When the sun goes down and lights go on—or not—a large number of information may be gathered by satellite from the evening sky, giving insights into the dynamic human actions taking place on the floor.
With remote sensing, issues like land use adjustments, city improvement, and forest administration may be reliably and precisely measured by daylight. At nighttime, we are able to collect totally different varieties of information. A technique to do that is with NASA’s Black Marble, a product suite that scans the sky every evening and is highly effective sufficient to sense all types of lights on the floor of Earth, from vacation lights to a single 12,000-lumen flashlight, from space.
Nonetheless, the information gathered at evening may be tough to investigate says Division of Pure Assets and the Setting Assistant Professor and Director of the World Environmental Distant Sensing (GERS) Laboratory Zhe Zhu. He explains nighttime satellite data may be influenced by many components, which ends up in a big diploma of temporal variation, even for the well-calibrated NASA Black Marble knowledge.
“The primary time I checked out a time collection of the information, I felt prefer it was nearly not possible to make use of,” says Zhu.
A crew of researchers from GERS together with Zhu and NRE Ph.D. scholar Tian Li, together with researchers from NASA and the College of Maryland Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Middle has developed a technique that’s able to offering day by day international reasonable decision nighttime gentle change maps. The outcomes are revealed within the journal Distant Sensing of Setting.
Although Black Marble already reduces fairly a little bit of exterior noise, Zhu and Li sought a method to additional scale back the fluctuations and make the information even higher.
Many components trigger temporal variation within the sign that reaches the sensors. Zhu provides the instance of moonlight, which impacts how a lot illumination the sensors obtain all through the moon’s phases and motion throughout the night sky. Some objects can distort the reflection of moonlight, like buildings, bushes, or different buildings. Atmospheric situations could cause additional sign deviations, with issues like aerosols or haze.
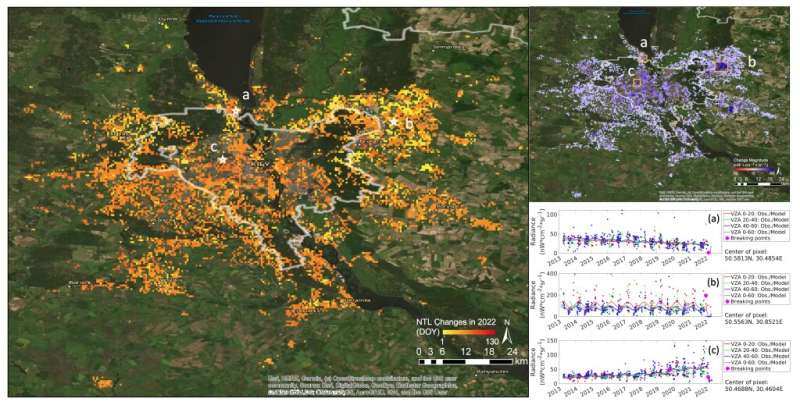
Zhu says they realized day by day fluctuations is also attributable to the view path and the unreal illumination supply; for instance, if the satellite is wanting from straight overhead at a tall constructing, it could not see the emission of sunshine from home windows, or in additional rural areas, there could also be bushes obstructing the view from the edges.
To beat a few of these obstacles, Zhu says three-dimensional digital fashions might be integrated to account for constructing peak or if there are bushes round to forecast the affect of those illumination variations, however it will be almost not possible to account for every little thing, similar to the peak of each single tree or constructing. As an alternative, Li discovered a special manner, by incorporating a number of viewing angles for particular person pixels, organizing them into teams, after which basing the observations from someplace in between.
“Tian spent a couple of years on this, and she or he found out a method to considerably scale back this knowledge variation,” says Zhu. “We created an algorithm known as VZA-COLD which stands for Viewing Zenith Angle stratified COntinuous monitoring of Land Disturbance.”
“We utilized totally different units of fashions to explain all the nighttime gentle knowledge time collection and the information subsets of various viewing zenith angle intervals. On this manner, we mitigated the viewing path and native geometry variations with out the necessity for three-dimension knowledge. A change shall be captured whether it is predicted by any of the viewing angle interval fashions.” says Li.
