A staff of astronomers together with McGill Professor Nicolas Cowan has unraveled the enigmatic environment of the exoplanet HAT-P-18 b, shedding mild on its intriguing mix of gases, clouds, and even the consequences of its star’s exercise
Exoplanets, planets positioned past our solar system, captivate each scientists and the general public, holding the promise of unveiling various planetary methods and probably liveable worlds. Regardless of being very a lot not like our Earth, massive gas giant planets discovered very near their stars have confirmed to be splendid take a look at targets for telescopes just like the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) to refine astronomers’ strategies of understanding exoplanets.
One such planet is HAT-P-18 b, a “sizzling Saturn” sort planet positioned over 500 light-years away with a mass just like Saturn’s however a dimension nearer to that of the bigger Jupiter. This offers the exoplanet a puffed-up environment that’s particularly splendid for evaluation.
Led by researchers from the Trottier Institute for Analysis on Exoplanets at McGill College and the Université de Montréal (UdeM), a staff of astronomers harnessed the ability of the revolutionary Webb Telescope to check HAT-P-18 b. Their findings, detailed within the journal Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS), present a complete portrait of the recent Saturn’s environment whereas delving into the complexities of distinguishing atmospheric alerts from stellar exercise.
“The James Webb Area Telescope supplies exoplanet observations so exact that we’re restricted by our understanding of their host stars. Fortuitously, those self same data- particularly with the made-in-Canada NIRISS instrument- enable us to measure what the star is doing throughout our observations and proper for it, so we will determine precisely what’s in these planets’ atmospheres,” stated Nicolas Cowan, Professor in McGill College’s Division of Earth and Planetary Sciences.
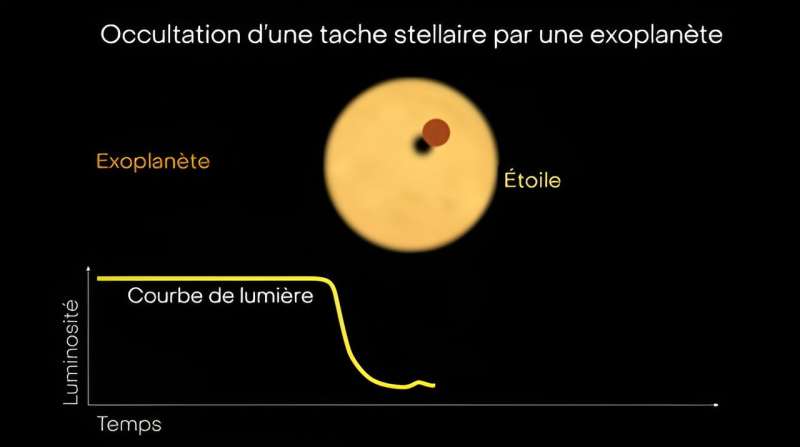
Passing over a noticed star
Observations from the Webb Telescope have been taken whereas the exoplanet HAT-P-18 b handed in entrance of its sun-like star. This second is known as a transit and is essential to detect and additional characterize an exoplanet from tons of of light-years away with stunning precision. Astronomers usually are not observing mild emitted instantly by the distant planet. Quite, they’re learning how the central star’s mild is blocked and affected by the planet orbiting it.
Exoplanet hunters should thus grapple with the problem of disentangling alerts brought on by the presence of the planet and people brought on by the star’s personal properties. Similar to our sun, stars shouldn’t have uniform surfaces.
They’ll have darkish star spots and vivid areas, creating alerts that mimic a planet’s atmospheric attributes. A current research of the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 b and its star TRAPPIST-1 led by UdeM Ph.D. scholar Olivia Lim witnessed an eruption, or flare, on the star’s floor, which affected their observations.
Within the case of planet HAT-P-18 b, Webb caught the exoplanet proper because it handed over a darkish spot on its star, HAT-P-18. That is known as a spot-crossing occasion, and its impact was evident within the information collected for the research. The staff additionally reported the presence of quite a few different star spots on HAT-P-18 b’s floor, which weren’t blocked out by the exoplanet.
To precisely decide the exoplanet’s atmospheric composition, the researchers decided it was essential to concurrently mannequin the planetary environment in addition to the star’s peculiarities. They state that such consideration might be essential in treating future exoplanet observations from the JWST to harness their potential absolutely.
H2O, CO2, and clouds in a scorching environment
Following their cautious modeling of each the exoplanet and the star within the HAT-P-18 system, the staff of astronomers then carried out a meticulous dissection of HAT-P-18 b’s atmospheric composition.
By inspecting the sunshine that filters by means of the exoplanet’s environment because it transits its host star, the researchers discerned the presence of water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The researchers additionally detected the attainable presence of sodium.
Including intrigue to the findings, the staff noticed sturdy indicators of a cloud deck in HAT-P-18 b’s environment, which seems to be muting the alerts of a lot of its molecules. Additionally they concluded that the star’s floor was coated by many darkish spots that may considerably affect the interpretation of the information.
An earlier evaluation of the identical JWST information led by a staff at Johns Hopkins College had additionally revealed a transparent detection of water and CO2, but additionally reported the detection of small particles at high-altitudes known as hazes and located hints of methane (CH4).
The work from the Université de Montréal astronomers, which was the primary time the celebrities’ floor traits have been thought of with the planet’s environment, revealed a distinct image. The CH4 detection was not confirmed, and the water abundance they decided was ten instances decrease than beforehand discovered.
Additionally they discovered that the earlier research’s detection of hazes might as an alternative be brought on by star spots on the star’s floor, highlighting the significance of contemplating the star within the evaluation.
Whereas molecules like water, carbon dioxide, and methane may be interpreted as biosignatures, or indicators of life, in sure ratios or together with different molecules, HAT-P-18 b’s scorching temperatures of near 600 levels Celsius don’t bode nicely for the planet’s habitability.
The info used from the JWST on this research have been collected by the Canadian-made NIRISS (Close to-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph) instrument, which has offered astronomers with the unparalleled capacity to distinguish a lot of HAT-P-18 b’s atmospheric traits from each other.
The outcomes present that observations taken on the far-visible to near-infrared inside the NIRISS instrument’s wavelength vary are important to disentangle the alerts from the planetary environment and the star. Future observations from one other JWST instrument, the Close to Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), would assist refine the staff’s outcomes, such because the CO2 detection, and shed much more mild on the intricacies of this sizzling Saturn exoplanet.
Extra info:
Marylou Fournier-Tondreau et al, Close to-Infrared Transmission Spectroscopy of HAT-P-18 b with NIRISS: Disentangling Planetary and Stellar Options within the Period of JWST, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3813. On arXiv: DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2310.14950
Supplied by
McGill University
Quotation:
Secrets and techniques of a sizzling Saturn and its noticed star unlocked (2024, January 9)
retrieved 10 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-secrets-hot-saturn-star.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




