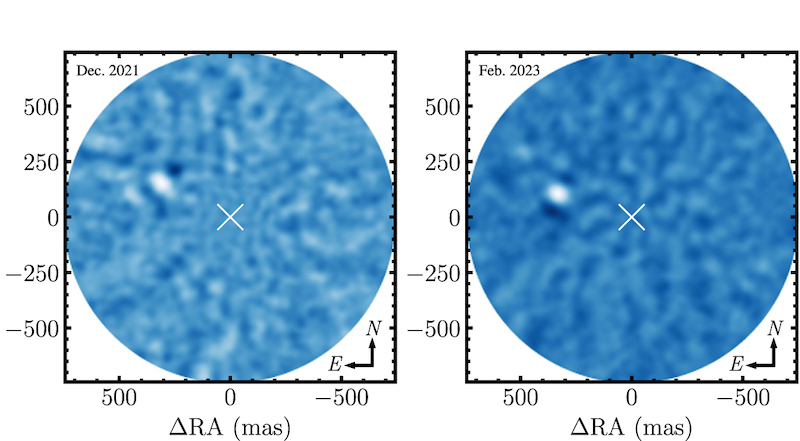
The variety of immediately imaged exoplanets could also be comparatively small in comparison with different detection strategies, however that’s beginning to change. Final week, astronomers utilizing the Keck II telescope on the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii released new photos of one of many lowest-mass exoplanets but to be seen this manner. The planet, AF Lep b, orbits a younger sun-like star 87.5 light-years away.
Kyle Franson on the College of Texas at Austin (UT Austin) led the brand new research. Franson and his colleagues published the peer-reviewed leads to The Astrophysical Journal Letters on June 22, 2023.
Meet exoplanet AF Lep b
AF Lep b is a gas giant planet, about thrice the mass of Jupiter. Its orbit round its star can also be much like these of the large planets in our personal solar system. It’s, nonetheless, a lot youthful. Its host star, AF Leporis, is simply about 24 million years previous. Because the paper notes, it nonetheless resides throughout the circumstellar debris disk surrounding the younger star.
Regardless of its dimension and mass, the planet is likely one of the lowest-mass exoplanets ever imaged immediately.
The astronomers initially found AF Lep b utilizing the astrometry method. With this method, astronomers monitor the motion of a star over a few years. The method could be very exact, detecting even tiny actions of the star. It’s one in all five techniques used to search out exoplanets.
The researchers started taking astrometric photos of the star again in 2021, persevering with till this yr. And, positive sufficient, they discovered a planet! Franson said:
After we processed the observations utilizing the Keck II telescope in actual time to fastidiously take away the glare of the star, the planet instantly popped out and have become more and more obvious the longer we noticed.
As well as, two different analysis groups imaged the planet since 2021.
A brand new device for exoplanet discovery
The invention is the primary time that astronomers have discovered a younger planet like AF Lep b utilizing astrometry. Thus far, this technique has discovered far fewer planets than the opposite 4 strategies. As co-author Brendan Bowler at UT Austin famous:
That is the primary time this technique has been used to discover a big planet orbiting a younger analog of the sun. This opens the door to utilizing this method as a brand new device for exoplanet discovery.
Astronomers had beforehand noticed AF Leporis with the European House Company’s Hipparcos and Gaia satellites. These observations, over 25 years, advised that the host star might need a planet. Now, the brand new observations have confirmed it.
Astrometry measures a star’s position relative to different stars. The tiny adjustments in place – a “wobble” of the star – are attributable to the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet. This system shouldn’t be confused with the radial velocity method, nonetheless, which additionally measure’s a star’s wobble.
Direct photos of AF Lep b
After the preliminary detection, the researchers used the Keck Observatory’s adaptive optics system to immediately picture the planet. Two technological advances made this attainable. The optics appropriate for fluctuations attributable to turbulence in Earth’s environment. As well as, the Keck II Telescope’s Close to-Infrared Digital camera 2 (NIRC2) Vector Vortex Coronagraph suppresses mild from the host star. This permits the planet to be seen extra clearly (even when nonetheless only a dot!). This was particularly wanted within the case of AF Lep b, since it’s 10,000 occasions fainter than its star. It additionally orbits about eight occasions as removed from its star as Earth does from the sun. Franson stated:
Imaging planets is difficult. We solely have about 15 examples, and we expect this new ‘dynamically knowledgeable’ method made attainable by the Keck II telescope and NIRC2 adaptive optics imaging shall be far more environment friendly in comparison with blind surveys which were carried out for the previous twenty years.
AF Lep b can also be a great goal for NASA’s Webb House Telescope and different telescopes. Bowler stated:
This shall be a wonderful goal to additional characterize with the James Webb House Telescope and the following era of enormous ground-based telescopes just like the Giant Magellan Telescope and the Thirty Meter Telescope. We’re already planning extra delicate follow-up efforts at longer wavelengths to check the bodily properties and atmospheric chemistry of this planet.
Backside line: Astronomers utilizing the Keck II telescope in Hawaii have obtained new direct photos of a younger exoplanet thrice the mass of Jupiter and 87.5 light-years away.