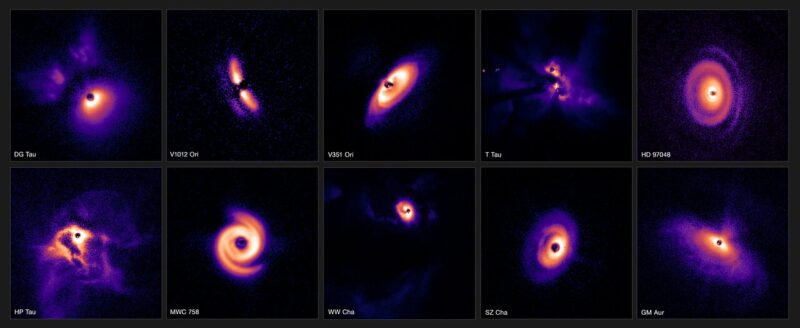
Take a look at the gorgeous new photographs of planet-forming disks round younger stars. These observations showcase 86 younger stars from three gasoline clouds in our Milky Way galaxy.
- A brand new research checked out 86 younger stars and their planet-forming disks in three gasoline clouds of the Milky Way.
- It’s one of many largest surveys of planet-forming disks, displaying all kinds of sizes and shapes.
- The research confirmed that multi-star methods have been much less more likely to have massive, planet-forming disks.
ESO revealed this original article on March 5, 2024. Edits by EarthSky.
Survey of planet-forming disks
The European Southern Observatory mentioned on March 5 that its Very Giant Telescope (ESO’s VLT) in Chile has captured photographs of planet-forming disks, in one of many largest-ever surveys of those disks. The analysis targeted on observations of greater than 80 younger stars believed to have planets forming round them. The brand new observations have given astronomers new knowledge and distinctive insights into how planets would possibly come up in several areas of our dwelling galaxy, the Milky Way.
Christian Ginski of the College of Galway, Eire, is a lead writer of considered one of three new papers revealed on March 5, 2024, in Astronomy & Astrophysics. Ginski said:
That is actually a shift in our subject of research. We’ve gone from the extraordinary research of particular person star methods to this big overview of complete star-forming areas.
Planet formation is various
To this point, astronomers have discovered greater than 5,000 planets orbiting stars aside from our sun. And sometimes they’re inside methods markedly completely different from our personal solar system. To know the place and the way this variety arises, astronomers should observe the dust- and gas-rich disks that envelop younger stars. These are the very cradles of planet formation. And so they’re finest present in big gasoline clouds the place the celebrities themselves are forming.
Very like mature planetary methods, the brand new photographs showcase the extraordinary variety of planet-forming disks. Ginski said:
A few of these disks present big spiral arms, presumably pushed by the intricate ballet of orbiting planets.
Antonio Garufi of the Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory, Italian Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), and lead writer of one of many papers, added:
Others present rings and enormous cavities carved out by forming planets, whereas but others appear clean and nearly dormant amongst all this bustle of exercise.
Specializing in 3 gasoline clouds and their planet-forming disks
The group studied a total of 86 stars throughout three completely different star-forming areas of our galaxy. The primary two areas are Taurus and Chamaeleon I. Each lie round 600 light-years from Earth. The third is Orion, a gas-rich cloud about 1,600 light-years from us. Scientists already knew it because the birthplace of a number of stars extra large than the sun. The observations have been gathered by a big worldwide group, comprising scientists from greater than 10 nations.
The group gleaned a number of key insights from the info. For instance, in Orion they discovered stars in teams of two or extra have been much less more likely to have massive planet-forming disks. This can be a important outcome as a result of most stars in our galaxy have companions. As well as, the uneven look of the disks suggests the potential for large planets embedded inside. This might be what’s inflicting the disks to warp and change into misaligned.
Whereas planet-forming disks can lengthen for distances a whole bunch of instances better than the space between Earth and the sun, their location a number of a whole bunch of light-years from us makes them seem as tiny pinpricks within the evening sky. So the group used the Spectro-Polarimetric Excessive-contrast Exoplanet Analysis instrument (SPHERE) mounted on ESO’s VLT. SPHERE’s state-of-the-art excessive adaptive optics system corrects for the Earth’s turbulent environment, yielding crisp photographs of the disks.
Thus, the group was capable of picture disks round stars with lots as little as half the mass of the sun. That measurement is often too faint for many different devices accessible at the moment. Further knowledge for the survey have been obtained utilizing the VLT’s X-shooter instrument. The X-shooter allowed astronomers to find out how younger and the way large the celebrities are. And the Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) helped the group perceive extra concerning the quantity of dust surrounding among the stars.
Pictures of the three gasoline clouds
Deeper photographs to come back
As know-how advances, the group hopes to delve even deeper into the center of planet-forming methods. The big 39-meter mirror of ESO’s forthcoming Extraordinarily Giant Telescope (ELT), for instance, will allow the group to check the innermost areas round younger stars. These are areas the place rocky planets like our personal could be forming.
For now, these spectacular photographs present researchers with a treasure trove of knowledge to assist unpick the mysteries of planet formation. Per-Gunnar Valegård, of the College of Amsterdam, the Netherlands, led the Orion research. Valegård hopes the pictures will encourage his pupils to change into scientists sooner or later and said:
It’s nearly poetic that the processes that mark the beginning of the journey in the direction of forming planets and in the end life in our personal solar system needs to be so lovely.
Specializing in one of many disks
Backside line: A brand new survey checked out 86 younger stars and their planet-forming disks in three gasoline clouds in our personal Milky Way. See them right here.
Sources: