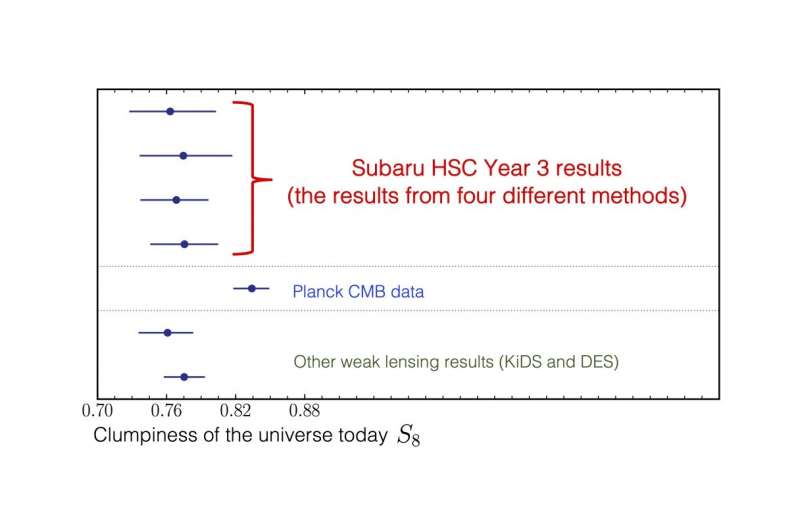
A global staff of astrophysicists and cosmologists at numerous institutes together with the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Arithmetic of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) have submitted a set of 5 papers, measuring a price for the “clumpiness” of the universe’s dark matter, recognized to cosmologists as S8, of 0.76, which aligns with values that different gravitational lensing surveys have present in wanting on the comparatively current universe, but it surely doesn’t align with the worth of 0.83 derived from the cosmic microwave background, which dates again to the universe’s origins when the universe was about 380,000 years previous. Their outcomes had been uploaded to the arXiv pre-print server as a set of 5 papers on April 3.
The hole between these two values is small, however as increasingly more research verify every of the 2 values, it does not seem like unintended. The chances are that there is some as-yet unrecognized error or mistake in certainly one of these two measurements or the usual cosmological mannequin is incomplete in some fascinating manner.
Darkish power and dark matter make up 95% of our universe we see at this time, however we perceive little or no about what they really are and the way they’ve developed over the historical past of the universe. Clumps of dark matter distort the sunshine of distant galaxies via weak gravitational lensing, a phenomenon predicted by Einstein’s basic concept of relativity.
“This distortion is a extremely, actually small impact. The form of a single galaxy is distorted by an imperceptible quantity. However combining the measurements for hundreds of thousands of galaxies permits one to measure the distortion with fairly excessive precision,” mentioned Kavli IPMU Professor Masahiro Takada.
The standard model is outlined by solely a handful of numbers: the growth price of the universe, a measure of how clumpy the dark matter is (S8), the relative contributions of the constituents of the universe (matter, dark matter, and dark energy), the general density of the universe, and a technical amount describing how the clumpiness of the universe on giant scales pertains to that on small scales.
Cosmologists are keen to check this mannequin by constraining these numbers in numerous methods, comparable to by observing the fluctuations within the cosmic microwave background, modeling the growth historical past of the universe, or measuring the clumpiness of the universe within the comparatively current previous.
A staff led by astronomers from Kavli IPMU, the College of Tokyo, Nagoya College, Princeton College, and astronomical communities of Japan and Taiwan, have spent the previous yr teasing out the secrets and techniques of this most elusive materials, dark matter, utilizing subtle pc simulations and knowledge from the primary three years of the Hyper Suprime-Cam survey. The observations from this survey used one of the vital highly effective astronomical cameras on this planet, the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) mounted on the Subaru Telescope on the summit of Maunakea in Hawaii.
Hiding and uncovering the information
“Scientists are human beings, they usually do have preferences. Some would love to actually discover one thing essentially new, whereas others would possibly really feel snug in the event that they discover outcomes that look according to foreseen outcomes. Scientists have grow to be self-aware sufficient to know that they may bias themselves, regardless of how cautious they’re, until they perform their evaluation with out permitting themselves to know the outcomes till the top,” mentioned Nagoya College Kobayashi-Maskawa Institute for the Origin of Particles and the Universe (KMI) Affiliate Professor Hironao Miyatake.
To guard the outcomes from such biases, the HSC staff hid their outcomes from themselves and their colleagues for months, successfully performing a “blinded evaluation.” The staff even added an additional obfuscating layer: they ran their analyses on three totally different galactic catalogs, one actual and two faux with numerical values offset by random values. The evaluation staff did not know which ones was actual, so even when somebody did unintentionally see the values, the staff would not know if the outcomes had been based mostly on the true catalog or not.
The staff spent a yr on the blind evaluation. On December 3, 2022, the staff gathered collectively on Zoom—one Saturday morning in Japan, Friday night in Princeton—for the “unblinding.” The staff unveiled the information, and ran their plots, instantly they noticed it was nice in response to Takada.
“Blinded evaluation means you can’t take a peak on the outcomes whereas working the evaluation, which was extraordinarily demanding, however as quickly I noticed the ultimate end result, all of that nervousness flew out of the window,” mentioned Kavli IPMU graduate scholar Sunao Sugiyama.
An enormous survey with the world’s largest telescope digital camera
HSC is the most important digital camera on a telescope of its measurement on this planet. The survey that the analysis staff used covers about 420 sq. levels of the sky, concerning the equal of two,000 full moons. It isn’t a single contiguous chunk of sky, however cut up amongst six totally different items, every concerning the measurement of an individual’s outstretched fist. The 25 million galaxies the researchers surveyed are so distant that as a substitute of seeing these galaxies as they’re at this time, the HSC recorded how they had been billions of years in the past.
Every of those galaxies glows with the fires of tens of billions of suns, however as a result of they’re so far-off, they’re extraordinarily faint, as a lot as 25 million instances fainter than the faintest stars we are able to see with the bare eye.
Extra data:
Hironao Miyatake et al, Hyper Suprime-Cam 12 months 3 Outcomes: Cosmology from Galaxy Clustering and Weak Lensing with HSC and SDSS utilizing the Emulator Primarily based Halo Mannequin. arxiv.org/abs/2304.00704
Surhud Extra et al, Hyper Suprime-Cam 12 months 3 Outcomes: Measurements of Clustering of SDSS-BOSS Galaxies, Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing and Cosmic Shear. arxiv.org/abs/2304.00703
Sunao Sugiyama et al, Hyper Suprime-Cam 12 months 3 Outcomes: Cosmology from Galaxy Clustering and Weak Lensing with HSC and SDSS utilizing the Minimal Bias Mannequin. arxiv.org/abs/2304.00705
Roohi Dalal et al, Hyper Suprime-Cam 12 months 3 Outcomes: Cosmology from Cosmic Shear Energy Spectra. arxiv.org/abs/2304.00701
Xiangchong Li et al, Hyper Suprime-Cam 12 months 3 Outcomes: Cosmology from Cosmic Shear Two-point Correlation Features. arxiv.org/abs/2304.00702
Journal data:
arXiv
Offered by
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Arithmetic of the Universe (Kavli IPMU)
Quotation:
Utilizing dark matter distribution to check the cosmological mannequin (2023, April 4)
retrieved 4 April 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-04-dark-cosmological.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

