists-legged-small-celestial-body.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

