Two galaxies within the early universe, which comprise extraordinarily productive star factories, have been studied by a group of scientists led by Chalmers College of Expertise in Sweden. Utilizing highly effective telescopes to separate the galaxies’ gentle into particular person colours, the scientists have been amazed to find gentle from many alternative molecules—greater than ever earlier than seen at such distances. Research like this might revolutionize our understanding of the lives of probably the most lively galaxies when the universe was younger, the researchers imagine.
When the universe was younger, galaxies have been very totally different from right now’s stately spirals, that are filled with gently shining suns and colourful gasoline clouds. New stars have been being born at charges lots of of instances quicker than in right now’s universe.
Most of this, nonetheless, was hidden behind thick layers of dust, making it a problem for scientists to find these star factories’ secrets and techniques—till now. By finding out probably the most distant galaxies seen with highly effective telescopes, astronomers can get glimpses of how these factories have managed to create so many stars.
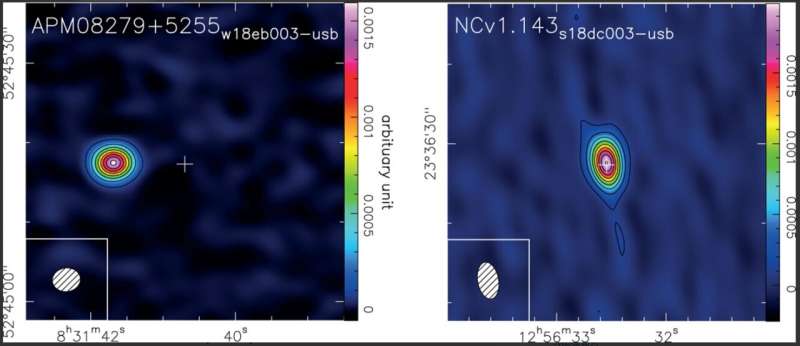
In a brand new study, revealed within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, a group of scientists led by Chalmers astronomer Chentao Yang, used the telescopes of NOEMA (NOrthern Prolonged Millimeter Array) in France to search out out extra about how these early star factories managed to create so many stars. Yang and his colleagues measured gentle from two luminous galaxies within the early universe—considered one of them categorized as a quasar, and each with excessive charges of star formation.
“We knew these galaxies have been prodigious star factories, maybe among the many largest the universe has ever seen. To have the ability to learn how they work, we measured their gentle at wavelengths round one millimeter, hoping to gather new clues,” says Chentao Yang.
Dramatic chemistry within the distant galaxies excites the astronomers
The measurements proved to achieve success past the scientists’ expectations. Within the gentle they recorded from each galaxies, they recognized traces of many alternative sorts of molecules. From deep inside these galaxies, gentle is emitted in many alternative wavelengths from the clouds of gasoline and dust the place new stars are born.
“It is an incredible explosion of colour, in shades that the human eye cannot see. However by combining our observations with our data of physics and chemistry, we will perceive what the colours imply and see what variations there are between totally different galaxies,” explains Sergio Martín, an astronomer at ESO and Joint ALMA Observatory, Chile, and member of the analysis group.
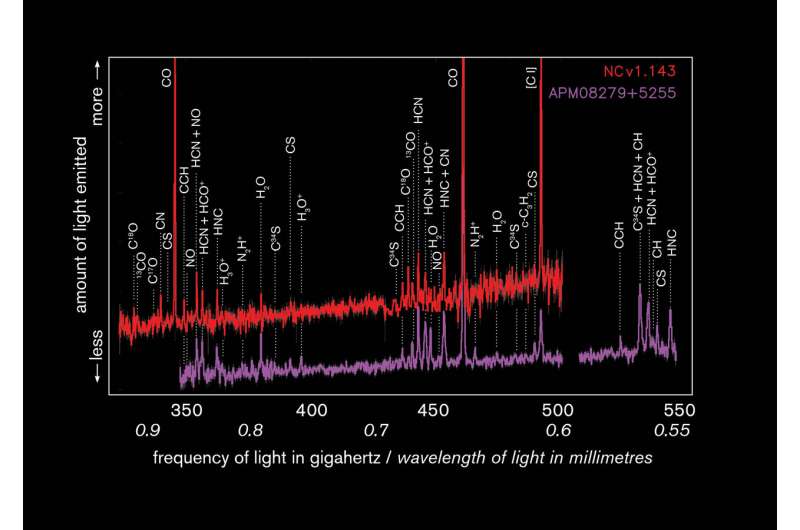
By analyzing every galaxy’s spectrum—the person colours of their gentle—the scientists have been capable of establish 13 molecules, a number of of which have by no means been seen earlier than in such distant galaxies. Every molecule provides totally different clues concerning the temperature, stress, and density within the space between the celebrities and about how starlight, radiation, and matter work together—offering key new info on the bodily and chemical situations in these galaxies.