With VZA-COLD, the researchers might use Black Marble knowledge to trace human activity and conduct adjustments constantly, on a worldwide scale. Zhu says this tremendously lowered the variation within the sign and inside every group they had been capable of detect change with excessive accuracy and in a well timed method.
The researchers can receive the change time, the change magnitude, and the change path. Zhu says that is necessary as a result of, at a sure view angle, change will not be seen, however is seen at one other interval of view angles.
“This makes the knowledge helpful, solves the problem of temporal variation, and supplies further angular change data for the unreal lights.”
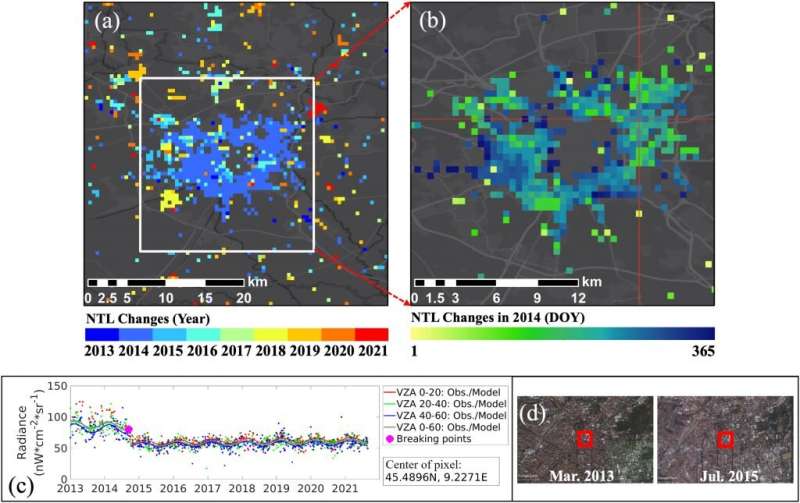
Previously, researchers would sometimes analyze a month’s value of information to create composite knowledge units. This evaluation is restricted and can’t present correct detection of short-term nighttime gentle adjustments. For instance, with latest hurricanes, Black Marble can now monitor nighttime gentle adjustments because it happens, rapidly pinpointing the place energy outages are quickly after the storm passes.
Different purposes vary from monitoring wars, similar to these in Ukraine and Syria, the place close to real-time data might support in humanitarian efforts.
Monitoring urbanization processes, migration, energy grid variations, gasoline flares, unlawful fishing operations, wildfires, and even the transition to LED lights are different purposes that this know-how can be utilized to observe. The probabilities are huge, as Zhu factors out, since human actions are so intently tied to how we use vitality, and this can inevitably present up within the satellite-measured nighttime lights.
Zhu says that nighttime gentle change can present totally different insights into individuals’s exercise and conduct, like public gatherings and holidays, than daytime observations. One instance he cites is the Olympic stadium in Seoul, South Korea.
“We will view when the constructing was began to be constructed and when the roof was full, then after the Olympics, it’s much less used,” he says. “That is an instance of transitions in development exercise phases and utilization exercise that we aren’t capable of monitor in the course of the daytime. I feel that is going to be game-changing for lots of issues.”
“We’re excited to see the patterns of all these several types of man-made gentle adjustments at evening previously decade, this supplies us distinctive alternatives to know the human-environment system over the globe,” says Li.
“We at the moment are working with NASA to create a worldwide product utilizing this algorithm that shall be launched in 2023. It will likely be up to date yearly for each Earth’s land floor location. There are additionally plans to get the near-real-time functionality embedded within the international product,” says Zhu.
Tian Li et al, Steady monitoring of nighttime gentle adjustments primarily based on day by day NASA’s Black Marble product suite, Distant Sensing of Setting (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2022.113269
Quotation:
Viewing Earth from space at evening: Monitoring our altering black marble (2022, October 12)
retrieved 12 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-viewing-earth-space-night-tracking.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




