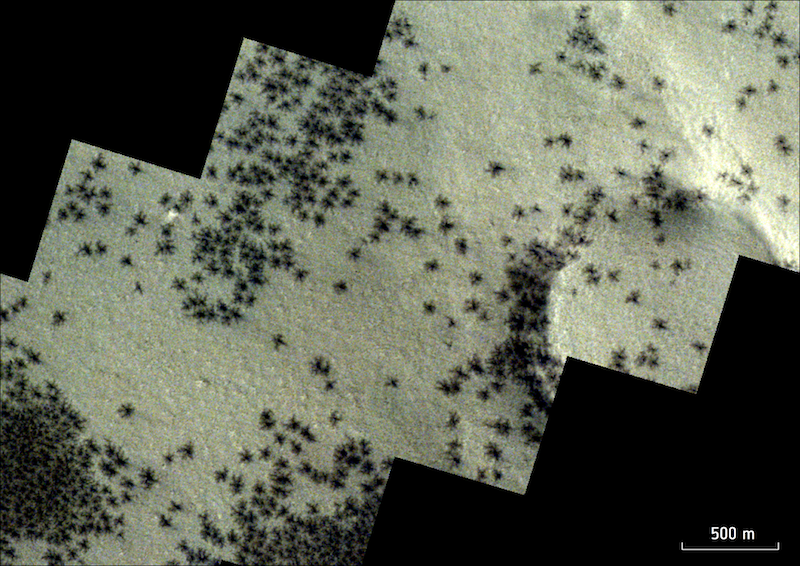
- The European Area Company (ESA) launched extra pictures of the enigmatic “spiders” and Inca Metropolis on the South Pole of Mars.
- The “spiders” are darkish patches resembling spiders. They’re created by geysers of carbon dioxide gasoline and dust erupting by means of layers of ice.
- Inca Metropolis is a sequence of hollows and ridges that appear to be an historic Incan damage. However scientists say it’s a pure geological formation and never made by historic Martians.
Are there spiders on Mars?
Have you ever seen the spiders on Mars? No, they’re not a creepy crawly type of life. And so they don’t have anything to do with David Bowie’s iconic album The Rise and Fall of Ziggy Stardust and the Spiders from Mars. The Martian spiders are options on the purple planet’s floor fashioned by geysers of carbon dioxide gasoline on the South Pole. The European Area Company’s Mars Express orbiter took some newly launched pictures of those fascinating formations and the “metropolis” they inhabit, Inca City. Formally known as Angustus Labyrinthus, it’s a big community of linear and geometric ridges that resemble historic Incan ruins. ESA released the brand new pictures on April 24, 2024.
The Martian spiders
The spiders are irregular darkish shapes on the panorama that appear to be spiders with a number of tendril-like legs. Sometimes, they vary from about 147 toes (45 meters) to 1/2 mile (one km) in measurement. When first discovered, they appeared like they is perhaps some type of vegetation. However nearer inspection by orbiting spacecraft, nonetheless, revealed what they are surely, which continues to be fascinating: deposits of carbon dioxide gasoline and darkish dust that type from geyser-like eruptions.
Within the Martian winter on the South Pole, carbon dioxide kinds layers on the floor. And carbon dioxide within the type of ice is the bottom layer. In spring, sunshine causes the ice to show into carbon dioxide gasoline. The gasoline step by step builds up beneath slabs of ice. Finally, it breaks by means of the ice as tall geysers. The gasoline additionally incorporates the darkish dust, which falls again onto the floor. Consequently, the spots of spray from the gasoline and dust appear to be spiders.
As well as, there are different spider-like or web-like patterns under the ice. Scientists say the identical processes possible create these as nicely.
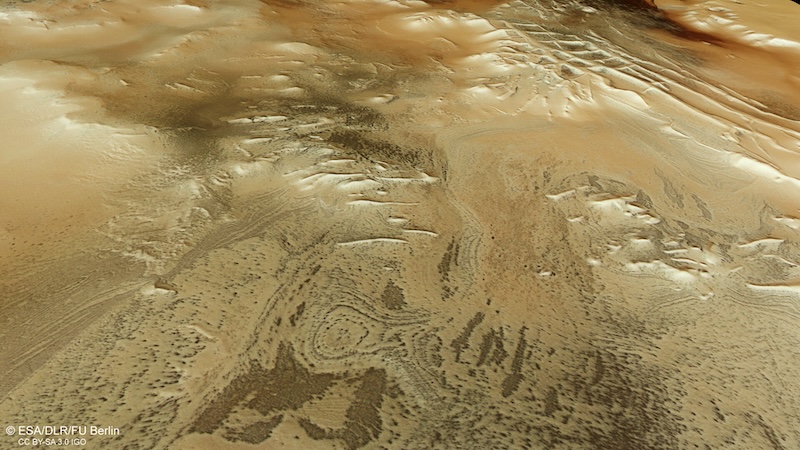

Martian spiders and Inca Metropolis
A lot of the spiders are on the outskirts of a geological formation known as Inca Metropolis. However fairly a number of are inside town, too. The “metropolis” – additionally formally often called Angustus Labyrinthus – is a protracted sequence of linear and geometric ridges or “partitions” which are harking back to archaeological ruins of the traditional Incas on Earth.
However to be clear, scientists don’t assume Inca Metropolis is a man-made damage. That stated, they’re not precisely certain the way it fashioned, both. Theories embody sand dunes that hardened over time to type the ridges or magma or sand seeping by means of fractured bedrock. Or the ridges is perhaps eskers, that’s, lengthy, winding ridges of stratified sand and gravel, which happen in glaciated and previously glaciated areas of Europe and North America.
An historic influence crater?
One doable clue is the ridges seem to type part of a larger circle. That circle can be about 53 miles (85 km) in diameter and would possible be the stays of an historic influence crater. The influence could have created faults within the floor that then stuffed up with lava. The faults then wore away over billions of years, forsaking the ridges.
The panorama close to Inca Metropolis options “swirling ovals.” These additionally could have fashioned when layered deposits of fabric slowly wore away over time. As well as, there are flat-topped mesas and hills close by, standing over 4,500 toes (1,400 meters) tall.
Whereas the spiders and metropolis don’t actually have something to do with Martians – residing or lifeless – they’re an interesting glimpse at a few of the geological processes on the purple planet. Mars is filled with surprises!
Backside line: The European Area Company (ESA) launched new pictures of the well-known Martian spiders and enigmatic Inca Metropolis in Mars’ south polar area. Have a look!
Read more: Mars has spidery channels at the South Pole
Read more: Winter wonderland on Mars