“Deciphering the indicators is a problem. We’re seeing a part of the electromagnetic spectrum that’s onerous to look at in close by galaxies. However because of the growth of the universe, the sunshine from distant galaxies like these is shifted to longer wavelengths that we will see with radio telescopes observing within the sub-millimeter,” says Chentao Yang.

Extra like a neon-lit metropolis than an evening below the celebrities
The 2 galaxies studied by the group are so distant that their gentle takes nearly 13 billion years to succeed in us.
“Taking a look at these galaxies is much less like an evening below the celebrities and extra like seeing a metropolis lit with neon lights,” says Susanne Aalto, Chalmers astronomer, and group member.
Astronomers are used to taking footage of our galaxy’s star factories, just like the Orion Nebula and the Carina Nebula, she explains.
“In these two distant galaxies, we’re as a substitute seeing star factories which are larger, brighter, filled with dust, and totally different in some ways. The Orion and Carina nebulae are lit up because of ultraviolet gentle from scorching, new child stars. In these two distant galaxies, ultraviolet gentle cannot get previous the layers of dust. A lot of the illumination is as a substitute because of cosmic rays—excessive power particles that may be created by exploding stars or near a supermassive black hole,” says Susanne Aalto.
The galaxies within the early universe can now inform their tales
Whereas galaxies like these two are uncommon, the scientists have plans to check extra of them, utilizing each NOEMA and its even larger sister telescope, ALMA (the Atacama Giant Millimeter/Submillimeter Array) in Chile. Each telescopes are delicate to gentle with wavelengths of round one millimeter.
“Our outcomes present how NOEMA, with its broadband receivers and highly effective correlator pc, has opened up new alternatives for finding out excessive galaxies like these within the northern sky. From the southern hemisphere, ALMA’s deliberate wideband sensitivity upgrades will supply much more thrilling prospects. Probably the most outstanding galaxies within the early universe are lastly capable of inform their tales by means of their molecules,” says Pierre Cox, an astronomer at CNRS and Sorbonne Université, France.
Extra concerning the analysis outcomes:
Over 100 totally different molecules have been detected in interstellar space. On this examine, the astronomers recognized molecules of carbon monoxide (CO), the cyano radical (CN), the ethynyl radical (CCH), hydrogen cyanide (HCN), the formyl cation (HCO+), hydrogen isocyanide (HNC), carbon monosulfide (CS), water (H2O), the hydronium ion (H3O+), nitric oxide (NO), diazenylium (N2H+), the methylidyne radical (CH), and cyclopropenylidene (c-C3H2). A number of of those (CH, CCH, c-C3H2, N2H+, and H3O+) have by no means been seen earlier than at such massive distances.
The 2 galaxies within the examine have catalog numbers APM 08279+5255 and NCv1.143. Earlier research have proven that they’re so distant that their gentle has been touring in the direction of us for almost 13 billion years, akin to redshifts of three.911 and three.565, respectively. Redshift implies that the growth of the universe stretches the sunshine from distant galaxies to longer wavelengths, which will be noticed with radio telescopes.
Regardless of their distance, the galaxies shine brightly at radio wavelengths. Their indicators are amplified because of clusters of different galaxies that lie alongside the sunshine’s path—an impact often known as gravitational lensing. One of many galaxies, APM 08279+5255, can be a quasar, a galaxy whose middle glows brightly all the way in which from radio waves to X-rays as a result of materials swirling round a supermassive black hole. NCv1.143 might also comprise a central black hole.
Extra info:
Chentao Yang et al, SUNRISE: The wealthy molecular stock of high-redshift dusty galaxies revealed by broadband spectral line surveys, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2023). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202347610
Supplied by
Chalmers University of Technology
Quotation:
Sudden chemistry reveals cosmic star factories’ secrets and techniques (2023, December 14)
retrieved 15 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-unexpected-chemistry-reveals-cosmic-star.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




