1st gentle for SKA telescope
Perhaps that radio waves – on the far finish of the electromagnetic spectrum – are longer than waves of seen gentle. That’s why radio astronomy advantages from very lengthy baselines … lengthy distances between coordinating antennas. The higher the space between antennas, the extra clearly the telescope can “see” in radio. For the reason that Nineteen Nineties, astronomers have been picturing and planning an especially huge radio telescope, the most important but! SKA stands for Sq. Kilometre Array. When its first stage is accomplished within the late 2020s, it’ll be the most important radio telescope on the planet. Its antennas are to be positioned at two websites, one in Australia and one in South Africa (and, finally, a number of different African international locations). The South Africa web site – referred to as Karoo – will host 197 dish-type antennas. On January 25, 2023, the SKA Observatory reported that its prototype telescope at Karoo – referred to as SKAMPI – achieved first light, with a picture of the southern sky in radio.
And that’s actual progress!
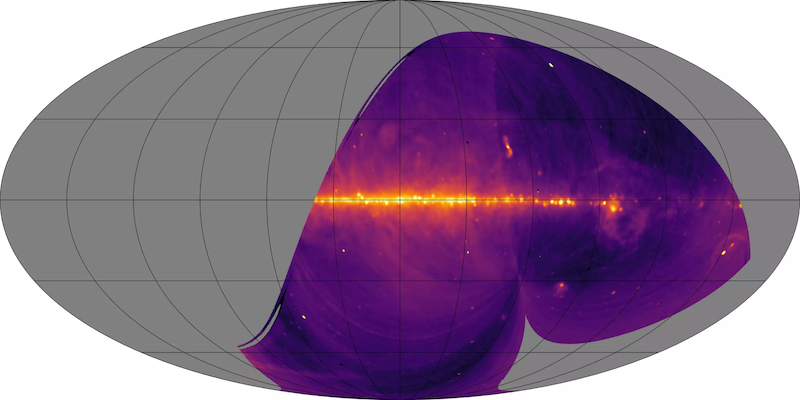
The uncalibrated picture above exhibits radio emission from a sweep of the heavens together with from the middle of our house galaxy the Milky Way and the radio supply on the Milky Way’s coronary heart know as Sgr A (seemingly associated to our galaxy’s central black hole), plus the brilliant radio galaxy Centaurus A, plus each of the Magellanic Clouds (giant and small), and some Milky Way star forming regions.
SKA’s South African prototype antenna – referred to as SKAMPI (an acronym of Sq. Kilometre Array and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy) – is itself a radio telescope. By itself, it’ll be taught of pulsars and radio emissions of our Milky Way galaxy. However that’s removed from its solely function. SKAMPI is a prototype for the 197-dish antenna array that can kind the South African portion of the SKA Observatory.
First gentle = first picture of a brand new instrument
A brand new astronomical instrument’s first use that leads to a picture is known as first light. This idea is just not as generally given to radio telescopes, as their development and first use is extra incremental, in contrast to, for instance, the Webb Area Telescope. The Webb’s first light image couldn’t be measured till it had arrived to its closing house in space. Additionally, a radio telescope observes within the radio section of the electromagnetic spectrum, not the optical gentle. However the one actual distinction is that radio waves are for much longer than the wavelengths of sunshine our eyes understand. (And on that notice, the Webb observes at infrared, only a bit longer wavelength than optical gentle).
Radio astronomy arrays get higher decision
In radio astronomy, combining many telescopes right into a so-called interferometric array, will increase the decision. Briefly, the bigger the telescope, the higher the decision, however sensible constraints makes it inconceivable to construct that enormous. Chinese language FAST is presently the world’s largest single-dish telescope at 500 m (1640 ft). An array has the decision of a digital telescope as giant because the longest distance between the antennas. Within the case of SKAO, this interprets to 1 telescope dish 150 km (93 miles) in diameter, as a substitute of the 15 m (50 ft) of every particular person antenna.
Three a long time of planning into fruition
The Sq. Kilometre Array thought was first conceived within the early Nineteen Nineties. It developed into an intergovernmental organisation in 2021 – the 2nd astronomical one after European Southern Observatory (ESO) – and presently consists of 9 member international locations. In December 2022, SKAO held groundbreaking ceremonies at each its observatory websites and began the development phase.
A primary gentle picture of the total observatory will seemingly be arduous to pinpoint, because the antennas will begin getting used as they’re constructed. However, if the science from precursor observatory MeerKAT, positioned on the similar web site, is a sign, we are able to seemingly count on some distinctive science to drop in as this radio facility retains rising in measurement. By the way in which, the 64 MeerKAT antennas will probably be integrated into the ultimate SKA, along with SKAMPI and its subsequent sibling antennas.
Two websites with totally different antennas
Why construct such a big observatory? What can we count on the radio to disclose that we are able to’t see in, say, infrared with the Webb? The 197 antennas in South Africa, referred to as the SKA-Mid, will observe from 350 MHz to fifteen.4 GHz in frequency. The Australian portion of the observatory, SKA-Low, will, because the identify implies, observe at decrease frequencies, from 50-350 MHz. Collectively, they’ll have a big accumulating space, rising the sensitivity by 10-100 occasions that of present observatories. The Australian telescopes are fairly totally different in construction and appears. They’re dipole antennas that largely resemble Christmas timber and there will probably be roughly 130,000 of them, collected in 512 stations.
Science objectives
When it comes to science, this interprets to with the ability to attain way back to to the epoch of reionization, when stars and galaxies began forming. Solely radio telescopes can measure impartial hydrogen, and, with the brand new means to measure faint alerts, can hint this constructing block of matter to earlier than stars ionized the gasoline within the early universe.
And there are various extra objectives. The telescopes will higher chart galaxy evolution, dark matter, and the way the energy of darkish vitality has grown over time. They may monitor gravitational waves by way of observations of fluctuations in pulsar radio bursts. SETI scientists will pay attention for faint alerts indicating superior life, whereas different exoplanet scientists will scrutinize delivery of stars and planets.
Different mysteries we need to be taught (a lot) extra about embody black holes and quick radio bursts. To not neglect extra “native” astronomy the place, for instance, the telescopes hint impartial hydrogen gasoline in our personal galaxy (there’s much more to find at house as properly!). However possibly probably the most thrilling discoveries to come back are those we have no idea about but. They are often anticipated, as a result of for each new instrument that comes into use, there have been surprises.
Backside line: The SKAMPI prototype has delivered its first gentle picture of the southern sky. The telescope will probably be included in a big 197-dish radio observatory in South Africa, as a part of the Sq. Kilometre Array Observatory.