Messier 52 (NGC 7654) and NGC 7789 are two of a trio of nice open clusters present in Cassiopeia (the opposite being NGC 457, the ET, or Owl Cluster), a constellation of the far northern sky that may lay declare to the title ‘the house of open clusters’. Messier 52, after Messier 11 (the Wild Duck Cluster) in Scutum, is maybe the richest and most dense open cluster within the Messier catalogue, internet hosting round 6,000 stars. NGC 7789 is a cluster stunner, straightforward to brush up in a pair of binoculars and its myriad stars majestically grace the sector of view of view of a moderate- to large-aperture telescope. All through the autumn each are properly positioned and simple to search out.
How one can observe
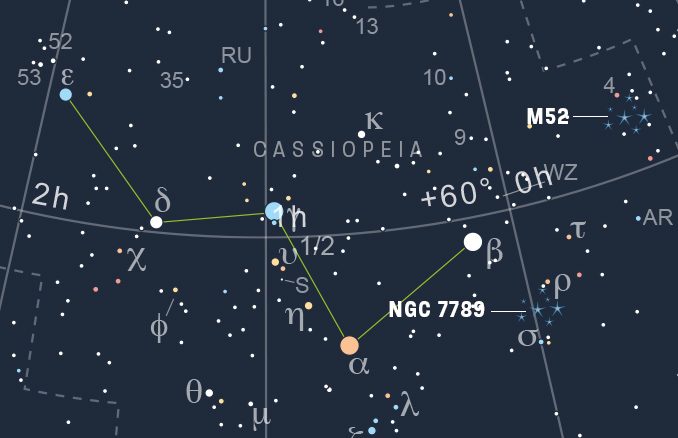
As Cassiopeia wheels round Polaris (the Pole Star), its location is fantastically marked by its acquainted ‘W-shaped’ asterism of 5 vivid stars. On the alternative aspect of the Polaris is one other nice asterism inside a fantastic constellation, the Plough in Ursa Main. Cassiopeia’s ‘W’ spans 13 levels throughout its main axis (a fist held at arm’s size covers round 10 levels throughout your knuckles), from magnitude +2.27 Caph (beta [β] Cassiopeiae (Cas) within the west to magnitude +3.38 Segin (epsilon [ε] Cas) within the east.
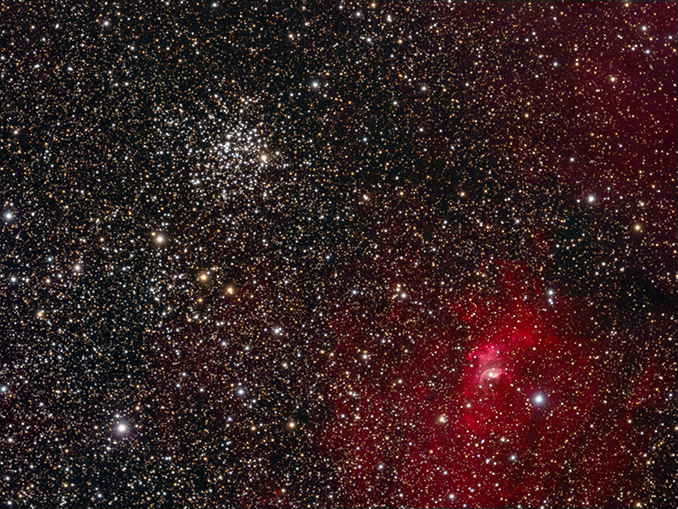

Messier 52: A bubble lives close by
In late October, dusk is at about 6pm BST from London. Cassiopeia lies properly up within the north-eastern sky (it’s circumpolar [always above the horizon] from the UK). Messier 52 culminates excessive overhead at about 9pm BST.
Messier 52 is kind of straightforward to trace down. First, find the 2 brightest and most westerly stars within the ‘W’, magnitude +2.23 Schedar (alpha [α] Cas) and the aforementioned Caph. Then draw an imaginary line between them and prolong it eastwards twice as far once more to only contained in the boundary with Cepheus. Sweeping with binoculars ought to get you there.
A pair of 10 × 50 binoculars exhibits Messier 52 as {a partially} resolved haze, whereas its look is remodeled telescopically, with 30 to 50 or so stars resolved throughout its 13’ kind via a 150–200mm (six- to eight-inch) telescope. The cluster’s brightest stars shine at magnitude +8.2 although usually are tenth magnitude, giving it an built-in magnitude of +6.9.
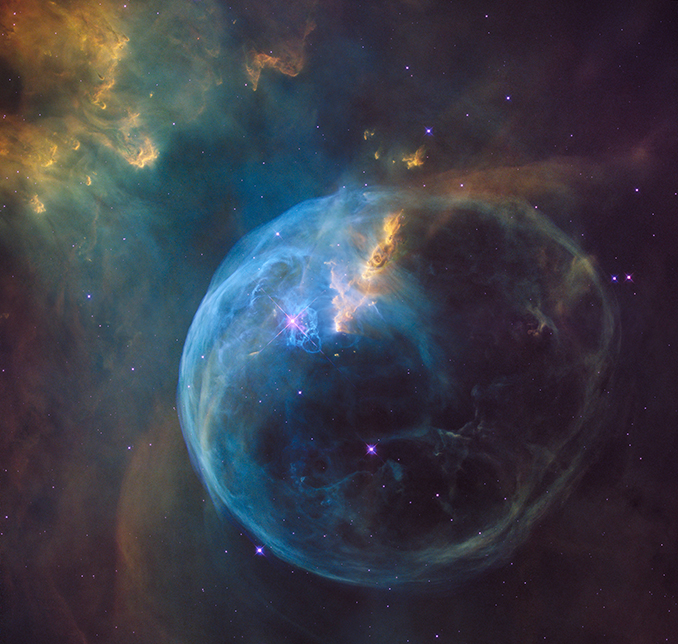
Messier 52’s attraction to visible observers and imagers alike is enhanced by the presence of the exceptional however faint Bubble Nebula (NGC 7635), which lies simply over half a level to its south-east. The Bubble is a seven-light-year-wide spherical object sculpted by the fierce wind from a close-by huge star. To watch this diffuse ring of fuel you’ll most likely want a minimum of a 250mm (ten-inch) telescope working underneath a clear sky when darker skies return within the autumn.

NGC 7789: Caroline’s Rose blooms sensible
NGC 7789 was found by Caroline Herschel in 1783 and is named Caroline’s Rose in her honour. It may be situated three levels south-west of magnitude +2.27 Caph (beta [β] Cassiopeiae, probably the most westerly mendacity of Cassiopeia’s 5 brightest stars that kind its acquainted ‘W’-shaped asterism. Shining with an built-in magnitude of +6.7, a pair of 10 x 50 binoculars simply exhibits it, even underneath suburban skies, as a gray haze comfortably framed between fifth-magnitude rho (ρ) and sigma (σ) Cassiopeiae.
NGC 7789 is circumpolar (by no means setting) from UK shores; it culminates overhead 45 minutes or so after Messier 52. Bodily, it’s a wealthy open cluster that’s one of many oldest recognized: its member stars are believed to have shaped round 1.6 billion years in the past. A 100mm (four-inch) telescope reveals round 40 to 50 stars, whereas wanting via the eyepiece of a telescope within the 200–250mm (eight- to ten-inch) class ought to reveal between 100 and 150 stars scattered throughout an obvious diameter of round 20 arcminutes.




