Researchers working within the Marsquake Service at ETH Zurich have been analyzing the measurements made by the NASA InSight mission’s seismometer on one in all our neighboring planets.
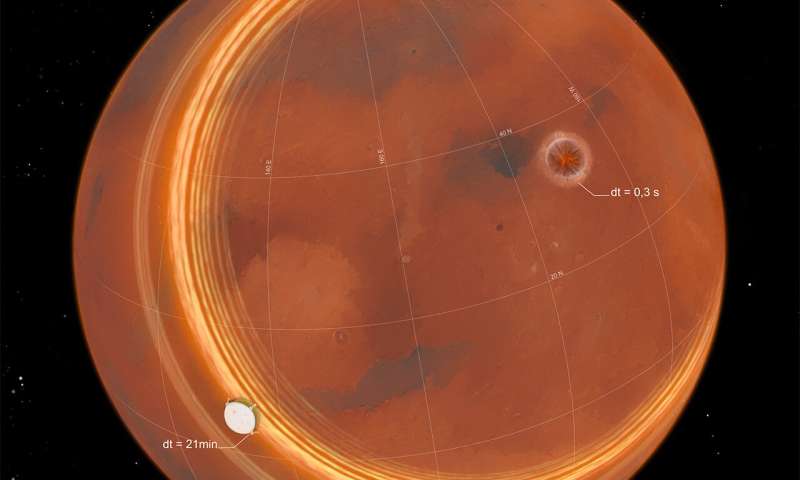
For nearly three years, the one seismic waves it detected on Mars had been ones that propagated from the respective quake’s focus, or hypocenter, by way of the depths of the planet. Nonetheless, the researchers had been hoping all alongside for an occasion that will additionally generate waves touring alongside the planet’s surface. Their wait was lastly rewarded on December24, 2021, when a meteorite impact on Mars yielded the kind of floor waves that they had been lengthy anticipating.
Atypical traits within the quake readings led the researchers to suspect its supply was close to the floor, in order that they contacted colleagues who had been working with a probe orbiting Mars. And certainly, pictures taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in late December 2021 confirmed a big influence crater about 3,500 kilometers from InSight.
“The placement was a great match with our estimates for the supply of the quake,” says Doyeon Kim, a geophysicist and senior analysis scientist at ETH Zurich’s Institute of Geophysics. Kim is the lead writer of a examine that has simply been printed within the journal Science. The researchers had been additionally capable of pinpoint a meteorite influence at slightly below 7,500 kilometers (about 5,000 miles) from InSight because the supply of a second atypical quake.
As a result of the hypocenter of every earthquake was on the floor, they generated not solely seismic physique waves much like beforehand recorded marsquakes through which the hypocenters had been at larger depth, but in addition waves that propagated alongside the planet’s floor. “That is the first-time seismic floor waves have been noticed on a planet apart from Earth. Not even the Apollo missions to the Moon managed it,” Kim says.
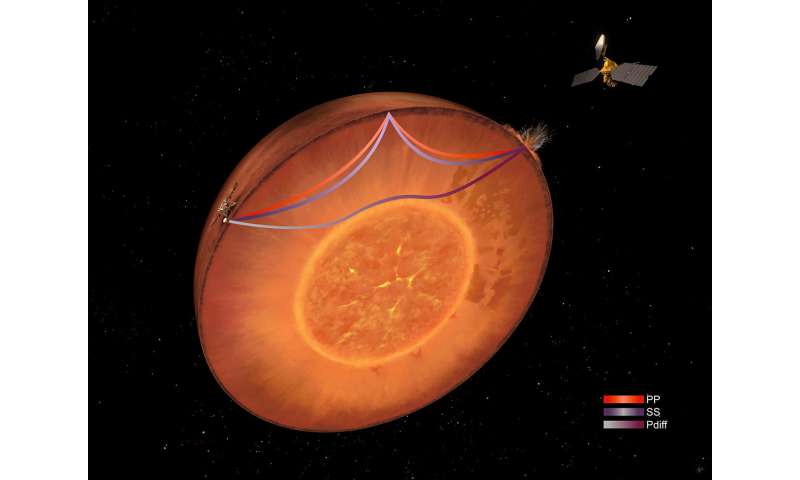
What makes the seismic floor waves so essential to researchers is that they supply details about the construction of the Martian crust. Seismic physique waves, which journey by way of the planet’s inside throughout a quake, have up to now offered insights into Mars’s core and mantle, however have revealed little in regards to the crust away from the lander itself.
