The universe is large, as Douglas Adams would say.
Probably the most distant mild we will see is the cosmic microwave background (CMB), which has taken greater than 13 billion years to achieve us. This marks the sting of the observable universe, and whilst you may assume which means the universe is 26 billion light-years throughout, because of cosmic expansion it’s now nearer to 46 billion light-years throughout. By any measure, that is fairly darn large. However most cosmologists assume the universe is far bigger than our observable nook of it. That what we will see is a small a part of an unimaginably huge, if not infinite creation. Nonetheless, a brand new paper revealed on the arXiv preprint server argues that the observable universe is usually all there’s.
In different phrases, on a cosmic scale, the universe is sort of small.
There are a number of the explanation why cosmologists assume the universe is massive. One is the distribution of galaxy clusters. If the universe did not lengthen past what we see, essentially the most distant galaxies would really feel a gravitational pull towards our area of the cosmos, however not away from us, resulting in asymmetrical clustering. Since galaxies cluster at across the similar scale all through the seen universe. In different phrases, the observable universe is homogenous and isotropic.
A second level is that spacetime is flat. If spacetime weren’t flat, our view of distant galaxies could be distorted, making them seem a lot bigger or smaller than they really are. Distant galaxies do seem barely bigger as a consequence of cosmic enlargement, however not in a method that suggests an total curvature to spacetime. Primarily based on the bounds of our observations, the flatness of the cosmos implies it’s a minimum of 400 occasions bigger than the observable universe.
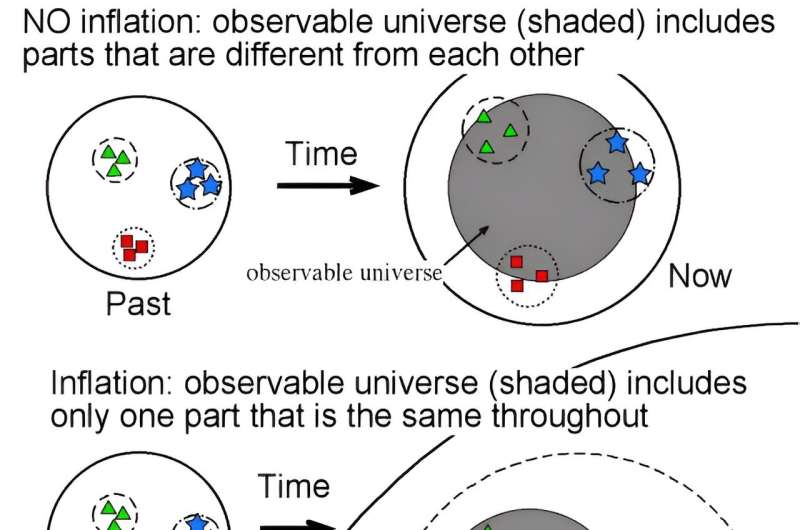
Then there’s the truth that the cosmic microwave background is nearly an ideal blackbody. There are small fluctuations in its temperature, however it’s way more uniform than it ought to be. To account for this, astronomers have proposed a interval of super enlargement simply after the Huge Bang, often called early cosmic inflation. We have now not noticed any direct proof of it, however the mannequin solves so many cosmological issues that it is extensively accepted. If the mannequin is correct, then the universe is on the order of 1026 occasions bigger than the observable universe.
So given all of this theoretical and observational proof, how may anybody argue that the universe is small? It has to do with string theory and the swamplands.
Though string idea is commonly offered as a bodily idea, it is really a group of mathematical strategies. It may be used within the growth of advanced bodily fashions, however it might probably additionally simply be arithmetic for its personal sake. One of many issues with connecting the arithmetic of string idea to bodily fashions is that the results would solely be seen in essentially the most excessive conditions, and we do not have sufficient observational knowledge to rule out various models. Nonetheless, some string idea fashions seem way more promising than others. For instance, some fashions are appropriate with quantum gravity, and others usually are not. So typically theorists will outline a “swampland” of theories that are not promising.
While you separate the promising theoretical lands from the swamp, what you might be left with are theories the place early cosmic inflation is not an possibility. Many of the inflationary string idea fashions are within the swampland. This leads one to ask whether or not you possibly can assemble a mannequin cosmology that matches statement with out early inflation. Which brings us to this new examine.
One technique to get round early cosmic inflation is to have a look at higher-dimensional constructions. Traditional basic relativity depends upon 4 bodily dimensions, three of space and certainly one of time, or 3+1. Mathematically you possibly can think about a 3+2 universe or 4+1, the place the worldwide construction will be embedded into an efficient 3+1 construction. It is a frequent strategy in string idea because it is not restricted to the usual construction of basic relativity.
The authors display that underneath simply the proper circumstances, you possibly can assemble a higher-dimensional construction inside string idea that matches statement and avoids the swampland. Primarily based on their toy fashions, the universe might solely be 100 or a thousand occasions bigger than the noticed universe. Nonetheless large, however downright tiny when in comparison with the early inflation fashions.
All of that is fairly speculative, however in a method so is early cosmic inflation. If early cosmic inflation is true, we should always have the ability to observe its impact by means of gravitational waves within the considerably close to future. If that fails, it could be value wanting extra carefully at string idea fashions that preserve us out of the theoretical swamp.
Extra data:
Jean-Luc Lehners et al, A small Universe, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2309.03272
Journal data:
arXiv
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
The case for a small universe (2023, September 11)
retrieved 12 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-case-small-universe.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