A shocking end result
“Till now, our data of the Martian crust has been primarily based on solely a single level measurement underneath the InSight lander,” Kim explains. The results of the floor wave evaluation shocked him. On common, the Martian crust between the influence websites and InSight’s seismometer has a really uniform construction and excessive density. Straight beneath the lander, nonetheless, the researchers had beforehand detected three layers of crust that implied a decrease density.
The brand new findings are exceptional as a result of a planet’s crust offers essential clues about how that planet shaped and developed. For the reason that crust itself is the results of early dynamic processes within the mantle and subsequent magmatic processes, it could actually inform us about circumstances billions of years in the past and the timeline of impacts, which had been significantly widespread in Mars’ early days.
Kim explains how the brand new measurement was made: “The pace at which floor waves propagate is determined by their frequency, which in flip is determined by their depth.” By measuring adjustments in velocity within the seismic data throughout totally different frequencies, it’s attainable to deduce how the rate adjustments at totally different depths, as a result of every frequency is delicate to totally different depths. This offers the premise for estimating the common density of the rock, as a result of the seismic velocity additionally is determined by the elastic properties of the fabric by way of which the waves journey. This information allowed the researchers to find out the construction of the crust at depths of between roughly 5 and 30 kilometers beneath the floor of Mars.
Better seismic velocity defined
Why then was the common pace of the floor waves just lately noticed significantly greater than could be anticipated primarily based on the sooner level measurement underneath the Mars InSight lander? Is that this primarily as a result of floor rock, or are different mechanisms in play? Typically, volcanic rocks are inclined to exhibit greater seismic velocities than sedimentary rocks. Additionally, the paths between the 2 meteorite impacts and the measurement web site go by way of one of many largest volcanic areas in Mars’ northern hemisphere.
Lava flows and the closure of pore areas from warmth created by volcanic processes, can improve the rate of seismic waves. “However, the crustal construction beneath InSight’s touchdown web site might have been shaped in a novel method, maybe when materials was ejected throughout a big meteoritic influence greater than three billion years in the past. That might imply the construction of the crust underneath the lander might be not consultant of the overall construction of the Martian crust,” Kim explains.
-
Credit score: IPGP / CNES / N. Starter
-
Credit score: © IPGP – CNES – N. Starter
-

Credit score: © IPGP -CNES – N. Starter
Fixing the thriller of the Mars dichotomy
The brand new analysis might additionally assist remedy a centuries-old thriller. Ever because the first telescopes had been pointed at Mars, it has been identified {that a} sharp distinction exists between the planet’s southern and northern hemispheres. Whereas the dominant function of the southern hemisphere is a plateau lined by meteorite craters, the northern hemisphere consists principally of flat, volcanic lowlands that will have been lined by oceans within the planet’s early historical past. This division into southern highlands and northern lowlands known as the Mars dichotomy.
“As issues stand, we do not but have a typically accepted rationalization for the dichotomy as a result of we have by no means been capable of see the planet’s deep construction,” says Domenico Giardini, ETH Zurich Professor of Seismology and Geodynamics. “However now we’re starting to uncover this.” The preliminary outcomes seem to disprove one of many widespread theories for the Mars dichotomy: the crusts within the north and within the south are in all probability not composed of various supplies, as has usually been assumed, and their construction could also be surprisingly comparable at related depths.
An extended await the wave
The ETH Zurich researchers expect additional outcomes quickly. In Could 2022, InSight noticed the biggest marsquake so far, with a magnitude of 5. It additionally recorded seismic floor waves generated by this shallow occasion. This occurred simply in time, because the InSight mission will quickly be coming to an finish now that the lander’s solar panels are lined in dust, and it’s working out of energy. An preliminary evaluation of the information confirms findings that the researchers obtained from the opposite two meteorite impacts.
“It is loopy. We might been ready for thus lengthy for these waves, and now, simply months after the meteorite impacts, we noticed this huge quake that produced extraordinarily wealthy floor waves. These permit us to see even deeper into the crust, to a depth of about 90 kilometers,” says Kim.
L. V. Posiolova, Largest current influence craters on Mars: Orbital imaging and floor seismic co-investigation, Science (2022). DOI: 10.1126/science.abq7704. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abq7704
Quotation:
Two main meteorite impacts make clear the inside of Mars (2022, October 27)
retrieved 27 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-major-meteorite-impacts-interior-mars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




